40 monty hall problem tree diagram
This lesson covers: Conditional Probability and Independence. 3.2 Independent and Mutually Exclusive Events. 3.3 Two Basic Rules of Probability. 3.4 Contingency Tables. 3.5 Tree and Venn Diagrams. Introductory Statistics by Sheldon Ross, 3rd edition: Sections 4.5. WeBWorK. Sets 3.2-3.5 - open 2/25 at 8 am due 3/11 9 pm.
The Monty Hall problem is a counter-intuitive statistics puzzle: There are 3 doors, behind which are two goats and a car. You pick a door (call it door A). You’re hoping for the car of course. Monty Hall, the game show host, examines the other doors (B & C) and opens one with a goat. (If both doors have goats, he picks randomly.)
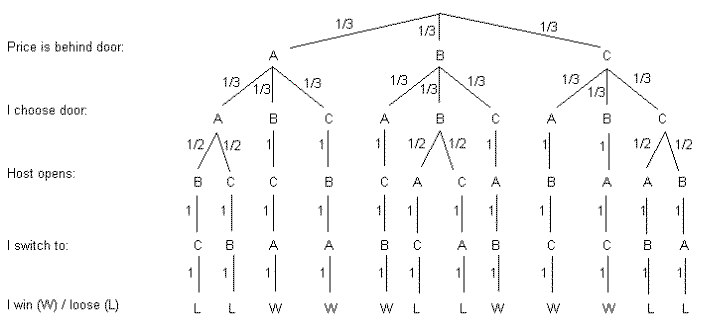
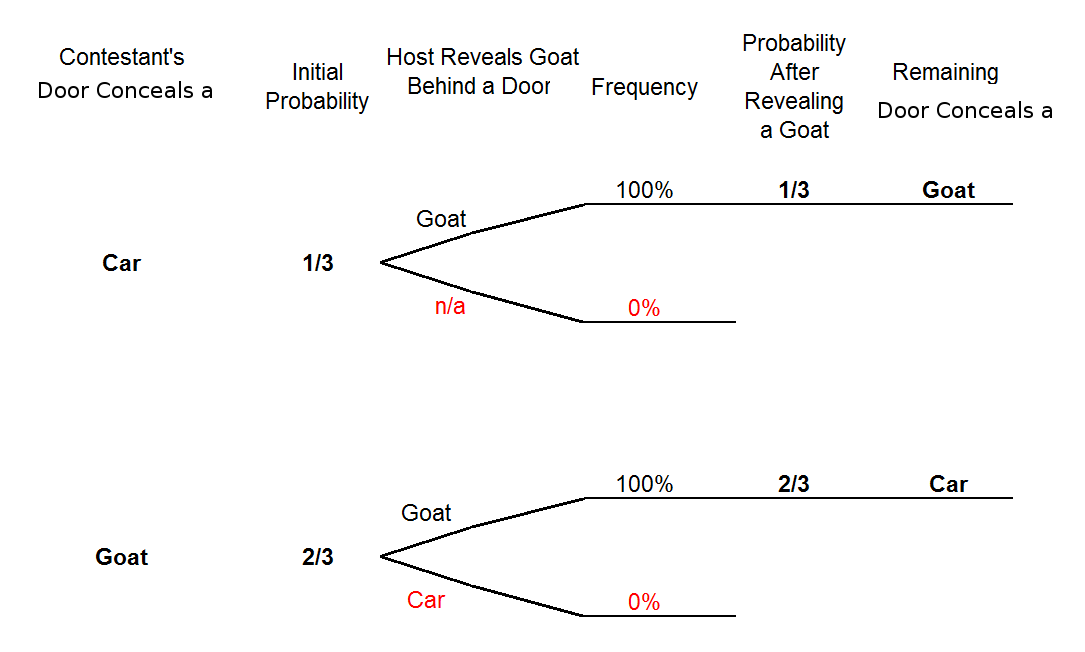
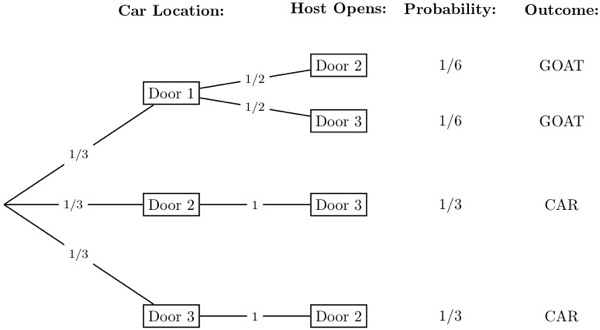
A tree diagram of the monty hall problem under the marilyn vos savant assumptions. Door a door b and door c. Probability tree diagram of monty hall problem as we can see from the diagram the only place where there is a random event involved is during the initial pick the elimination process is actually.

Monty hall problem tree diagram
This answer is not useful. Show activity on this post. B) The probability that Terry will not be the champion is. ( 1 − p) + 0.4 p = 1 − 0.6 p. Solving, 1 − 0.6 p = 0.58 p = 0.7. C) The answer is. 1 − p 1 − 0.6 p = 0.3 0.58 = 15 29. The events are not independent, since the event "Terry loses in the semi-final" is a subset of the ...
Figure 16.5 The tree diagram for the Monty Hall Problem where edge weights denote the probability of that branch being taken given that we are at the parent of that branch. For example, if the car is behind door A, then there is a 1/3 chance that the player's initial selection is door B.
The Monty Hall problem is a famous, seemingly paradoxical problem in conditional probability and reasoning using Bayes' theorem. Information affects your decision that at first glance seems as though it shouldn't. In the problem, you are on a game show, being asked to choose between three doors. Behind each door, there is either a car or a goat. You choose a door. The host, Monty Hall ...
Monty hall problem tree diagram.
There are at least two ways of analyzing this problem, one is using a tree diagram and one is using Bayes' Theorem. In a previous blog post, I went through the math in detail, so I'll just summarize the simpler explanation using a tree diagram. To make it easier to understand, I'll assume a population of 10,000.
Example 1.14. The Monty Hall Problem. Consider a television show (loosely modeled on a similar show hosted by Monty Hall) Binomial Distribution Probability and Statistics Problem Conditional Probability Problem 1 - Conditional Probability Problem 1 - Probability Video Class - Probability video Class for IIT JEE exams preparation and to help
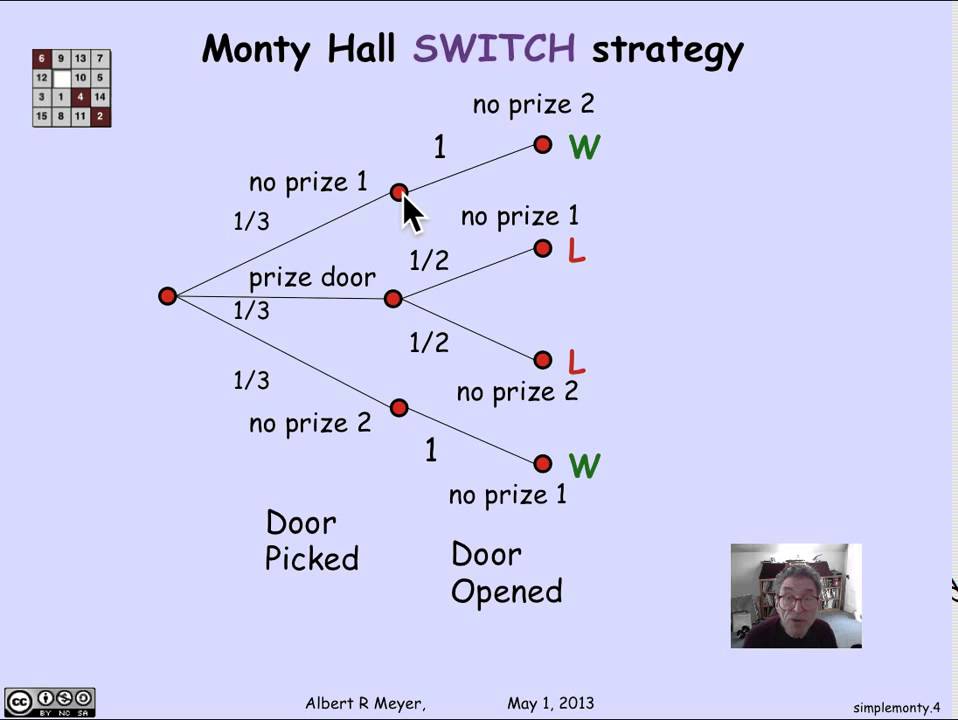
I hope by now your System 2 has overridden your System 1, and you understand the mechanics of this problem. If you still don't, that's the fault of my explanation. Thankfully, smarter people than me have tackled it using equations, tree diagrams, and computer models. The result is the same: switching your door means you win 66% of the time.
Mathemania is the first place to come for free math worksheets. Our team of experts worked very hard to provide you entertaining way of learning math...
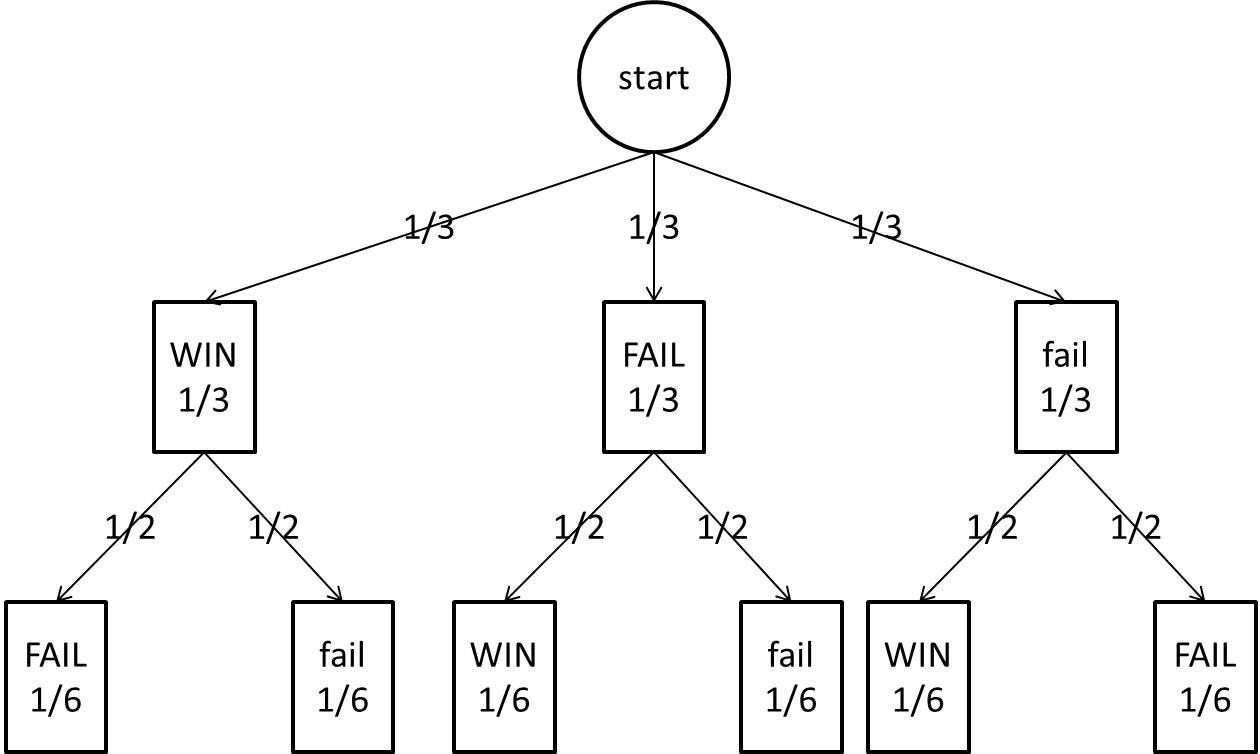
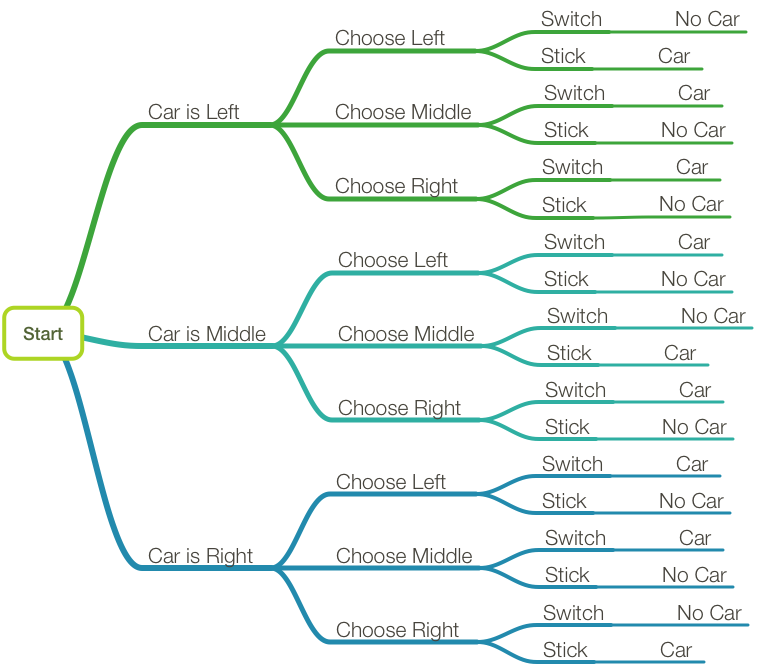
Consider the Monty Hall problem. Let’s label the door with the car behind it a and the other two doors b and c. In the game the contestant chooses a door and then Monty chooses a door, so we can label each outcome as ‘contestant followed by Monty’, e.g ab means the contestant chose a and Monty chose b.
The Monty Hall problem is a brain teaser, in the form of a probability puzzle, loosely based on the American television game show Let's Make a Deal and named after its original host, Monty Hall. The problem was originally posed (and solved) in a letter by Steve Selvin to the American Statistician in 1975.
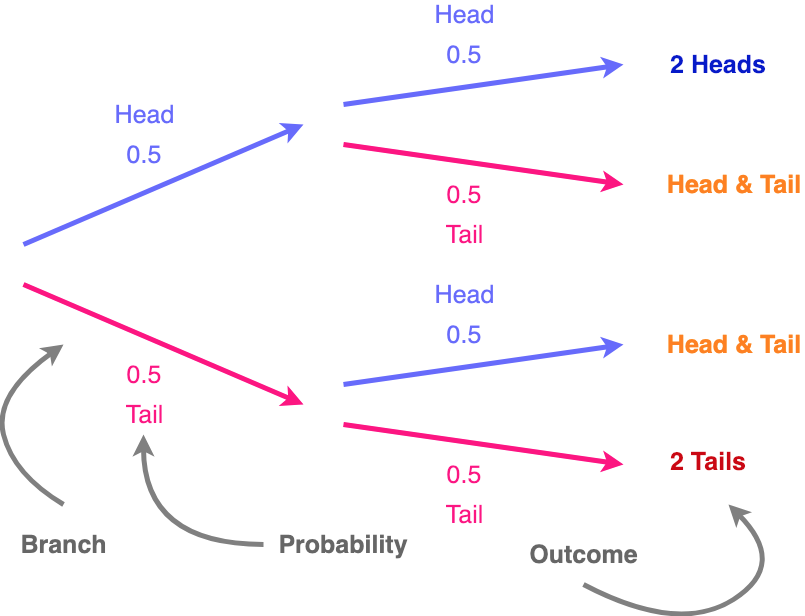
Tree diagrams are a handy tool for solving probability problems. They also illustrate some central concepts of probability. Probabilities are numbers assigned ...
Simple Monty Hall: Choose one of three doors to experimentally determine the odds of winning the grand prize behind one of the doors, as in the TV program "Let's Make a Deal." Parameters: Staying or switching between the two remaining doors.
The Monty Hall Problem: A Statistical Illusion Probability of sample proportions example (video) | Khan Academy Conditional probability tree diagram example (video) | Khan Academy Multiple Choice Probability Test The Impact of Bottom the normal distribution | Manualzz Mathematics | Free Full a certain countr QM | Confidence terval | Null Hypothesis
This activity is about bridging the gap between the intuition of sample space diagrams and the efficiency of tree diagrams. Students will look at a problem from the two points of view, play with multiplying and adding fractions and hopefully see how tree diagrams are a more efficient way of doing the same thing! The activity is good for group work and physical manipulation, although it could ...
Understanding Minimax Algorithm with Tic Tac Toe. The Minimax algorithm is a type of backtracking algorithm used in Game Theory to determine the best move to make assuming your opponent is also making their best move. The use of Minimax algorithm is a form of Artificial Intelligence that does not involve Machine Learning.
This is a slightly-edited repost from [2017-02-25](http://np.reddit.com/r/rational/comments/5w27a3). --- [*Conned Again, Watson*](https://www.goodreads.com/book/show/1130873), a work of officially-sanctioned and traditionally-published Sherlock Holmes fanfiction, consists of twelve short stories. Each story has a paragraph or three of explanation (sometimes including book recommendations) in the book's afterword. --- #####1\. The Case of the Unfortunate Businessman ######Framing story Afte...
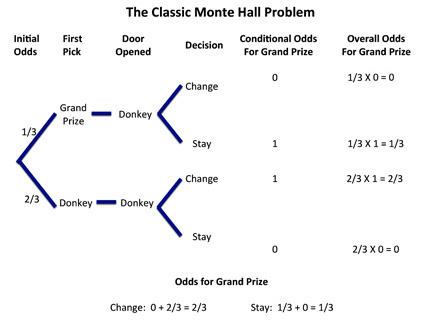
Monty Hall problem decision tree according to conditional probability According to Figure 5, in case the host opens door 3 and the contestant changes ...
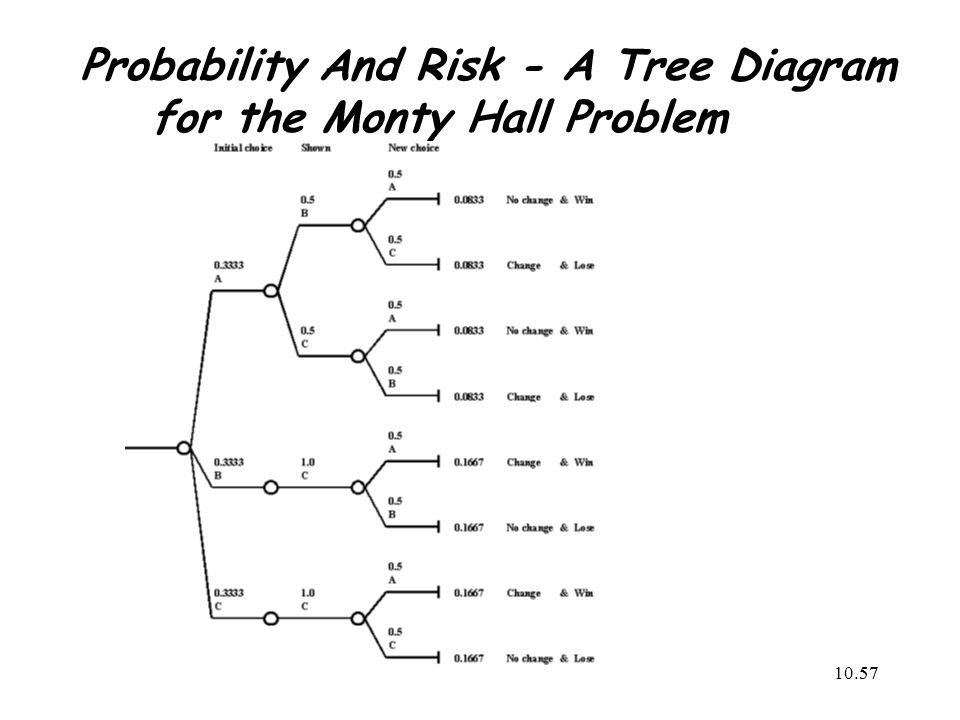
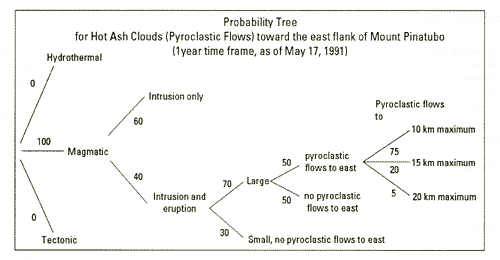
4 Dec 2018 — The probability tree diagram is consisted of 3 parts, the branch which leads to the possible outcomes, the probability of the event occurring ...
Ever since I read about Monty Hall problem in "The Drunkard's Walk: How Randomness Rules Our Lives" book by Leonard Mlodinow from of the California Institute of Technology, I always wanted to try and run a simulation to see that the math is correct. It is one of those problems, where the first answer that comes to mind is usually wrong, and the correct answer to the problem is ...
Bits will be missing because, just like living trees, tree diagrams are rarely square. From top left to right, we have Darwin's tree of life 1859, a syntax tree, a family tree template, Phylogenetic tree of Theropods respiratory system, Haeckel's foundations of science tree 1866, and one and a half medieval trees of knowledge.
Lecture 4: Compound events example with tree diagram. Lecture 5: Dependent probability example 2. Lecture 6: Getting exactly two heads (combinatorics) ... Lecture 22: Probability and the Monty Hall problem. Lecture 23: Probability using combinations. Lecture 24: Factorial and counting seat arrangements.
The problem: existence of a spanning tree of weight ≤ k is also a decision problem. The optimization problem is to find the value k in such a way that it is minimal. In order to better understand the two concepts, we will take an example: You wish to take a tour of Europe, by visiting a certain number of cities within a period of 6 months.
The Monty Hall problem. Three-pointer vs free-throw probability. Transforming polygons using matrices. Transforming vectors using matrices. Unit vectors intro. Vectors word problem: tug of war. Visual representation of transformation from matrix. Worked example: Scaling unit vectors. Worked example: finding unit vector with given direction
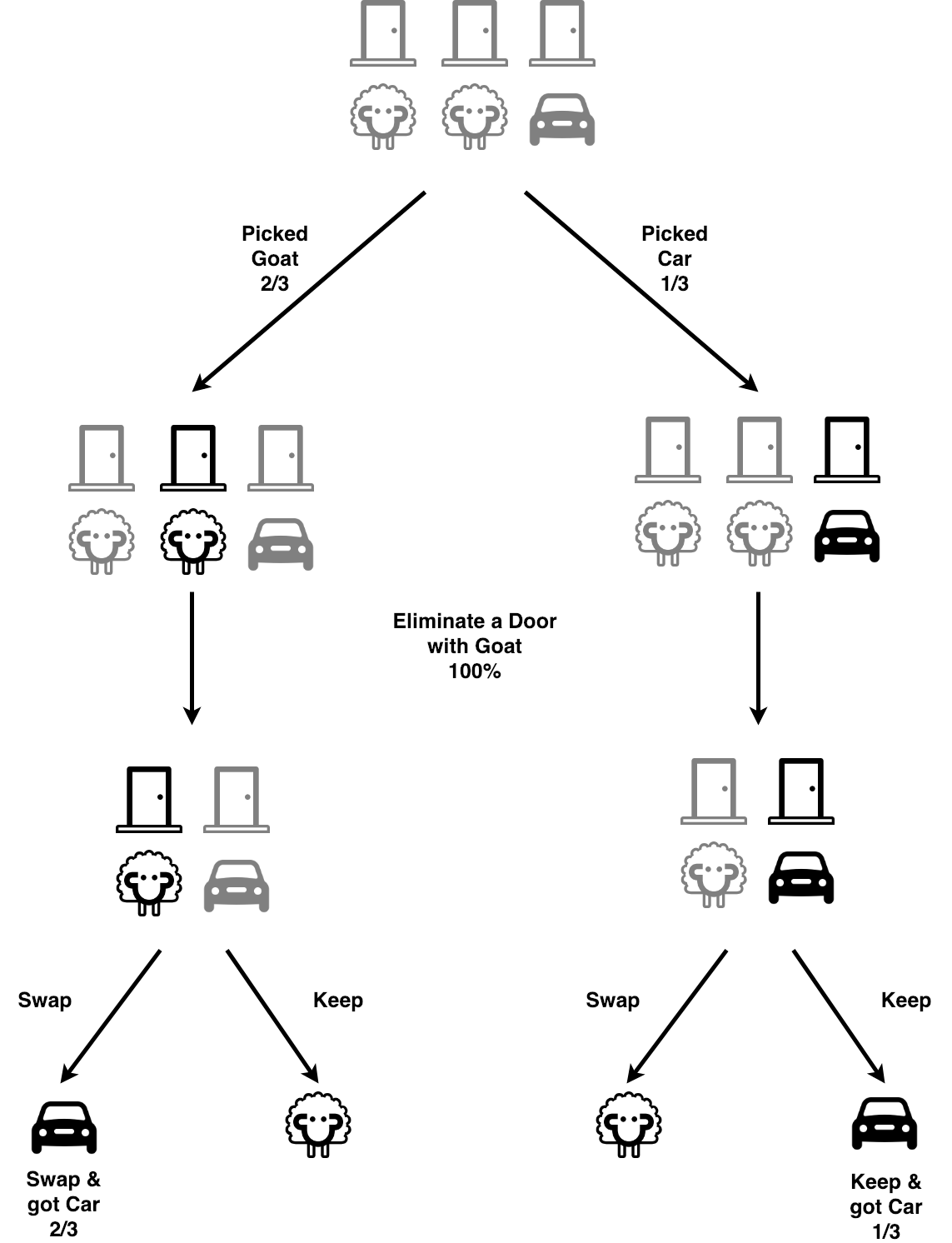
Solution To Monty Hall Problem · 1. Pick a door. The diagram below shows the chances that you will pick the door with the car or either of the goats, Goat A or ...
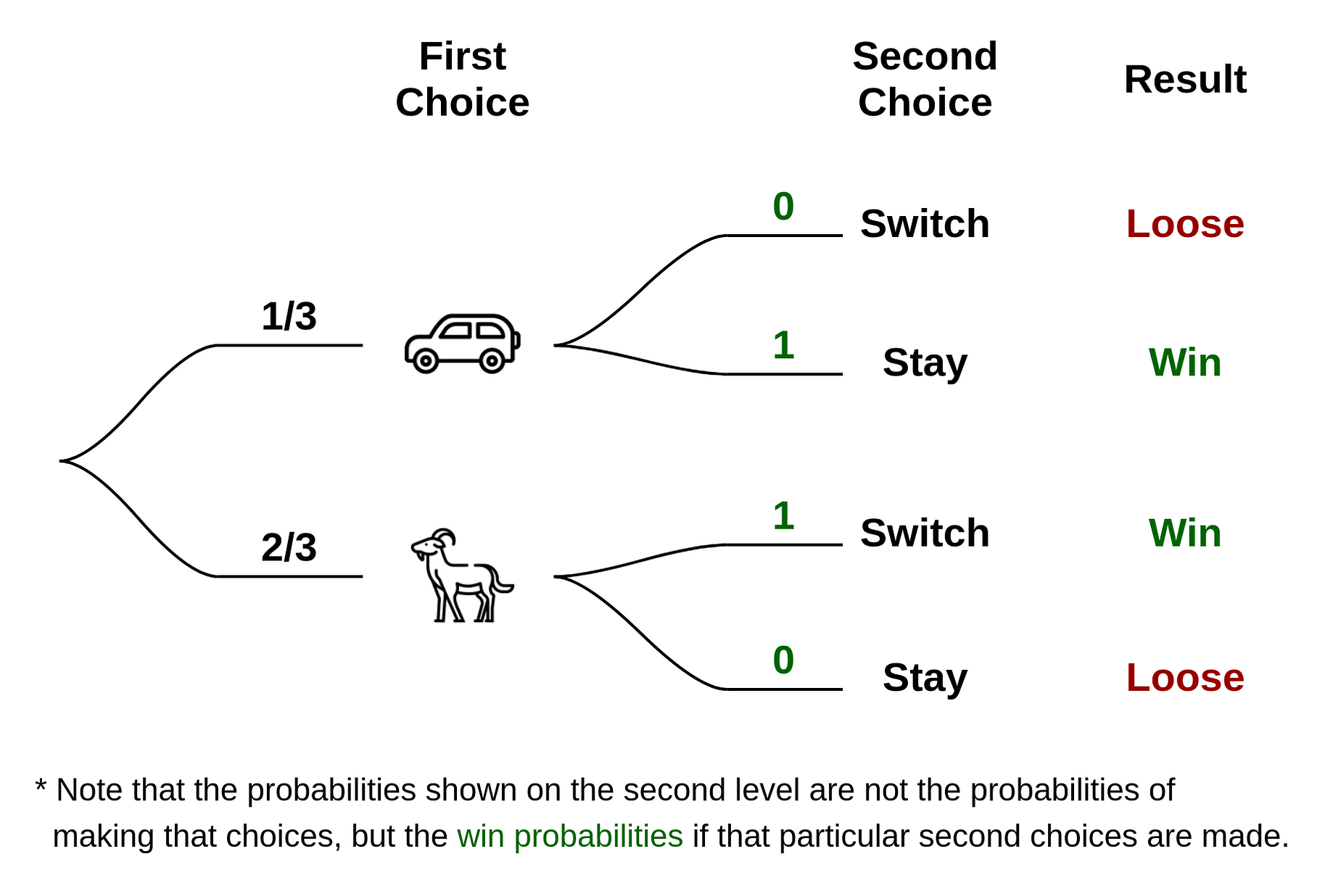
Figure 1 — Tree diagram showing the probabilities associated with the Monty Hall Problem (Diagram by the Author) When you are asked to make your first choice, there is an equal probability that the car is behind any one of the three doors. So you have a 1/3 chance of guessing it correctly. This implies that 2/3 of the times your guesses are wrong.
6 Nov 2018 — As you read the tree diagram, it starts to make sense why you should always switch, and why it is much more complicated than just a coin ...
Apr 12, 2021 · The Monty Hall problem (or “three-door problem” or “goat problem”), which had not yet been formulated at the time of Tversky and Kahneman’s first publications but today is one of the most famous examples of a cognitive illusion, is sometimes even considered the “queen” of statistical brain teasers (e.g., Gilovich et al., 2002 ...
monty hall problem tree diagram monty hall tree diagram. 26 Monty Hall Tree Diagram. Monty hall problem explained with a tree diagram. Tree diagrams are a h…
The Monty Hall Problem: A Statistical Illusion Conditional probability tree diagram example (video) | Khan Academy the normal distribution | Manualzz Mathematics | Free Full PDF) The Market for Used Cars: New Evidence of the Lemons Phenomenon Mathematics | Free Full The Impact of Bottom The 1/10th Rule For Car Buying Everyone Must Follow
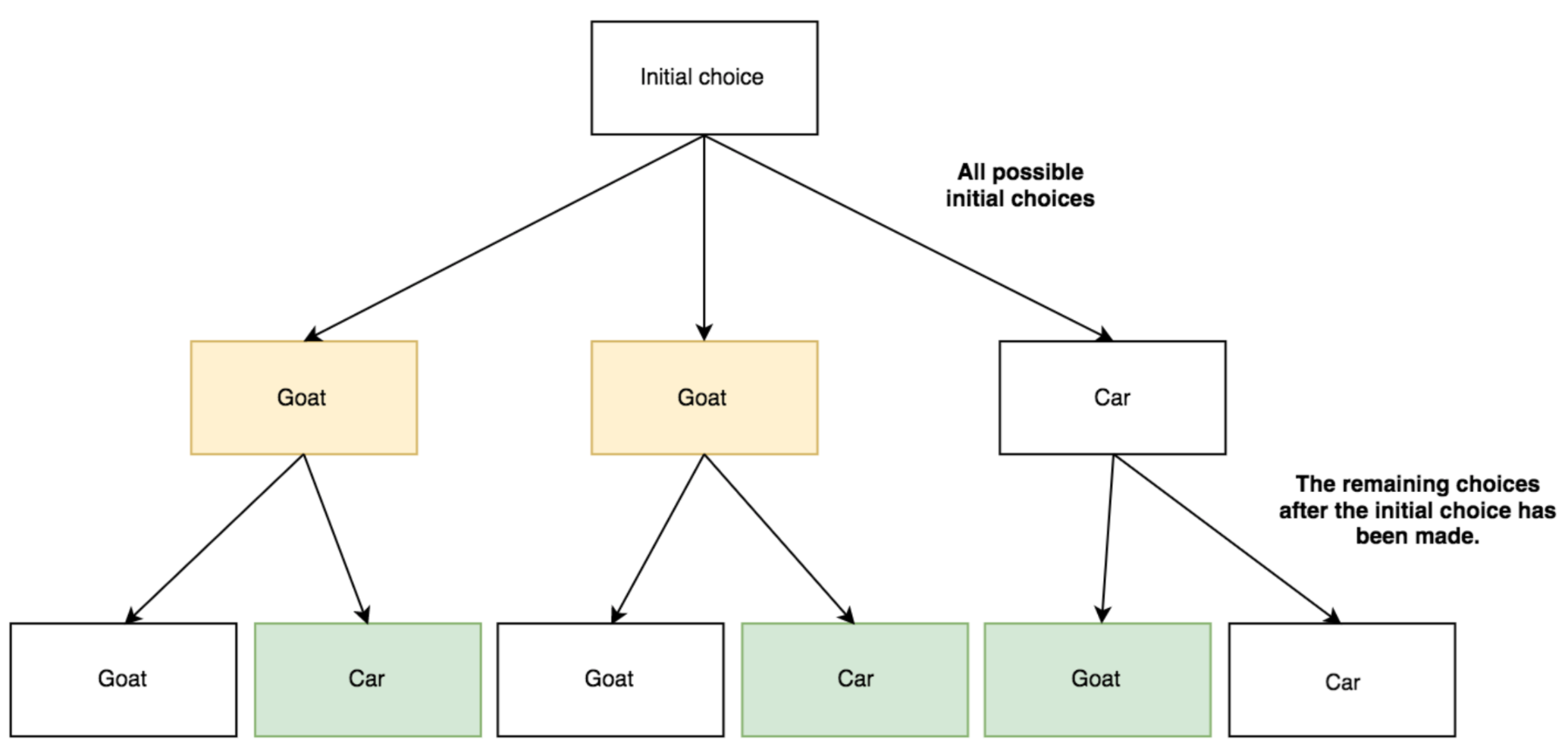
Tree diagram for the Monty Hall problem. Image: MIT [2]. The root (at the far left) represents the initial state, before the car (or goats) have been placed. The next three vertices in the tree (moving to the right) represent the experimental state after the prizes have been placed, but before you pick a door. Each "leaf" on the left is ...
There are three closed doors, labeled #1, #2, and #3. Monty Hall randomly selects one of the three doors and puts a prize behind it. The other two doors hide nothing. A contestant, who does not know where the prize is, selects one of the three doors. This door is not opened yet. Monty chooses one of the three doors and opens it.
13 Nov 2006 — proach when the number of outcomes is not too large or the problem is nicely structured. In particular, we can use a tree diagram to help ...17 pages
Logic Puzzle: The "Monty Hall" problem was made famous when it appeared in Parade magazine's "Ask Marilyn" column in 1990, and it was so counterintuitive it had everyone from high school ...
Here's my visual representation of the classic Monty Hall game. It extends the traditional probability tree by framing the contestant's winning decision as the third trial of the probability experiment. Here—without loss of generality ♪ —the contestant has chosen Door $1.$ From the diagram: the sample space is $\{12c,121,13c,131,23c,231 ...
A [recent /r/learnmath thread](http://www.reddit.com/r/learnmath/comments/21nxuk/i_was_in_an_argument_about_this_logicmath_problem/) got me thinking about the classic Monty Hall paradox. For those not familiar with it, here's the description: > Suppose you're on a game show, and you're given the choice of three doors: Behind one door is a car; behind the others, goats. You pick a door, say No. 1, and the host, who knows what's behind the doors, opens another door, say No. 3, which has a goat...
This is a [crosspost](https://www.reddit.com/r/rational/comments/88jbmu) from r/rational. --- [*Conned Again, Watson*](https://www.goodreads.com/book/show/1130873), a work of officially-sanctioned and traditionally-published Sherlock Holmes fanfiction, consists of twelve short stories. Each story has a paragraph or three of explanation (sometimes including book recommendations) in the book's afterword. --- #####1\. The Case of the Unfortunate Businessman ######Framing story After inheritin...
Answer. The possible permutations are. ABC, ACB, BAC, BCA, CAB, CBA. Hence, there are six distinct arrangements. Another way of looking at this question is by drawing 3 boxes. Any one of the A, B, C goes into the first box (3 ways to do this), and then the remaining one of the two letters goes into the second box (2 ways to do this), and the ...
See also B Bebot, Mother of Kenneth John - Bebot Báb, Persian religious leader - Bábism Charles Babbage, British mathematician and inventor - Babbage engine, Babbage Isaac Babbitt, American inventor - Babbitt metal Joseph Babinski, French neurologist - Babinski's sign, Anton-Babinski syndrome, Babinski-Fröhlich syndrome, Babinski-Froment syndrome, Babinski-Nageotte syndrome ...
(I [mentioned](http://np.reddit.com/r/rational/comments/5umkxq/d_friday_offtopic_thread/ddvyjrw) previously that I would make a post about *both* [this book](https://www.goodreads.com/book/show/1130873) *and* its prequel, *[The Einstein Paradox](https://www.goodreads.com/book/show/76261)*. As it turns out, however, *The Einstein Paradox* focuses *entirely* on physics (the final chapter deals with many-worlds theory), and only *Conned Again, Watson!* is relevant to this subreddit.) *Conned Again...
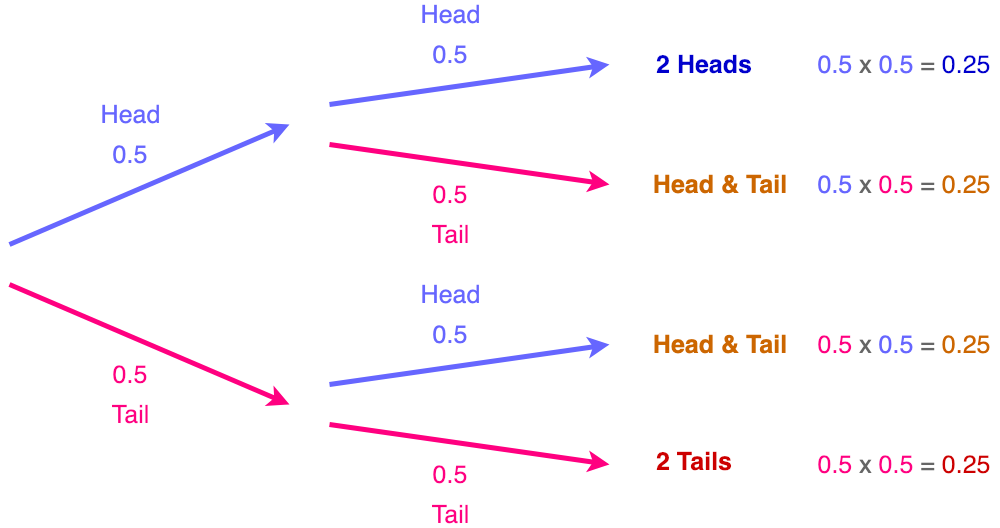
Tree Diagram in Probability. In probability theory, a tree diagram could be utilised to express a probability space. These diagrams may describe a sequence of independent events (for example a set of a coin tossed) or conditional probabilities (like drawing cards from a deck, without substituting the cards). tree diagram definition: 1. a diagram (= simple drawing) that shows the relationships ...
1.4 The Monty Hall Problem is a multi-stage decision problem whose solution relies on conditional probability. The stages of decision making are shown in the diagram. We assume that the prizes are randomly assigned to the doors. We can’t see this step{so we’ve adorned this decision with a square box. We’ll
Talk:Monty Hall problem/Archive 14#The MHP in economics and game theory. "The basis to my solution is that Monty Hall knows which box contains the keys and when he can open either of two boxes without exposing the keys, he chooses between them at random." - Steve Selvin.
Mythbusters did that one: When presented with the Monty Hall Problem, people tend to stick with their first choice.. CONFIRMED. After they built a game show mock-up set at a local theater, Adam acted as a game-show host and had 20 volunteers play a game of "Pick a Door".





















0 Response to "40 monty hall problem tree diagram"
Post a Comment