41 calvin cycle simple diagram
Calvin cycle diagram miguelferig.png 2,206 × 1,315; 114 KB. Calvin cycle overall.svg 775 × 250; 110 KB. Calvin cycle step 1.svg 600 × 175; 47 KB. Calvin cycle step 2 (doubled).svg 710 × 120; 48 KB. Calvin cycle step 2.svg 710 × 78; 26 KB. Calvin cycle step 3.svg 713 × 250; 62 KB. Calvin cycle.PNG 2,051 × 2,189; 169 KB. The Calvin Cycle LSM 3.3-3 The molecule released from the Calvin cycle is used to form. This can be stored as molecules. is reduced using to form . One molecule of leaves the cycle as a final product, while the other five molecules continue through the Calvin cycle. The five molecules go through a series of reactions
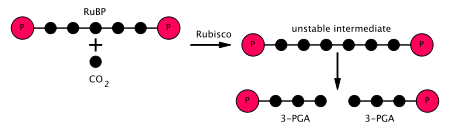
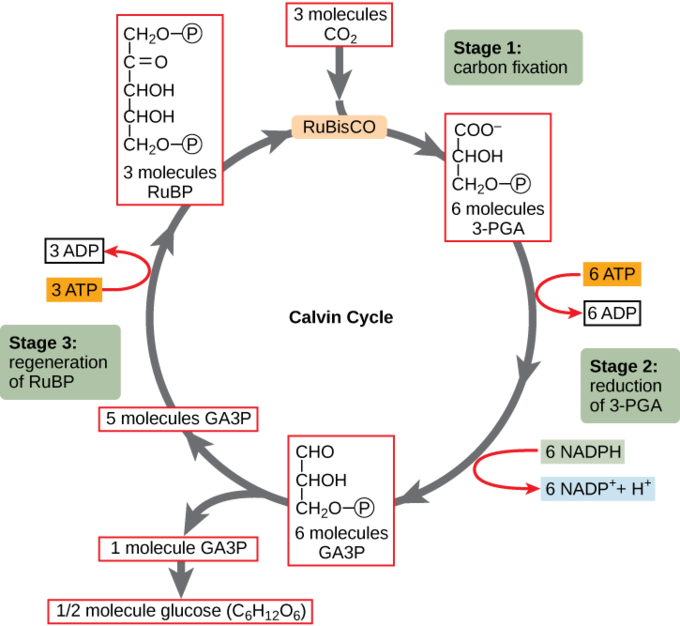
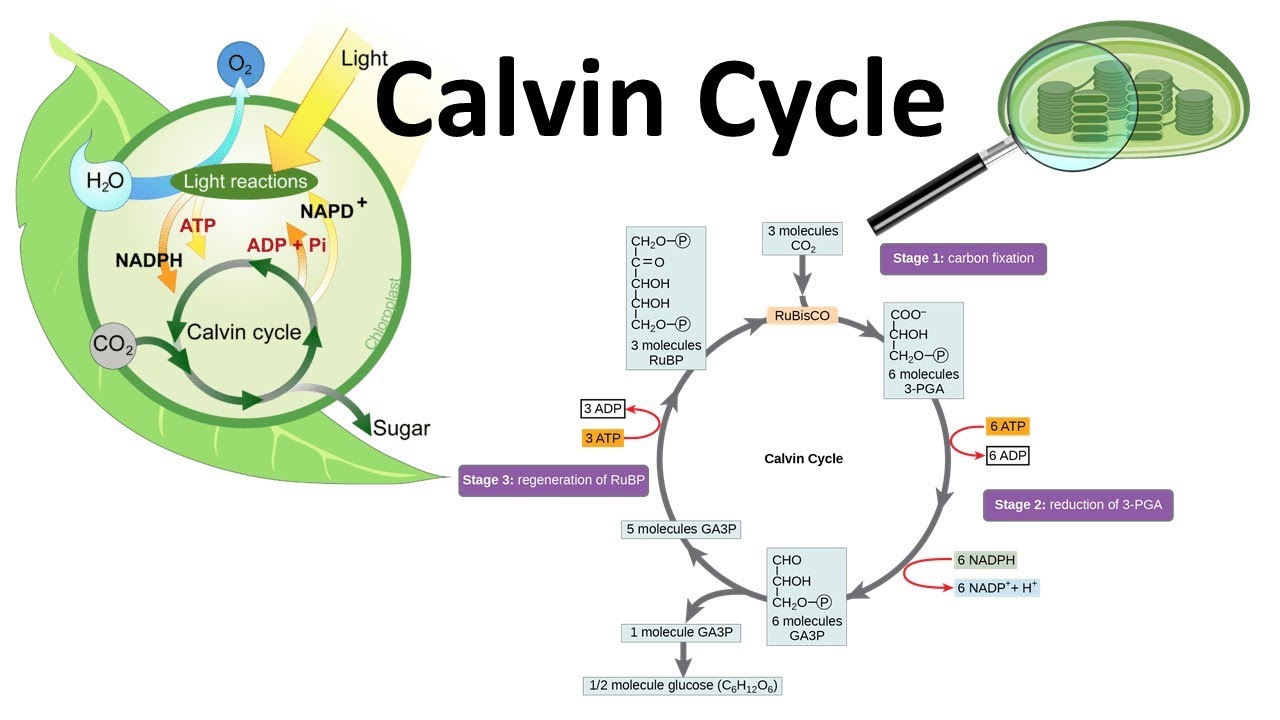
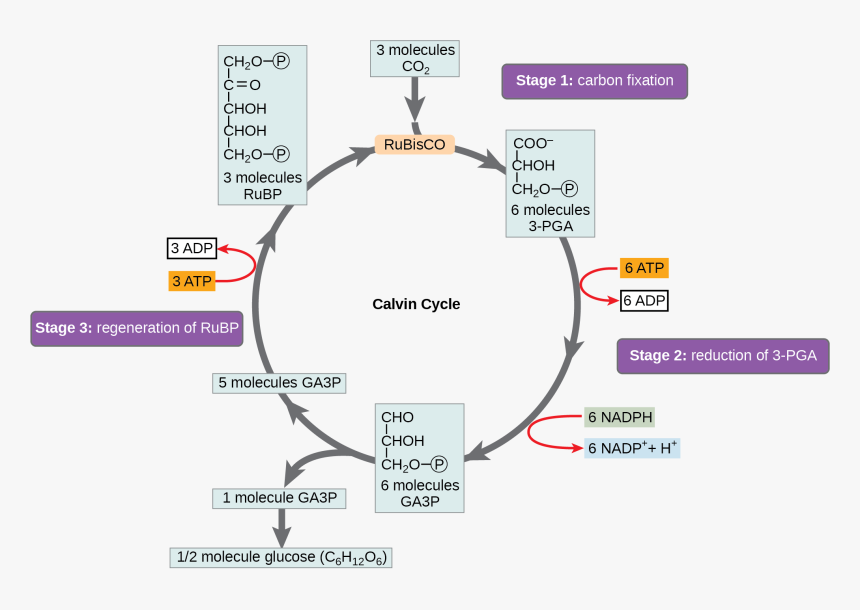
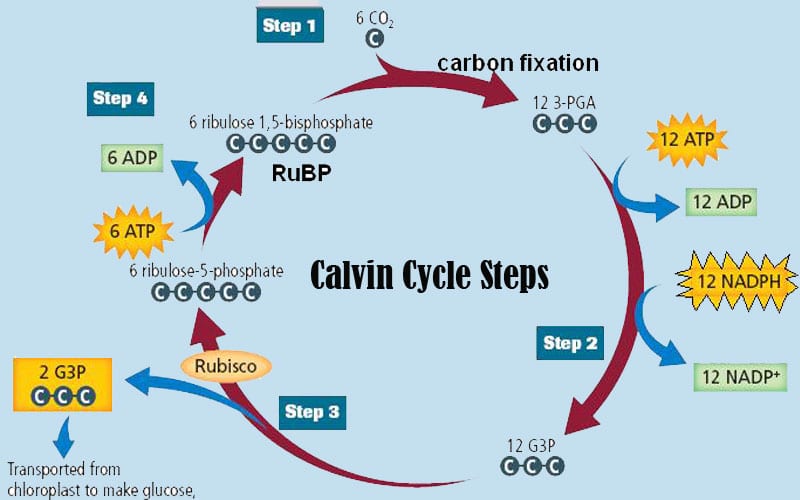
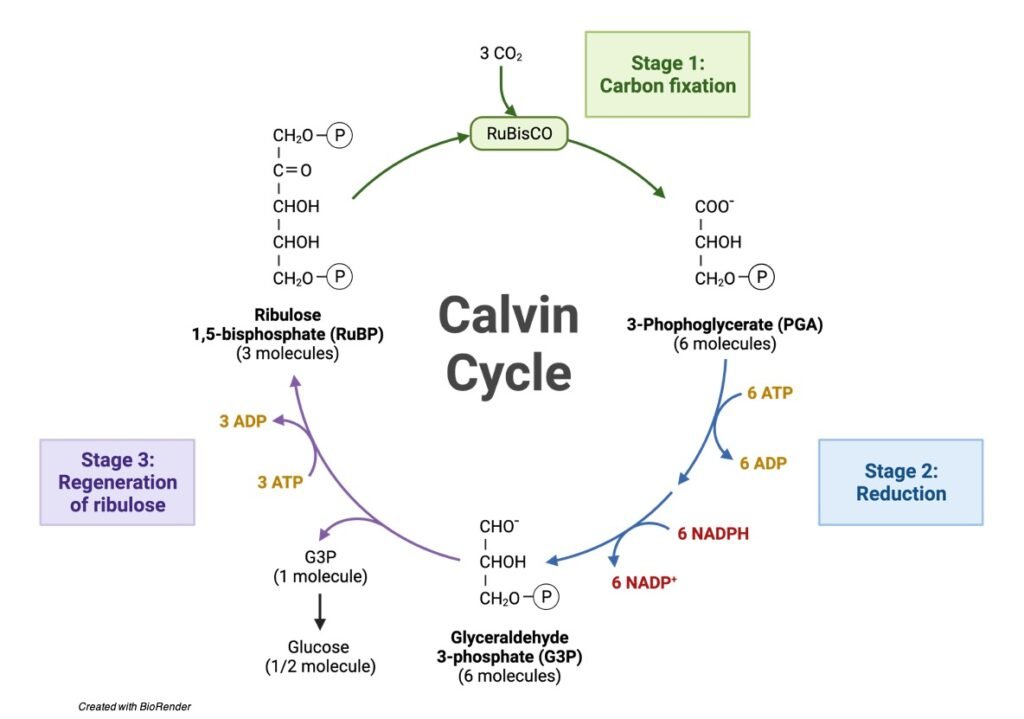
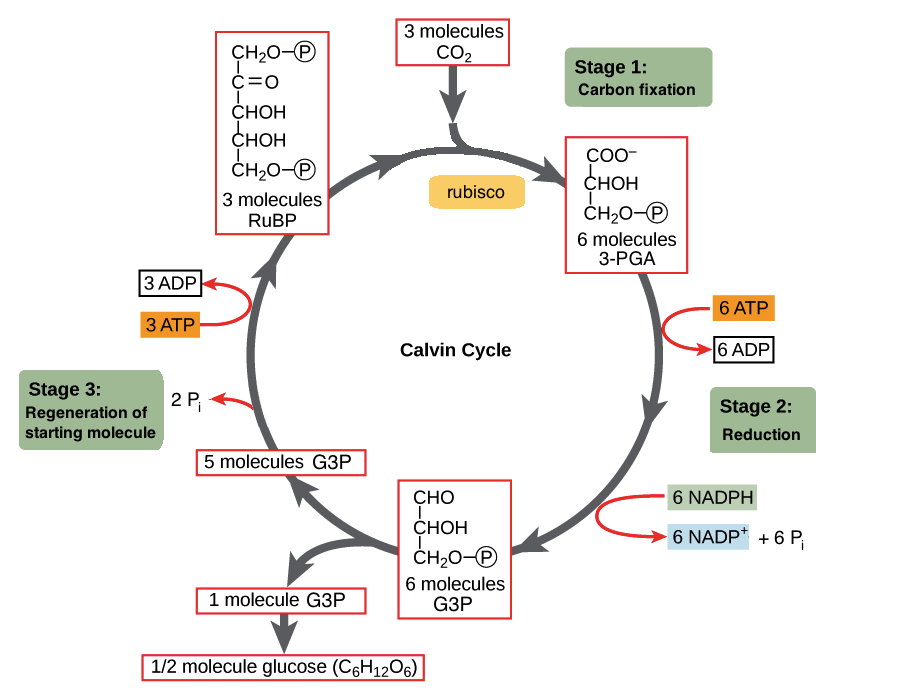
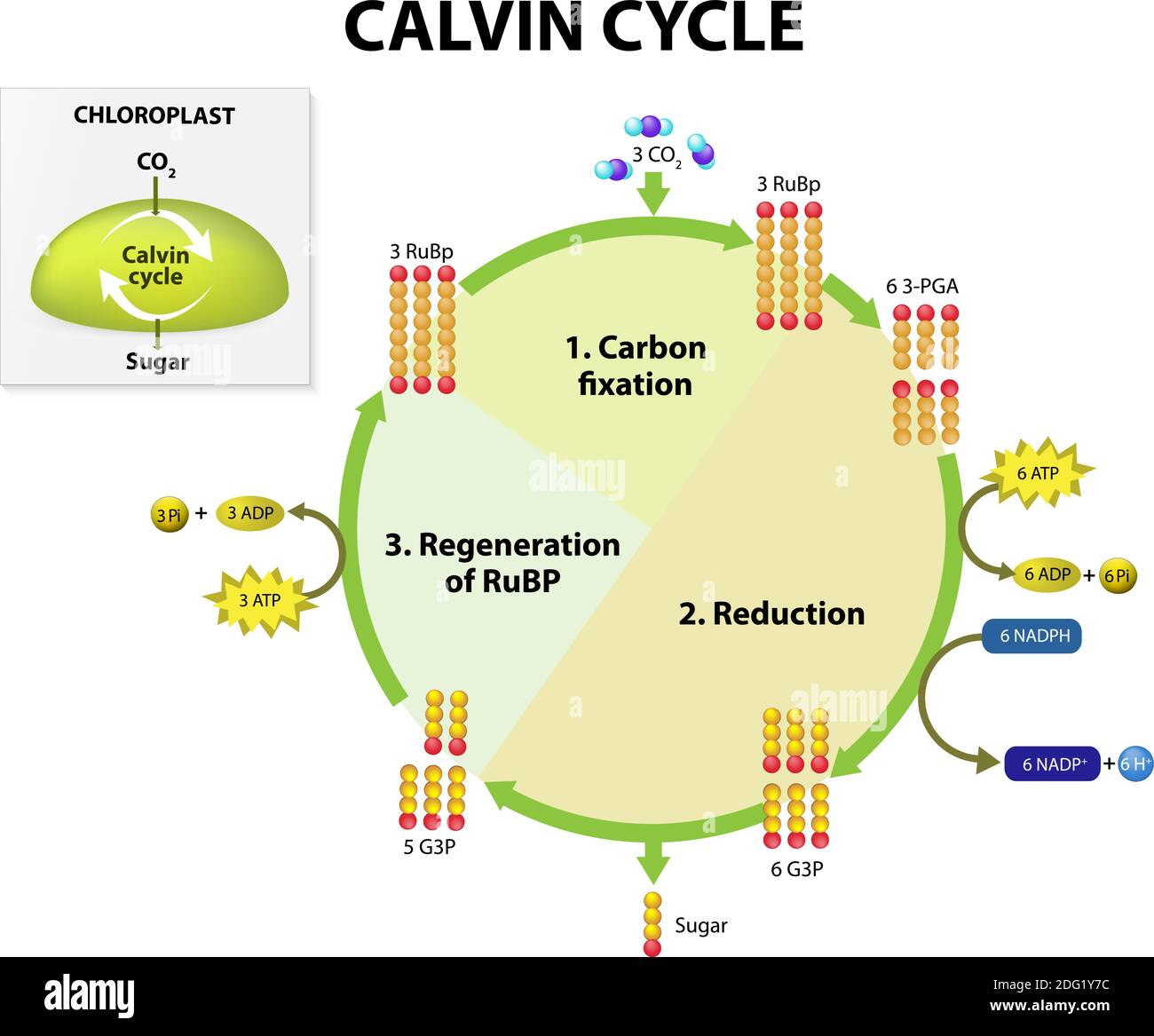
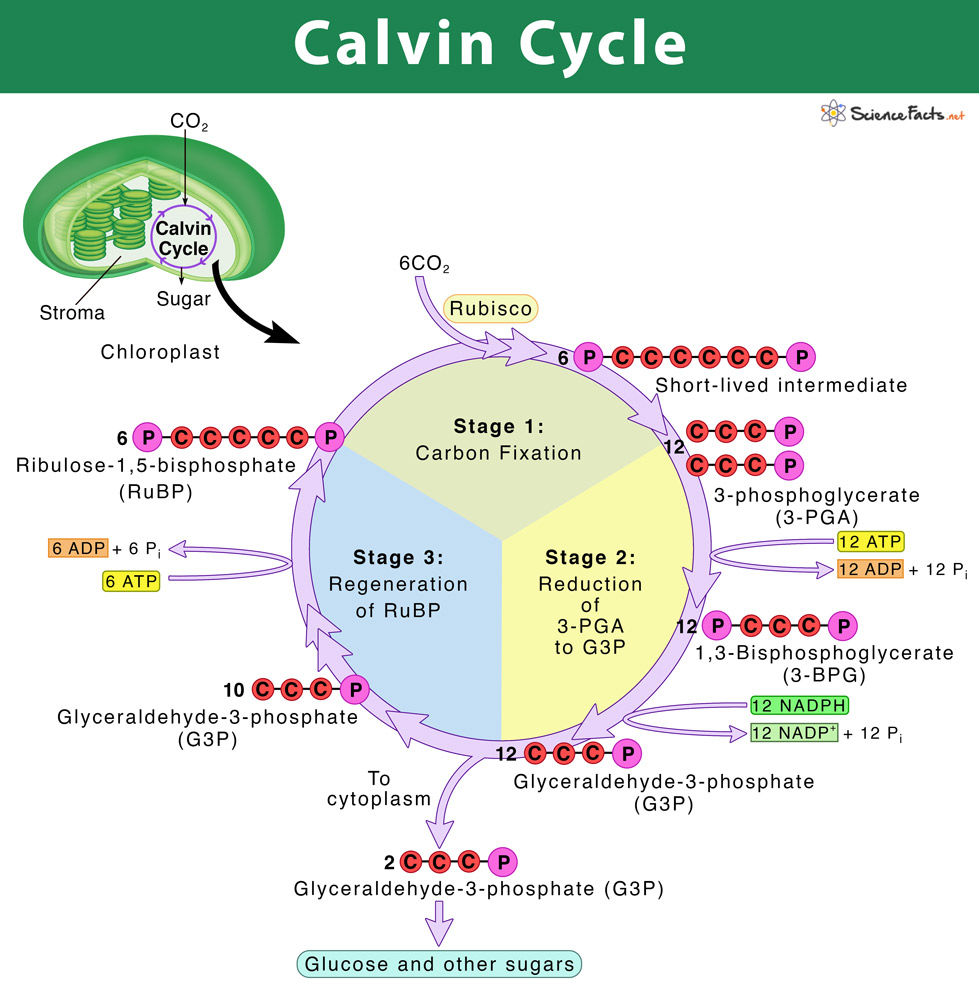
Calvin cycle was given by the Melvin Calvin, James Bassham and Andrew Benson. In this cycle, phosphoglyceric acid (3 carbon compound) is produced as a first product and thus called as C 3 cycle. From the given diagram we can understand the stages of the Calvin cycle. Calvin cycle can be divided into three stage: 1.

Calvin cycle simple diagram
The PGA molecule enters the calvin cycle to make carbohydrates, but one CO 2 molecule released in mitochondria during photorespiration has to be re-fixed. In other words, 75% of the carbon lost by oxygenation of RuBP is recovered, and 25% is lost as release of one molecule of CO 2 . Need more help! a. Draw a simple flow diagram of the Calvin cycle to show the relative positions in the cycle of the following molecules: CO 2 (1C) GP/PGA (3C) triose phosphate (3C) RuBP (5C). b. Show the point in the cycle at which the enzyme rubisco is active. The Calvin cycle is a set of light independent redox reactions that occur during photosynthesis and carbon fixation to convert carbon dioxide into the sugar glucose. These reactions occur in the stroma of the chloroplast, which is the fluid-filled region between the thylakoid membrane and inner membrane of the organelle. Here is a look at the redox reactions that occur during the Calvin cycle.
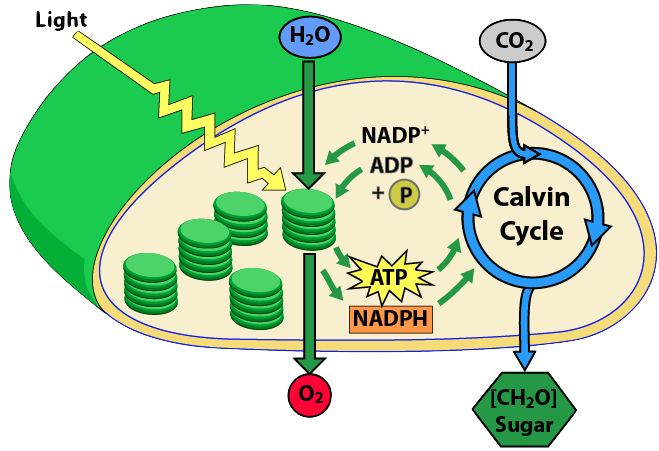
Calvin cycle simple diagram. The Calvin cycle diagram below shows the different stages of Calvin Cycle or C3 cycle that include carbon fixation, reduction, and regeneration. Stages of C3 Cycle. ... The 3-PGA molecules created through carbon fixation are converted into molecules of simple sugar - glucose. The Calvin cycle is a process that plants and algae use to turn carbon dioxide from the air into sugar, the food autotrophs need to grow. Every living thing on Earth depends on the Calvin cycle. Plants depend on the Calvin cycle for energy and food.Other organisms, including herbivores, also depend on it indirectly because they depend on plants for food. The Calvin Cycle, also known as the Calvin-Benson Cycle, refers to the set of light independent redox reactions that takes place in the chloroplasts during photosynthesis and carbon fixation that would convert carbon dioxide into the sugar glucose. Furthermore, the cycle also refers to the reactions involved in photosynthesis that use the ... Calvin Cycle Diagram. The Calvin cycle occurs in the chloroplast stroma, the region between the thylakoid membrane and the organelle's inner membrane just after completing the light reaction of photosynthesis. The light reaction helps the Calvin cycle by providing ATP which is its energy source, and NADPH for reducing ability.
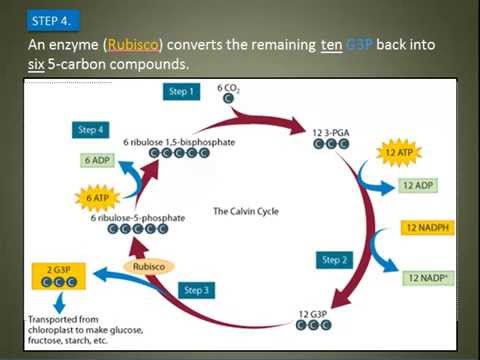
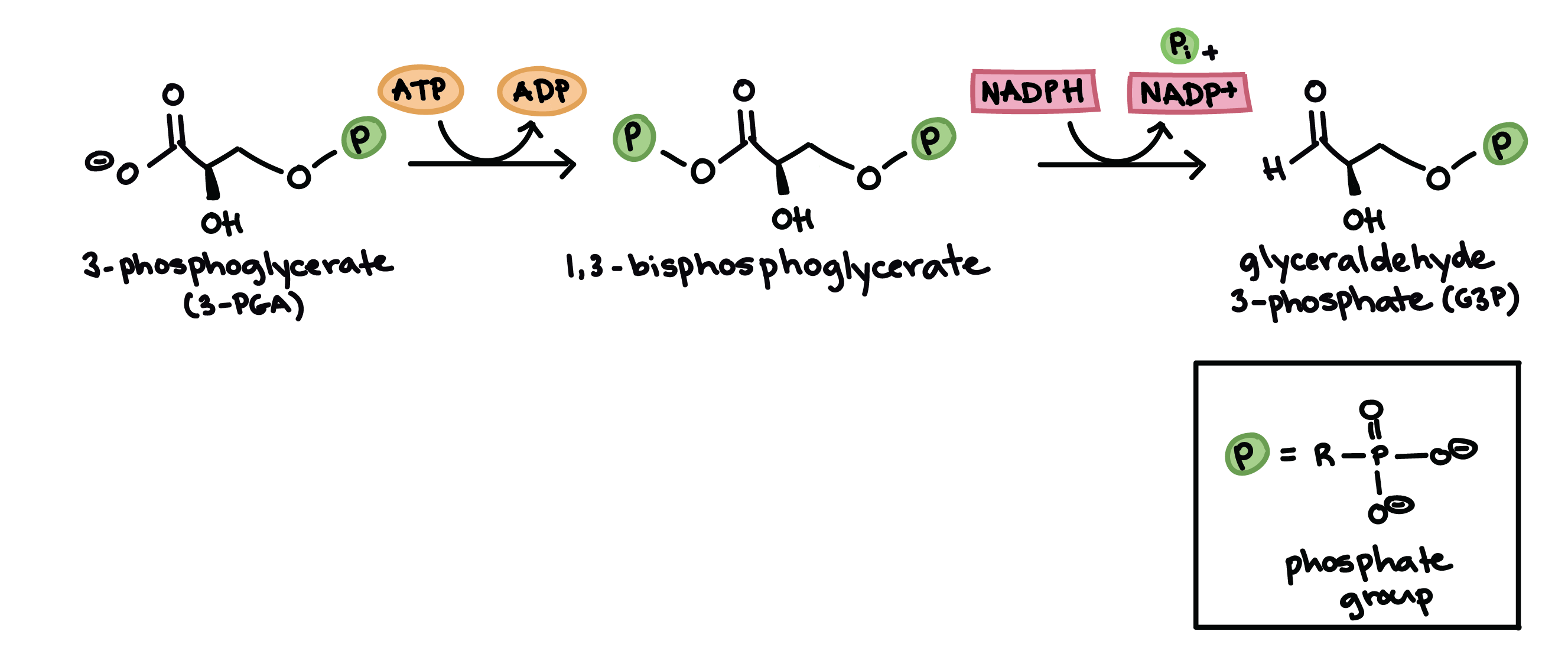
Calvin Cycle Simple Diagram angelo. December 2, 2021. What Is The Calvin Cycle Light Reaction Photosynthesis Flow Chart . The Calvin Cycle Biology College Interactive Science Notebook Biology Lessons . Co2 Is Plant Food Photosynthesis Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Biology Classroom . Feb 12, 2016 - Simple diagram of the Calvin Cycle (the light independent reaction of photosynthesis) As the first molecules in the process, if regenerated, this stage of photosynthesis results in a cycle (Calvin cycle). Reaction. 3 CO 2 + 9 ATP + 6 NADPH + 6 H + → glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P) + 9 ADP + 8 P i + 6 NADP + + 3 H 2 O. A G3P molecule contains three fixed carbon atoms, so it takes two G3Ps to build a six-carbon glucose molecule. So then we have these 12 PGALs. Now the reason why it's called a Calvin Cycle-- as you can imagine-- we studied the Kreb Cycle. Cycles start reusing things. The reason why it's called the Calvin Cycle is because we do reuse, actually, most of these PGALs. So of the 12 PGALs, we're going to use 10 of them to-- let me actually do it this way.
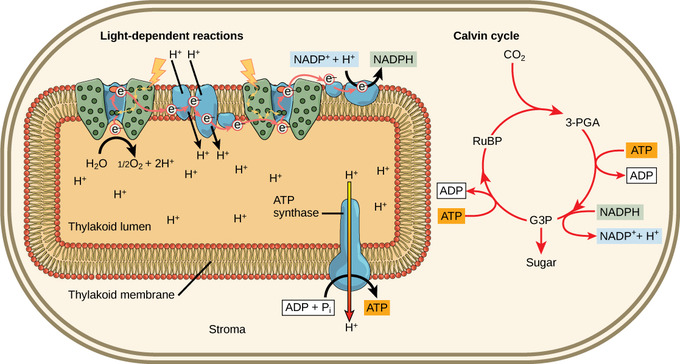
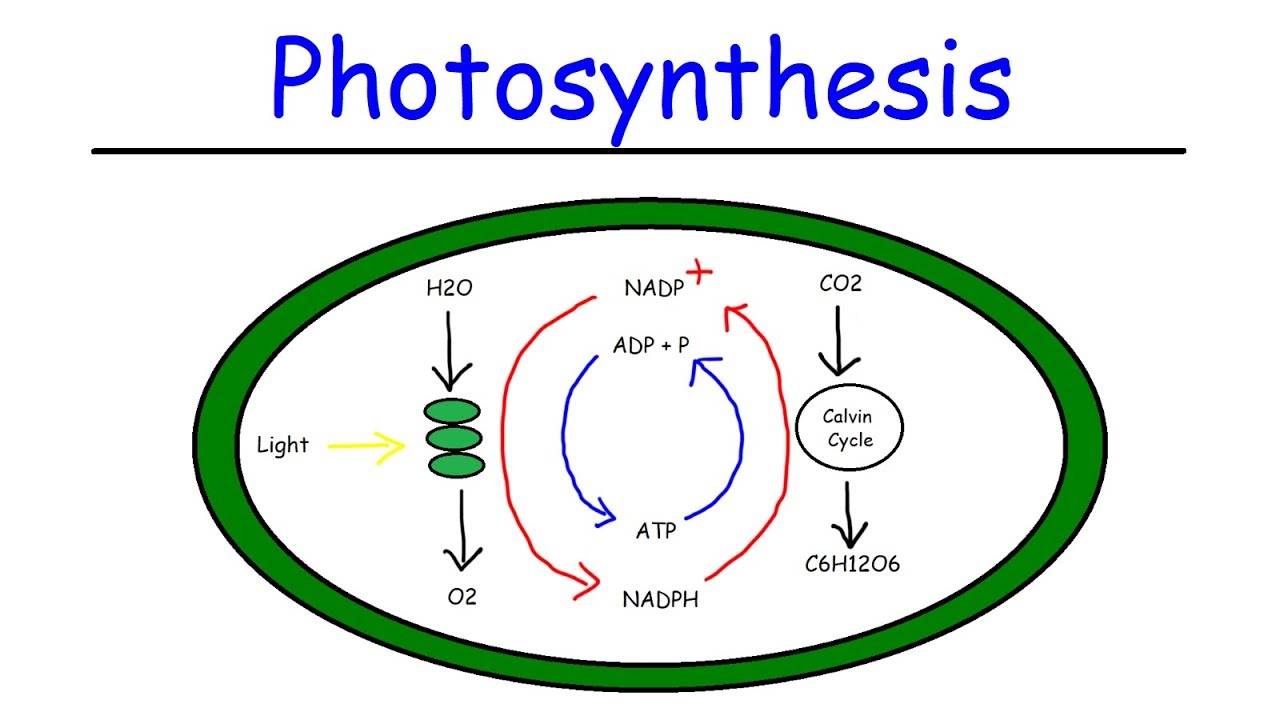
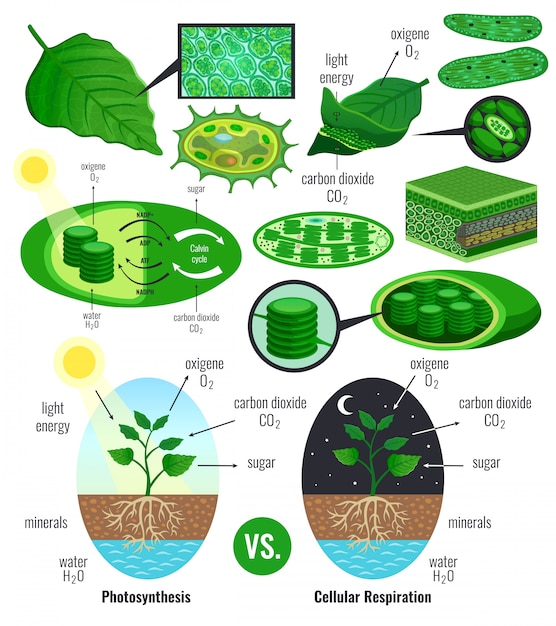
Chloroplast has a structure called chlorophyll which functions by trapping the solar energy and is used for the synthesis of food in all green plants. Produces NADPH and molecular oxygen (O 2) by photolysis of water. Produces ATP - Adenosine triphosphate by the process of photosynthesis. The carbon dioxide (CO2) obtained from the air is used ... The Calvin cycle, Calvin-Benson-Bassham (CBB) cycle, reductive pentose phosphate cycle (RPP cycle) or C3 cycle is a series of biochemical redox reactions that take place in the stroma of chloroplast in photosynthetic organisms.The cycle was discovered in 1950 by Melvin Calvin, James Bassham, and Andrew Benson at the University of California, Berkeley by using the radioactive isotope carbon-14. In the Calvin cycle, carbon atoms from are fixed (incorporated into organic molecules) and used to build three-carbon sugars. This process is fueled by, and dependent on, ATP and NADPH from the light reactions. Unlike the light reactions, which take place in the thylakoid membrane, the reactions of the Calvin cycle take place in the stroma (the ... An explanation of the Calvin Cycle as well as C4 and CAM pathways.
Calvin Cycle Definition. The Calvin cycle is the cycle of chemical reactions performed by plants to "fix" carbon from CO 2 into three-carbon sugars.. Later, plants and animals can turn these three-carbon compounds into amino acids, nucleotides, and more complex sugars such as starches.. This process of "carbon fixation" is how most new organic matter is created.
Calvin cycle simple diagram. As shown in Fig. A Rate equations The reactions in the Calvin cycle are shown in Fig. A simplified model of the Calvin cycle Our simplified model of the […] To begin with 6 mols. Atoms are represented by the following colors. Pin On Biology These reactions actually have several names associated.
The Calvin Cycle - Reduction - This step is the sequence of reactions using electrons from NADPH and some of the ATP to reduce carbon dioxide. 5. The Calvin Cycle - Regeneration - In the final step, ribulose 1,5- bisphosphate is regenerated. For every three turns of the cycle, five molecules of glyceraldehyde-3- phosphate are used to re-form 3 ...
- This simple schematic diagram gives a basic overview of what occurs during the Calvin Cycle. Carbon dioxide enters the cycle from the atmosphere and is joined to RuBP by Rubisco. NADPH and ATP are used to "turn" the cycle, and organic compounds (such as G3P/PGAL) are produced.
Complete the diagram of the Calvin cycle by filling in the missing labels. The Calvin cycle uses carbon dioxide molecules as well as ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent reactions to make sugars. The reactions of the Calvin cycle use ATP and NADPH as energy sources. They do not directly require light. The compound with which CO 2 from the air ...
Calvin cycle, also known as the light independent reaction, is the second stage of photosynthesis which is a very important stage. In this stage the carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere is taken in by the plant and is converted into carbon in the form of sugar, lipids and protein, in the form of glucose.
The Calvin cycle (also known as the Benson-Calvin cycle) is the set of chemical reactions that take place in chloroplasts during photosynthesis.. The cycle is light-independent because it takes place after the energy has been captured from sunlight.. The Calvin cycle is named after Melvin C. Calvin, who won a Nobel Prize in Chemistry for finding it in 1961.
Top 3 Stages of Calvin Cycle (With Diagram) Let us make an in-depth study of the three stages of Calvin cycle. The three stages are: (a) Carboxylation (b) Reduction and (c) Formation of Hexose Sugar and Regeneration of RuBP. The Calvin cycle (C3-cycle) or PCR-cycle can be divided into three stages: (a) Car-boxylation, during which atmospheric ...
The Calvin Cycle. In plants, carbon dioxide (CO 2) enters the leaves through stomata, where it diffuses over short distances through intercellular spaces until it reaches the mesophyll cells.Once in the mesophyll cells, CO 2 diffuses into the stroma of the chloroplast, the site of light-independent reactions of photosynthesis. These reactions actually have several names associated with them.
Simple diagram of the calvin cycle. August 10, 2021, 09:01. Our custom writing service is a reliable solution on your academic journey that will always help you if your deadline is too tight. You fill in the order form with your basic requirements for a paper: your academic level, paper type and format, the number of pages and sources ...
In the Calvin cycle, carbon dioxide molecules (CO2) are combined with each other and with the electrons and H's from NADPH to form glucose (C6H12O6). How can cells store the sugar that is produced in photosynthesis? It is stored as starch. Label the diagram below to summarize the two stages of photosynthesis. Use the word bank below the ...
The Calvin cycle is a set of light independent redox reactions that occur during photosynthesis and carbon fixation to convert carbon dioxide into the sugar glucose. These reactions occur in the stroma of the chloroplast, which is the fluid-filled region between the thylakoid membrane and inner membrane of the organelle. Here is a look at the redox reactions that occur during the Calvin cycle.
Need more help! a. Draw a simple flow diagram of the Calvin cycle to show the relative positions in the cycle of the following molecules: CO 2 (1C) GP/PGA (3C) triose phosphate (3C) RuBP (5C). b. Show the point in the cycle at which the enzyme rubisco is active.
The PGA molecule enters the calvin cycle to make carbohydrates, but one CO 2 molecule released in mitochondria during photorespiration has to be re-fixed. In other words, 75% of the carbon lost by oxygenation of RuBP is recovered, and 25% is lost as release of one molecule of CO 2 .

/2000px-Calvin-cycle4.svg-58a397c25f9b58819c5ba0d6.png)



/2000px-Calvin-cycle4.svg-58a397c25f9b58819c5ba0d6.png)

















0 Response to "41 calvin cycle simple diagram"
Post a Comment