39 h2+ molecular orbital diagram
In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule.This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The terms atomic orbital and molecular orbital were introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 to mean one … The energy curves for ψ + and ψ-reveal the following properties of the ion H 2 +. The curve for ψ + refers to the ground state of the molecule where a minimum energy is found for a nuclear distance of approximately 2a o (i.e. 100pm). Thus, H 2 + should exist as a stable molecule. The calculated bonding energy is 1.77 eV. This is a quite satisfying result; from experiments we get 2.77 eV.
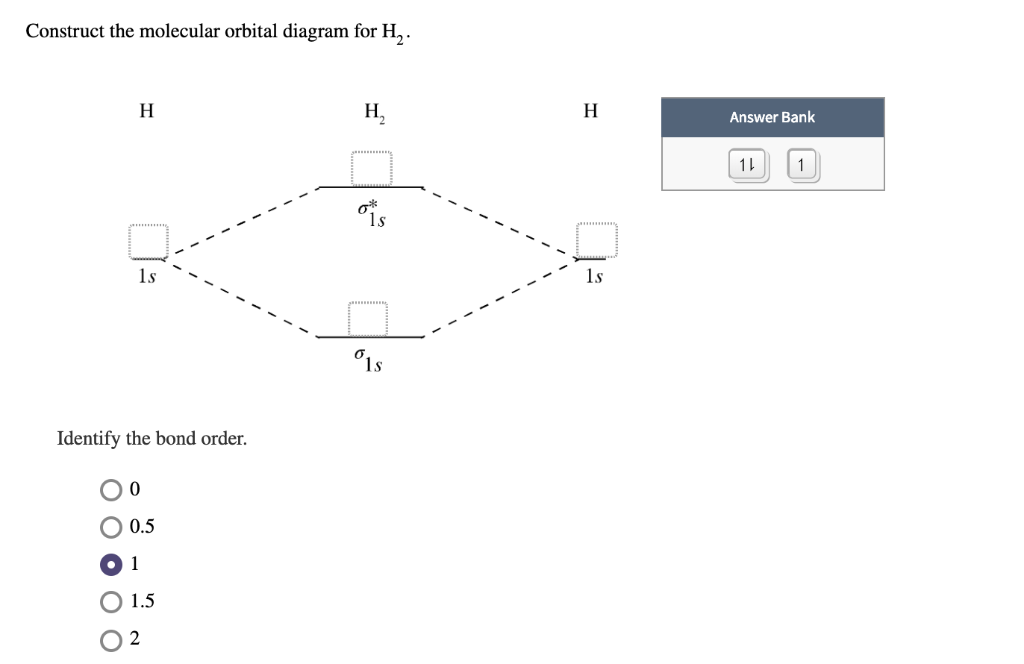
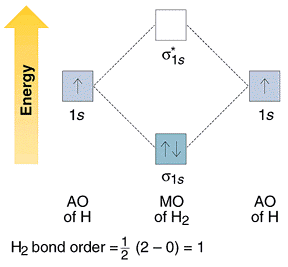
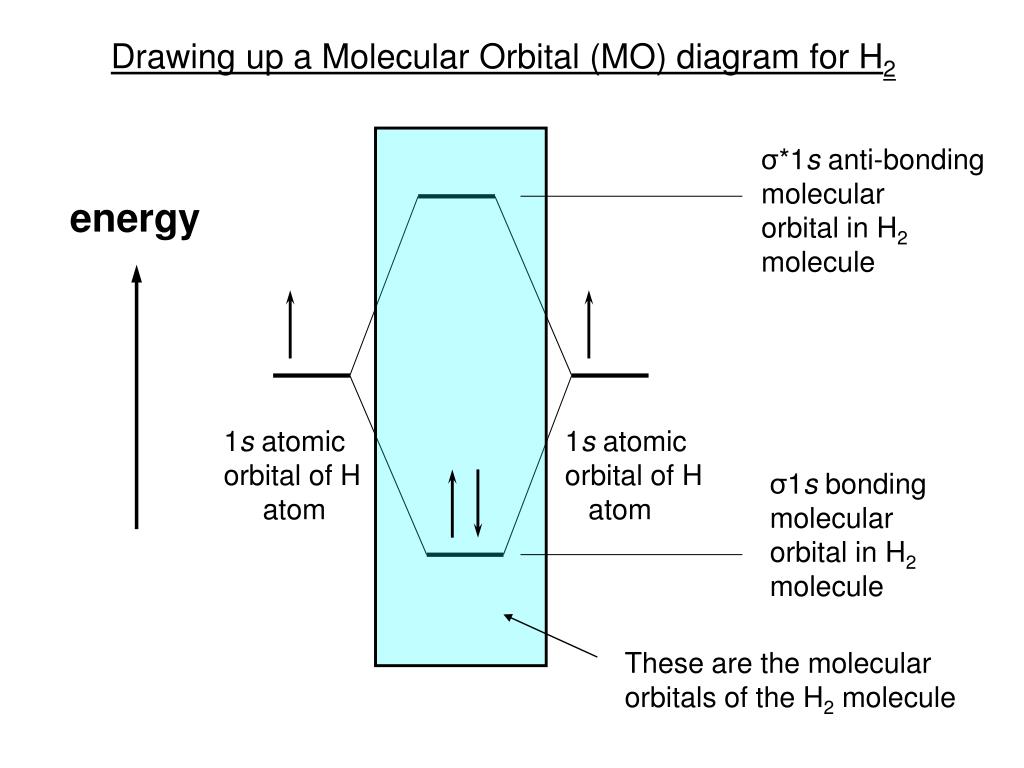
02.08.2021 · H 2 is formed by the overlap of 1s atomic orbitals. Its shell has two molecular orbitals. one is bonding (σ 1s) and the other is anti-bonding (σ * 1s).The H 2 molecule has two electrons and these can be accommodated in the σ 1s molecular orbital. Following the Pauli exclusion principle, this electron must have opposite spins.. Bond order of H 2 :. As we discuss …

H2+ molecular orbital diagram
Molecular Orbital Theory. considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals ( s, p, d …) and hybrid orbitals ( sp, sp2, sp3 …) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*) forms σ or π bonds. Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory of the H2 molecule: Following the MO treatment of H2+, assume the (normalized) ground electronic ... Spin‐orbitals of type 1 and 3 have the same symmetry, and therefore can "mix" (to give improved wavefunctions and energy eigenvalues): 1 ψψ αβ ... is called Molecular Orbital Theory. • MO theory assumes that the valence electrons of the atoms within a molecule become the valence electrons of the entire molecule. • Molecular orbitals are constructed by taking linear combinations of the valence orbitals of atoms within the molecule. For example, consider H2:
H2+ molecular orbital diagram. The molecular orbital energy-level diagram shown in Figure 13 also applies (with changes of detail in the energies of the molecular orbitals) to the hypothetical species He 2. However, this species has four valence electrons, and its configuration would be 1σ 2 2σ 2. Molecular hydrogen (H2) is an agent with potential applications in oxidative stress-related and/or inflammatory disorders. H2 is usually administered by inhaling H2-containing air (HCA) or by oral intake of H2-rich water (HRW). Despite mounting evidence, the molecular mechanism underlying the therapeutic effects and the optimal method of H2 ... In molecular orbital theory, bond order is also defined as the difference, divided by two, between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons; this often, but not always, yields the same result. Bond order is also an index of bond strength, and it is used extensively in valence bond theory. Dihydrogen (H 2) This MO diagram depicts the molecule H 2, with the contributing AOs … Integumentary System Diagram Labeled; Pioneer Avh 4200nex Wiring Diagram; Sears Bench Grinder 397 19671 Wiring Diagram; Construct The Molecular Orbital Diagram For H2 And Then Identify The Bond Order. Troy Bilt Bronco Parts Diagram; Fallout 4 Auto Door Wiring Diagram; Wiring Stove Outlet 3 Prong; 2jz Swap Wiring Diagram Rx7; P0500 Jeep Liberty ...
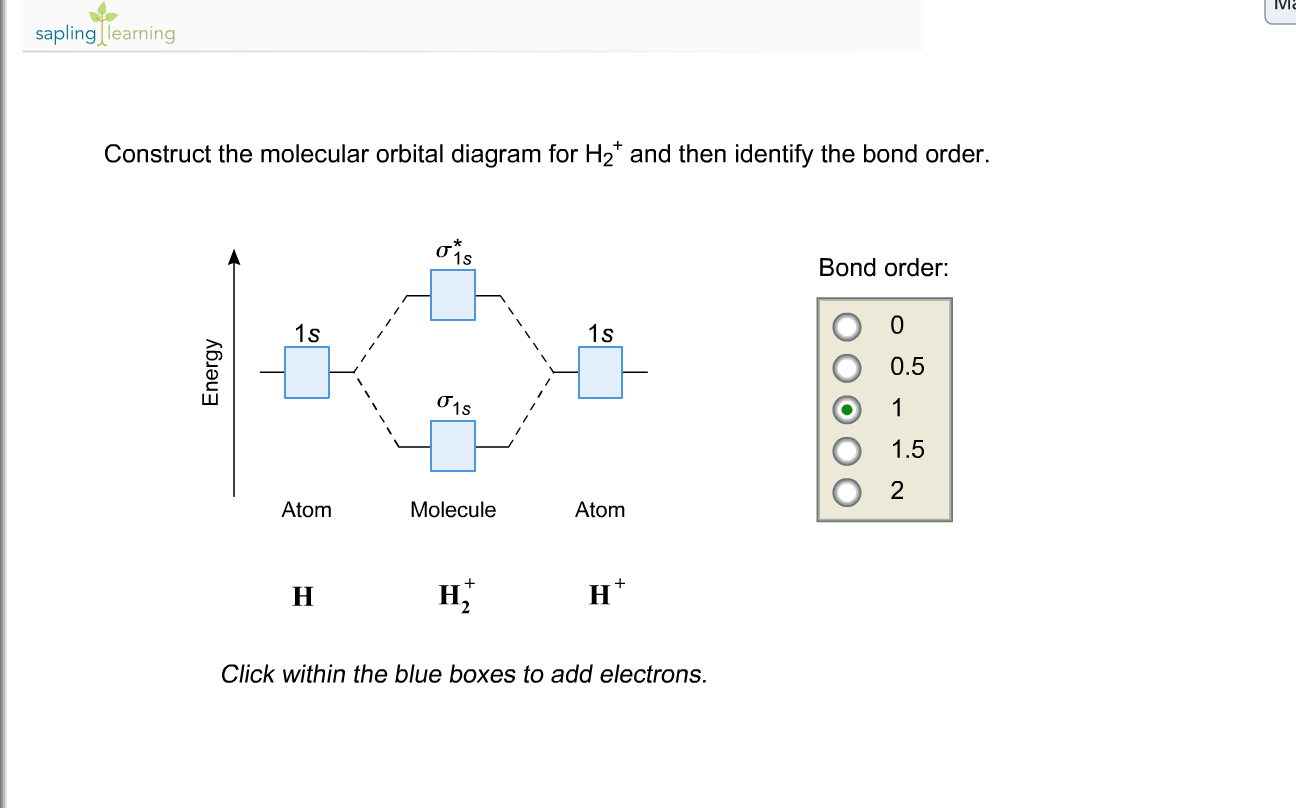
The bonding and anti-bonding orbitals are usually depicted by the molecular orbital diagram. Below mentioned is the molecular orbital diagram of the dihydrogen ion H2+. The atomic valence electrons (which are represented by the left and right boxes) at first fills the lower-energy molecular orbitals, and then it fills the higher ones. molecular orbitals in the diagram suggest a double bond. c. The 2s, 2s *, 2p, and 2p * orbitals exhibit C v symmetry, with the NF bond axis the infinite-fold rotation axis. The 2p and 2p * orbitals exhibit Cs symmetry. The latter do not possess C2 rotation axes coincident to the Apr 01, 2017 · Well, build the molecular orbital (MO) diagram. Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and thus, "H"_2^(-) has three electrons while "H"_2^(+) has one. Each hydrogen atom contributes one 1s atomic orbital, and thus, the orbitals overlap according to MO theory to form one sigma_(1s) and one sigma_(1s)^"*" MO by conservation of orbitals. Mo · Construct The Molecular Orbital Diagram For H2 And Then Identify The Bond Order. chemical bonding molecular orbitals of h2 and he2 as before the greater the number of these nodal planes the more the electrons that occupy the orbitals are excluded from the region between the nuclei and hence the higher the energy the resulting molecular ...
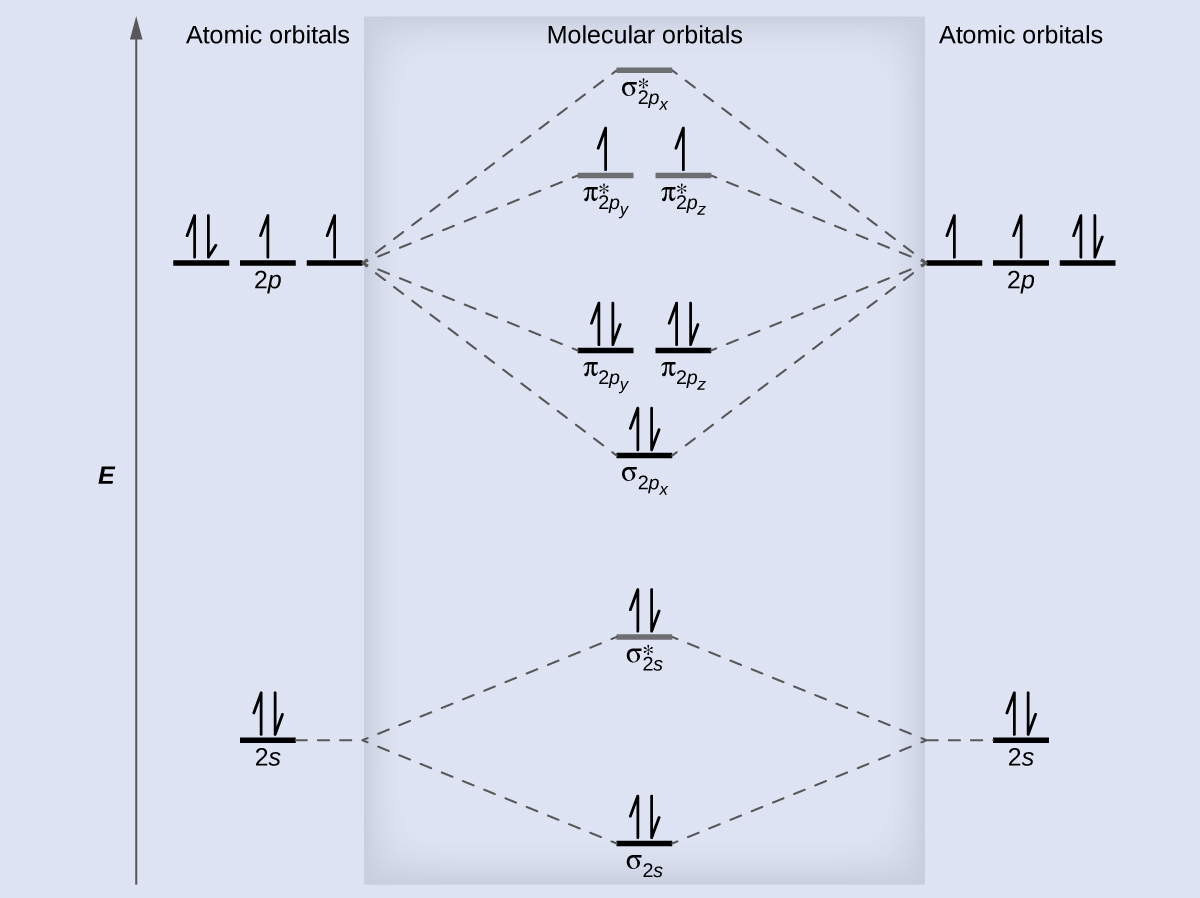
The head-to-head overlap giving σ molecular orbitals results in greater overlap, making its bonding molecular orbital the most stable and lowest energy, while the σ* antibonding is least stable and has the highest energy (Figure 9.24 "Molecular orbital energy diagram for homonuclear diatomic molecules made from atoms of atomic number 8-10"). of the orbitals is specified. b. Molecular Orbital Picture We are now in a position to discuss the basic principles of the molecular orbital (MO) method, which is the foundation of the electronic structure theory of real molecules. The first step in any MO approach requires one to define an effective one electron Hamiltonian, hˆ eff. To this ... Answer (1 of 4): In order to predict the bond order, molecular orbital diagram for H2- is to be drawn. According to MOT number of atomic orbitals combined is equal to total number of molecular orbitals formed.Electronic configuration of H is 1s1. when two hydrogen atoms come closer, then on combi... 1 day ago · To showcase the relative energy levels of the AOs and the resultant MOs, we have the Molecular Orbital diagrams. The lower energy molecular orbital is the bonding and the higher energy is the anti-bonding orbital. The below-mentioned diagram gives us the individual MO diagrams of Oxygen and Fluorine separately, the atoms that make up a molecule ...
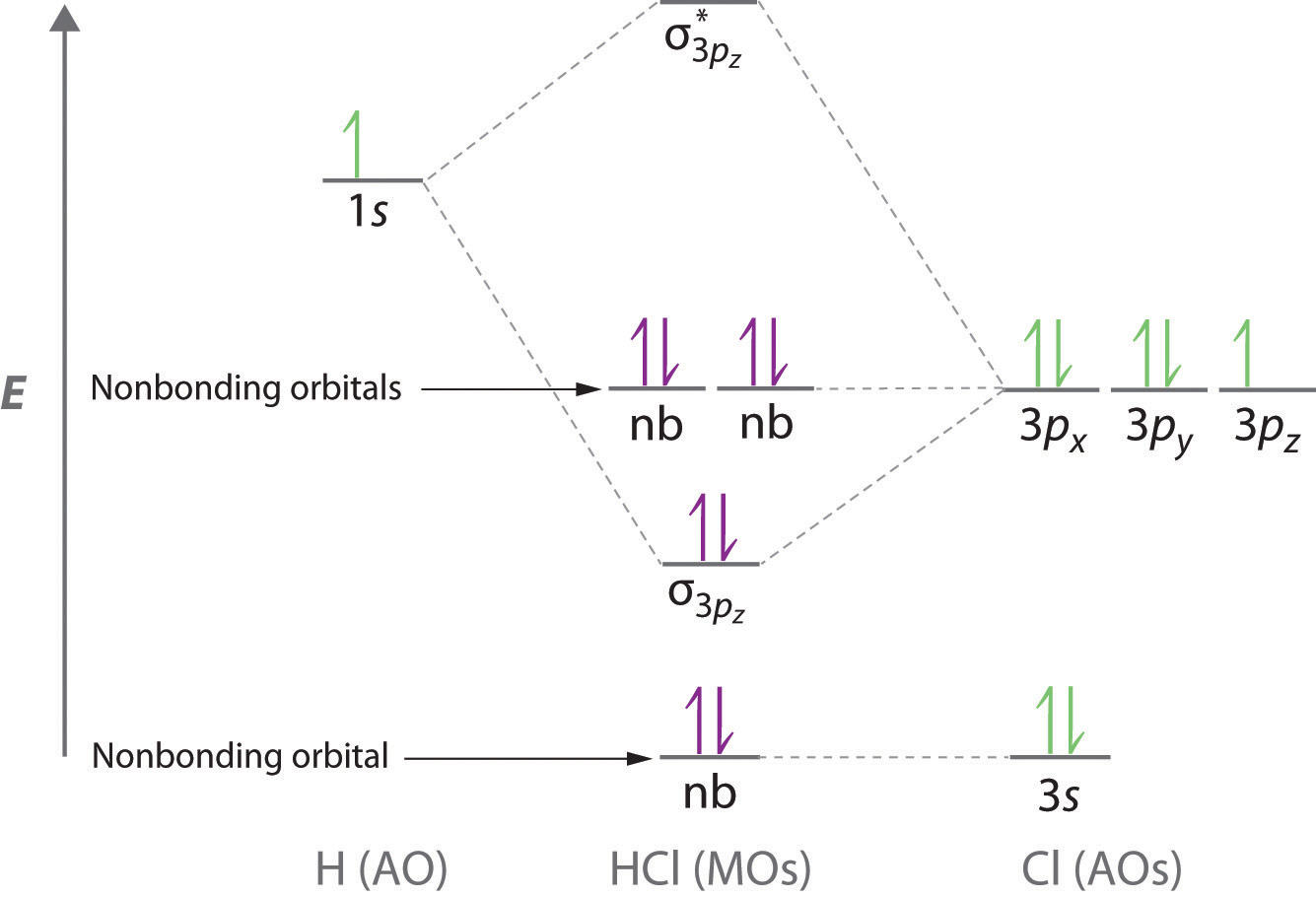
11.01.2022 · CH3 − CH2Cl + H2 —— Zn/H+ —–> CH3 − CH3 + HCl. 2CH3Cl + 2Na ——Dry ether——> CH3 − CH3 + 2 NaCl . 2 CH3COONa + 2H2O —–Electrolysis——> CH3 − CH3 + 2NaOH + H2 + 2CO2. Let us discuss the basic concepts of ethane such as its Lewis structure, polarity, hybridization of carbon atom in ethane, and its Molecular orbital (MO) diagram to …
This problem has been solved! A.Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2^2+ and then identify the bond order. B.Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2 and then identify the bond order. C.Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2^- and then identify the bond order. D.Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2^+ and then ...
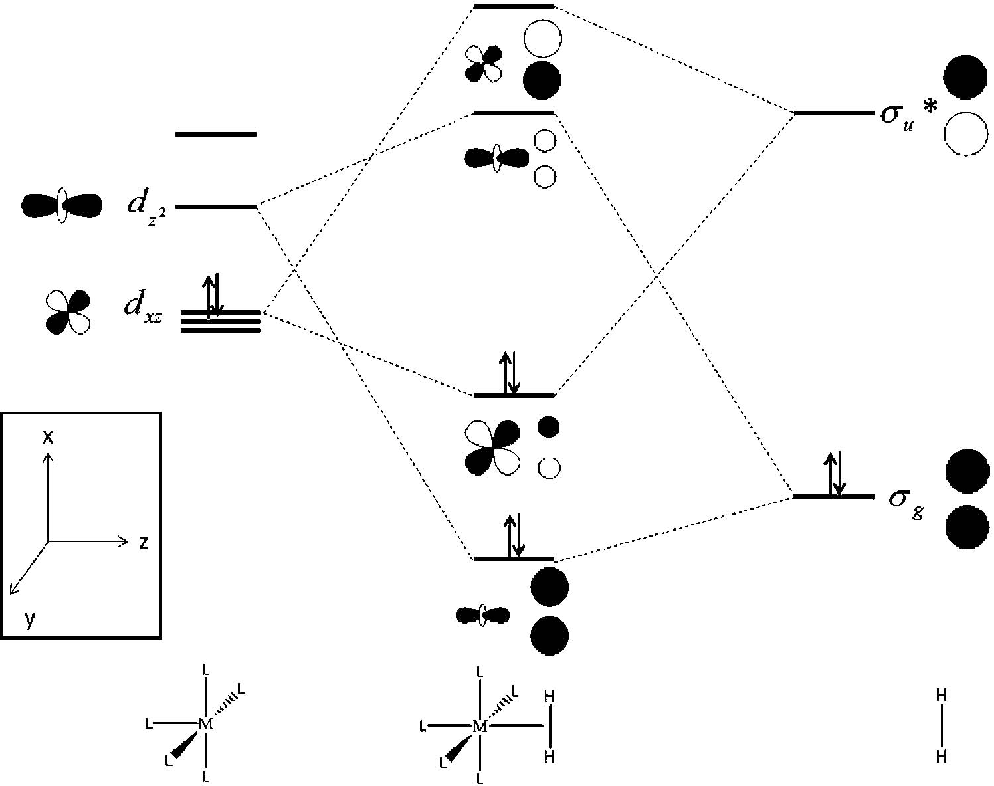
Jul 02, 2021 · Schematic illustration of orbital interactions between adsorbed CO (5σ and 2π*) and 3d orbital (d z 2, d xz /d yz) of Fe site in a Fe-SAC and b NiFe-DASC. Differential charge density on c Fe-SAC ...
Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click thin the blue boxes. The hydrogen atom is the simplest atom, and its molecule \ (\ce {H2}\) is get a sigma (s) bonding orbital, denoted as s1s in the diagram here.
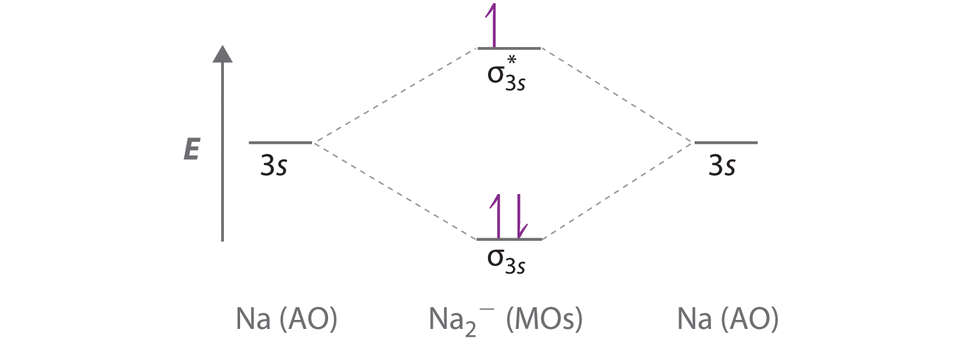
The energy-level diagram for He2 is shown above, the two electrons in each of the 1s atomic orbital give total of 4 electrons in this molecule. Two are placed in the bonding orbital, the other two in antibonding orbital. The bond order = 1/2 x (Number of Bonding Electrons - Number of Antibonding Electrons) = .
Molecular Orbital Diagram for Hydrogen Gas (H2).Fill from the bottom up, with 2 electrons total.Bonding Order is 1, and it is Diamagnetic.sigma2s(2)Check me ...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine …

A technician using a microtome at the Advanced Technology Research Facility (ATRF), Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute. A microtome is an instrument that cuts extremely thin sections of material for examination under a microscope.
Molecular Orbital Theory is primarily used to explain the bonding in molecules that cannot be explained by Valence Bond Theory. These are molecules that generally involve some form of resonance. Resonance implies that a bond is neither single nor double but some hybrid of the two. Valence bond theory only describes the bonding of single or double or triple bonds. It does …
04.03.2021 · Construct a "molecular orbital diagram" of the kind shown in this lesson for a simple diatomic molecule, and indicate whether the molecule or its positive and negative ions should be stable. The molecular orbital model is by far the most productive of the various models of chemical bonding, and serves as the basis for most quantiative calculations, …
04.09.2021 · Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\): This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic \(\ce{Be2+}\), showing the molecular orbitals of the valence shell only. The molecular orbitals are filled in the same manner as atomic orbitals, using the Aufbau principle and Hund’s rule. We predict the distribution of electrons in these molecular orbitals by filling the orbitals in …
Jan 11, 2022 · For example, an ‘s’ and a ‘p’ orbital come together to form an sp hybrid orbital, one ‘s’ and two ‘p’ orbitals ( e.g. px, py ) fuse to form an sp2 hybrid orbital, and so on. Let us check what the hybridization of NH2- ion is: For finding out hybridization, we can use the following formula: H= 1/2 ( V + M – C + A) H ...
Molecular orbital diagram of h2 Answer General guidance Concepts and reason The bonding and anti - bonding interaction of the molecules can be explained with the help of a molecular orbital diagram. It also gives a detailed description of bonding in molecules. Bond order represents the number of bonds present in between two bonded atoms.
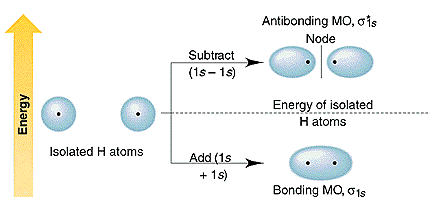
the molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the h 2 molecule is shown in figure on either side of the central ladder are shown the energies of the 1 s orbitals of atoms a and b, and the central two-rung ladder shows the energies of the bonding and antibonding.the …
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.The Hydrogen Molecule Ion H2+Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Diatomic Molecules - Chem
Relationship between electronic configuration and Molecular behaviour. 1) Stability of molecules in terms of bonding and antibonding electrons . Number of electrons present in the bonding orbitals is represented by N b and the number of electrons present in antibonding orbitals by Na.. 1) If N b > Na,the molecule is stable because greater number of bonding orbitals are occupied than ...
brings only a 1s orbital to the mixing. Just as in the molecules H2 and H2 +, the molecular orbitals for He2 are created by the combination of two 1s atomic orbitals (Fig. 1.46). Each helium atom brings two electrons to the molecule, though, so the electronic occupancy of the orbitals will be different from that for H2 or H2 +. The
starting with the lowest energy molecular orbital. The two electrons associated with a pair of hydrogen atoms are placed in the lowest energy, or bonding, molecular orbital, as shown in the figure below. This diagram suggests that the energy of an H2molecule is As a result, the H2molecule is more stable than a pair of isolated atoms.
Draw a molecular orbital diagram of ${N_2}$ or ${O_2}$ with magnetic behavior and bond order. Answer. Verified. 73.1k+ views. Hint: Generally the molecular orbital diagrams are used to understand the bonding of a diatomic molecule. You should know that molecular orbital diagrams are used to deduce magnetic properties of a molecule; they also ...
In this video, we take a detailed look at the molecular orbitals of the H2 molecule, with an introduction to molecular orbital diagrams. Discussed in this v...
is called Molecular Orbital Theory. • MO theory assumes that the valence electrons of the atoms within a molecule become the valence electrons of the entire molecule. • Molecular orbitals are constructed by taking linear combinations of the valence orbitals of atoms within the molecule. For example, consider H2:
Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory of the H2 molecule: Following the MO treatment of H2+, assume the (normalized) ground electronic ... Spin‐orbitals of type 1 and 3 have the same symmetry, and therefore can "mix" (to give improved wavefunctions and energy eigenvalues): 1 ψψ αβ ...

DNA Genotyping and Sequencing. A technician reviews data from high-throughput DNA genotyping and sequencing at the Cancer Genomics Research Laboratory, part of the National Cancer Institute's Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics (DCEG).
Molecular Orbital Theory. considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals ( s, p, d …) and hybrid orbitals ( sp, sp2, sp3 …) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*) forms σ or π bonds.




















0 Response to "39 h2+ molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment