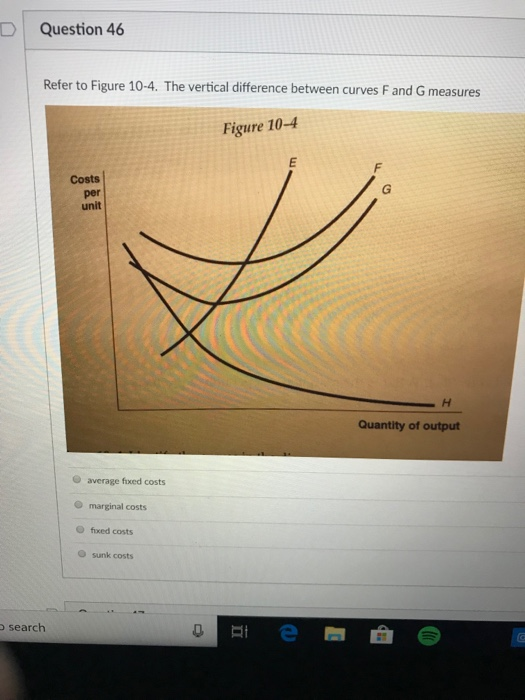
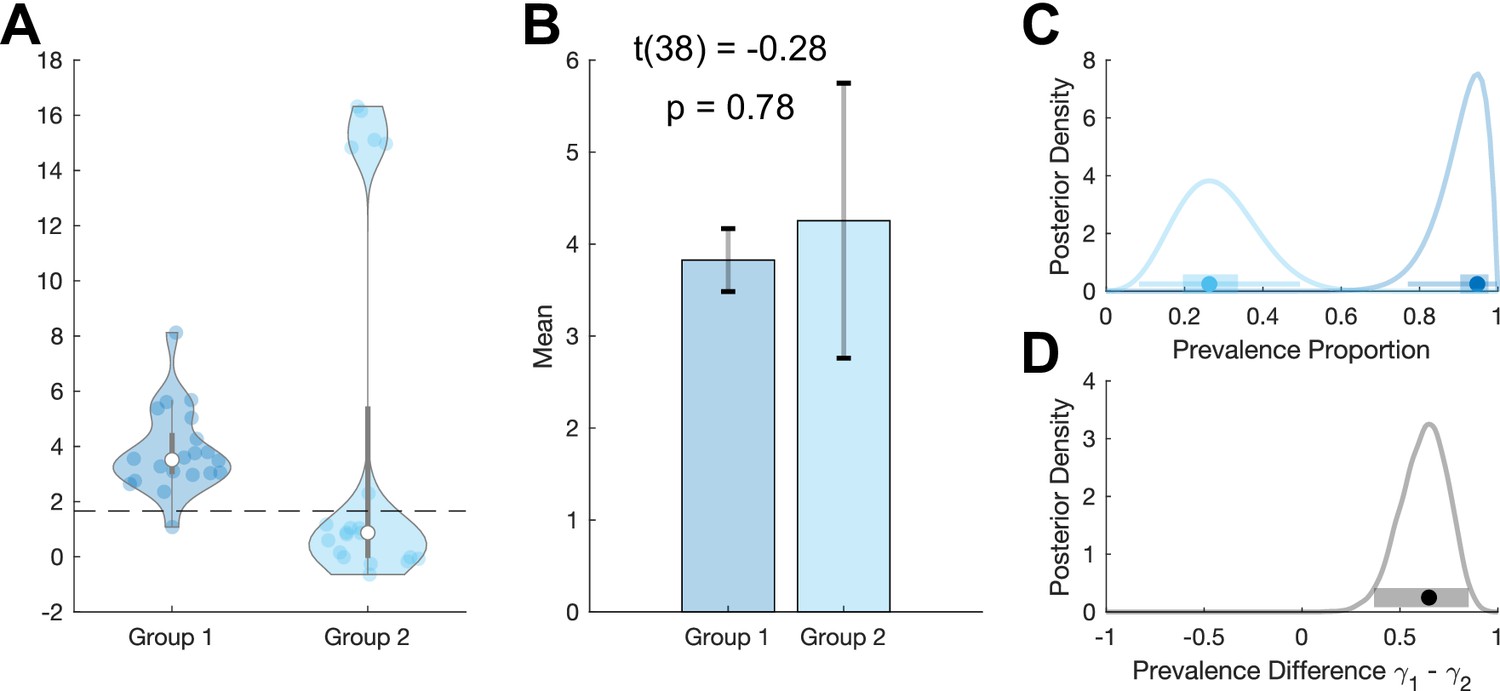
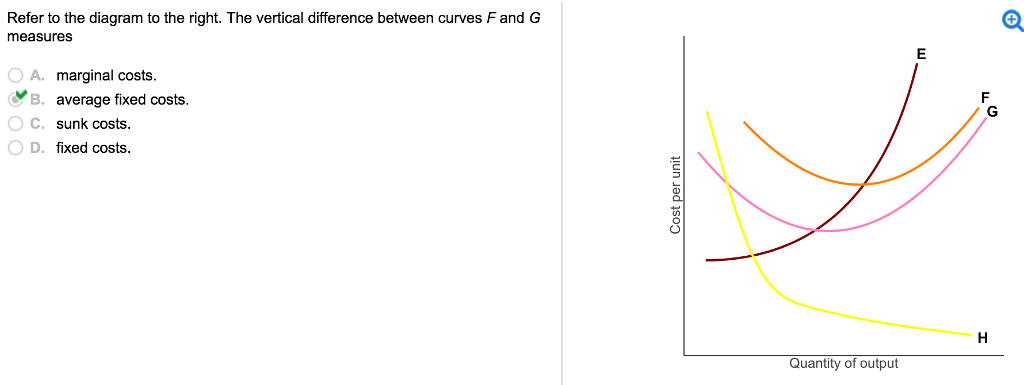
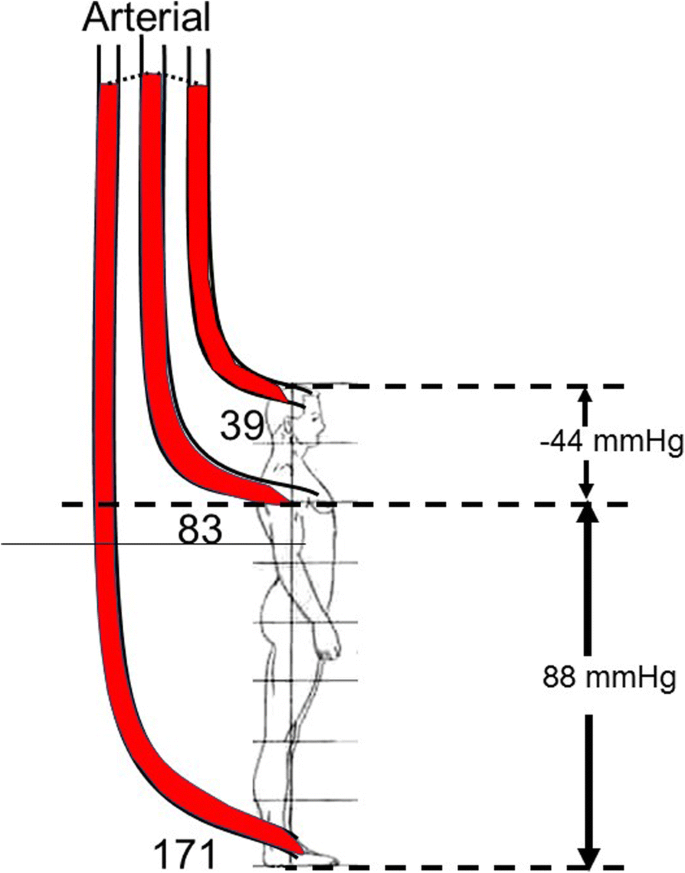
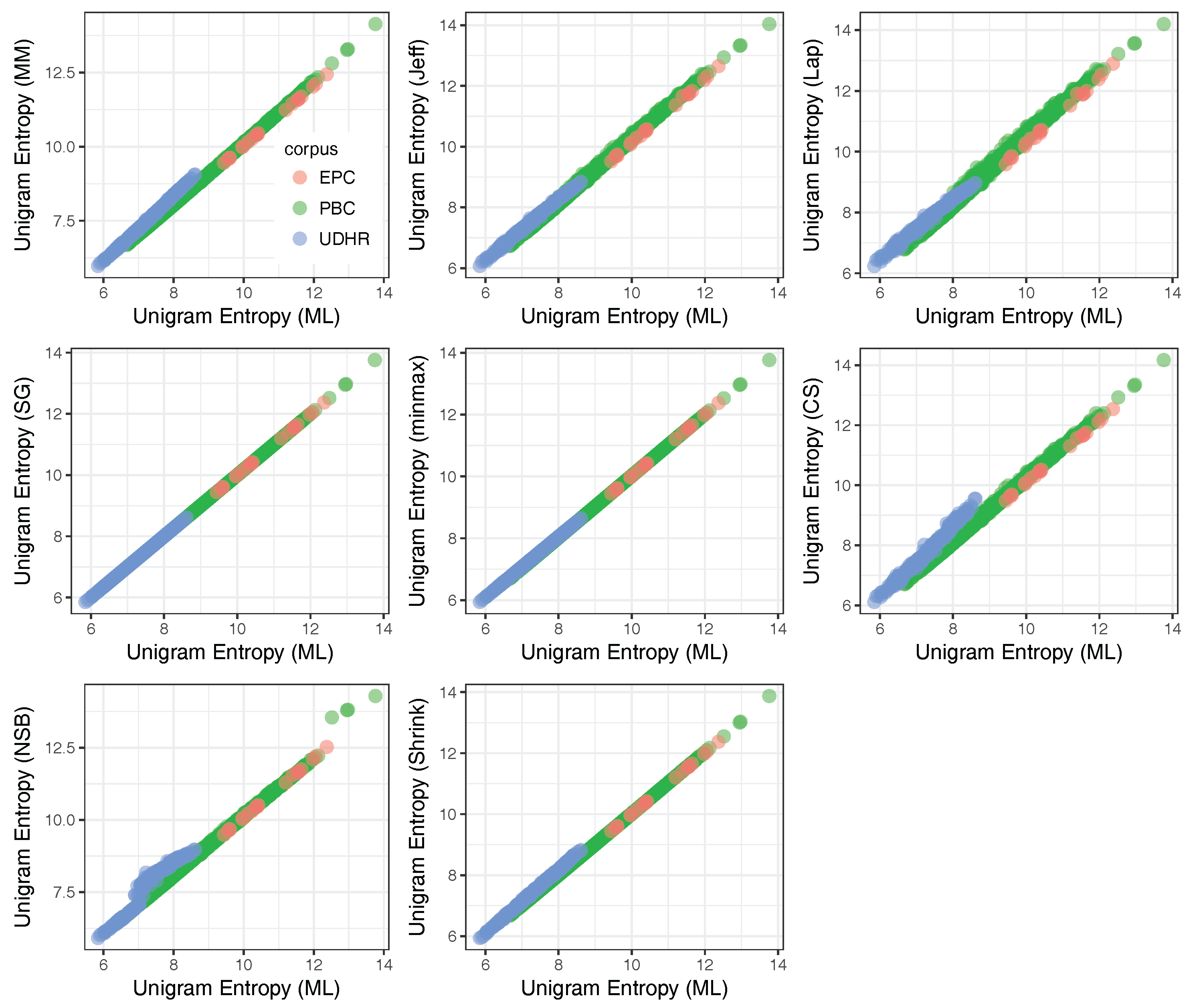
39 refer to the diagram to the right. the vertical difference between curves f and g measures
I'm referring to digital EQs that aren't linear and aren't trying to emulate any analog gear. Something I've done before, and I don't know if this is just a colossal waste of time, is create an EQ curve via boosting and cutting, and then find a way to create the exact same curve purely through cutting. The curve will be lower than the original but then I turn up the output level to compensate. Keep in mind, the curve is the exact same shape. If I make the plugin transparent and lay it over t... (Refer to Chapter 9,"Total Station System"). 15-02.5 Modified Conventional Method There are times when it is advantageous to use the Data Controller with a Roading-type slope staking module to set out slope stakes. Input roadway design templates, horizontal and vertical alignments, and superelevation rate data in the Data Controller before ...
IT major in college here. No matter how many books I read and diagrams I look at I can never remember these measurements and make them stick

Refer to the diagram to the right. the vertical difference between curves f and g measures
assumed vertical center of gravity, using the Cross Curves of Stability. 7. Correct a GZ curve for a shift of the ship's vertical center of gravity and interpret the curve. Draw the appropriate sectional vector diagram and use this diagram to show the derivation of the sine correction. 8. I understand that 2 actin monomers put together make up the actin filament. So is it correct to say that the individual monomer is called G-actin and the 2 G-actins put together are called F-actin? reverse curves. In the case of stream crossings or bluffs, it is a matter of not starting a curve until a certain point is reached. In the case of reverse curves, the total tangent distance between PI's must be shared by two curves and not overlap. Some road standards may call for a minimum tangent between curves. In any
Refer to the diagram to the right. the vertical difference between curves f and g measures. measures of radiation Other units include Bequerels and Curies - /u/The\_camperdave Label area between MAC1 and MAC2 to the right of e1 as a. Label area below MAC2 to the right of e1 as b. Label area bounded by the charge line, MAC2, and e1 line as d. Label area bounded by MAC2, e1 line, and e2 line as c. Label area bounded by the charge line, e2 line, and the two axes as f. Compliance cost with MAC1 technology = (a+b+c+d+f) [Paul Krugman, Robin Wells] Microeconomics(z-lib.org) Drivers gradually turn into curves, with the path following a spiral curve. Roadway segments with spiral curve transitions have the potential for fewer crashes than segments without spiral curve transitions. Refer to Section 2C-1 for spiral curves. Coordination with Vertical Alignment Do not design horizontal and vertical alignments separately.
4.1.1 Recognize a function of two variables and identify its domain and range. 4.1.2 Sketch a graph of a function of two variables. 4.1.3 Sketch several traces or level curves of a function of two variables. 4.1.4 Recognize a function of three or more variables and identify its level surfaces. Our first step is to explain what a function of ... Vertical Curves are determined by their length and/or radius. They should be at least 20m long and have a radius appropriate to the design line speed. The speed/radius limitations are shown in the TDH page B4.1.It is possible to connect gradients without using vertical curves if they are of a similar gradient with less than 0.02% difference. ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the Theoretically Analysis of the Production Process. Production Process: The business firm is basically a producing unit it is a technical unit in which inputs are converted into output for sale to consumers, other firms and various government departments. Production is a process in which economic resources […] Identify the curves in the diagram. E= Marginal Cost Curve F= Average total cost curve G= Average variable cost curve H= Average fixed cost curve. Refer to figure 11-10. Identify the minimum efficient scale of production. Qb. 17 Refer to Figure 11 4 Identify the curves in the diagram A E marginal cost from ECO 101 at Miami University
b. supply curve downward (or to the right). c. demand curve upward (or to the right). d. demand curve downward (or to the left). ____ 25. When a tax is imposed on a good for which demand is elastic and supply is elastic, a. sellers effectively pay the majority of the tax. b. buyers effectively pay the majority of the tax. They run horizontally from left to right and are labeled on the left side of the diagram. Pressure is given in increments of 100 mb and ranges from 1050 to 100 mb. Notice the spacing between isobars increases in the vertical (thus the name Log P). Topic # 625-000-015 DRAFT May - 2012007 Manual of Uniform Minimum Standards Printed 2/73/4/20110 for Design, Construction and Maintenance for Streets and Highways The AA-DD model integrates the workings of the money-Forex market and the G&S model into one supermodel. The AA curve is derived from the money-Forex model. The DD curve is derived from the G&S model. The intersection of the AA and DD curves determines the equilibrium values for real GNP and the exchange rate.
average fixed cost curve. 37. Refer to the figure. The vertical difference between curves F and G measures. A) average fixed costs. B) marginal costs.10 pages
The slope of Plant 1's production possibilities curve measures the rate at which Alpine Sports must give up ski production to produce additional snowboards. Because the production possibilities curve for Plant 1 is linear, we can compute the slope between any two points on the curve and get the same result.
A demand curve shows the relationship between price and quantity demanded on a graph like Figure 1, with quantity on the horizontal axis and the price per gallon on the vertical axis. (Note that this is an exception to the normal rule in mathematics that the independent variable (x) goes on the horizontal axis and the dependent variable (y ...
F g F net F g T ma T m(g a) Movement (a) Increasing speed: v f >v 0 a>0 T<; F g (b) Decreasing speed: v f < v 0 a<0 T>; F g Q8. The figure below shows a train of four blocks being pulled across a frictionless floor by force F. What total mass is accelerated to the right by (a) F, (b) cord 3 (c) cord 1? (d) Rank the
29. Refer to the diagram to the right. Identify the curves in the diagram. A.E = average fixed cost curve, F = variable cost curve, G = total cost curve, H = marginal cost curve B. E = average fixed cost curve, F = average total cost curve, G = average variable cost curve, H = marginal cost curve
103. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be: A. between f and g. B. h. C. g. D. f. 104. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit: A. cannot be determined from the information given. B. will be ae per unit sold. C. will be bc per unit sold. D. will be ac per unit sold. 105.
15.02.2006 · INTRODUCTION. It is well known that even small changes in the composition of cell membranes can strongly affect the functioning of intrinsic membrane proteins, such as ion and water channels, which regulate the chemical and physical balance in cells (1,2).Such changes may occur due to the introduction of short-chain alcohols, or other anesthetics, at membrane …
C. Steinem, A. Janshoff, in Encyclopedia of Analytical Science (Second Edition), 2005 Love-Wave, Shear-Horizontal SAW and Acoustic Plate Mode Sensors. A Love wave is a propagating shear mode wave supported on semiinfinite substrates with a waveguide layer that exhibits a shear acoustic speed lower than that of the substrate. Other acoustic wave sensors utilizing …
01.11.2021 · In this regard, if f(x) is a periodic function with period 2π and integrable between – π and π, the form of the Fourier transformation useful to geologists is (Fossen, 2016): (4) f x = b 1 sin x + b 3 sin 3 x + b 5 sin 5 x … where b 1 and b 3 are called the Fourier Coefficients, which are considered as significant inputs into the description of fold shapes and are unique to each …
RhinoPython; Rhino.Python 101; 8 Geometry. by Skylar Tibbits and Arthur van der Harten and Steve Baer (Last modified: 05 Dec 2018) 8.1 The openNURBS™ kernel. Now that you are familiar with the basics of scripting, it is time to start with the actual geometry part of Rhino.
Refer to the diagram to the right. The vertical difference between curves F and G measures marginal costs. average fixed costs. sunk costs. fixed costs. Question: Refer to the diagram to the right. The vertical difference between curves F and G measures marginal costs. average fixed costs. sunk costs. fixed costs.
Start studying ECON&201 - Chapter 6. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Requirement is that the star must be radially symmetrical, and it can only be stars created from straight lines from vertex to vertex without lifting the pen. To further illustrate... 1. Star of David would not work because it's two separate triangles overlayed on top (you must lift the pencil). 2. Every f(x) is at least one (x is integer >0), since you can have a "star" of every consecutive vertex connected (triangle, square, pentagon, hexagon, and every n-gon etc). Here are samples start...
• Railway vertical curves - old formula: L = D / R D = algebraic difference of grade (ft. per 100-ft. station) R = rate of change per 100-ft. station •0.05 ft. per station for crest on main track •0.10 ft. per station for sag on main track •Secondary line may be twice those for main line
That's the maximum it can measure! - /u/PositivityReloaded
Some examples: Left hand. Middle finger, 3" Tip of pinky to a mole on wrist, 6" Index finger to a mole on forearm, 12" It helps out when quick, small measurements are needed and a ruler isn't handy(ehehehe).
Consider our diagram of a negative externality again. Let's pick an arbitrary value that is less than Q 1 (our optimal market equilibrium). Consider Q 2.. Figure 5.1b. If we were to calculate market surplus, we would find that market surplus is lower at Q 2 than at Q 1 by triangle e.. The market surplus at Q 2 is equal to area a+b. [(a+b+c) - (c)].
22. Refer to the above diagram. The quantity difference between areas A and C for the indicated price reduction measures: A) marginal cost. B) marginal revenue. C) monopoly price. D) a welfare or efficiency loss
The relation between the radius and the degree of the curve may be determined as follows: Refer to fig 11.6: Let R= The radius of the curves in meters . D= The degree of the curve . MN= The chord, 30m long . P= The mid-point of the chord . The approximate relation holds good up to 5° curves. For higher degree curves, the exact relation should ...
The correct answer is 'Option C'. The vertical distance between the curves F and G represents …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Question 25 4 pts Refer to Figure 11-5. The vertical difference between curves F and G measures Figure 11-5 Costs per unit Quantity of output marginal costs sunk costs average fixed costs fixed costs.
Appendix B: Indifference Curves Economists use a vocabulary of maximizing utility to describe people's preferences. In Consumer Choices, the level of utility that a person receives is described in numerical terms. This appendix presents an alternative approach to describing personal preferences, called indifference curves, which avoids any need for using numbers to measure utility.
Copy/Paste from a previous time I answered a question of this sort: Okay, so you've got a bunch of different terms all pertaining to radiation. A few are redundant (as in one is the older term, now replaced with a newer unit), but most are just used to measure radiation at different points or situations. The _Curie_measures radioactivity, that is the amount of particles being outputted from the source. It's a measure of decays per second, meaning how often an unstable atom breaks apart, releas...
Geometry Questions and Answers. Get help with your geometry homework! Check out the answers to hundreds of geometry questions, explained in a …
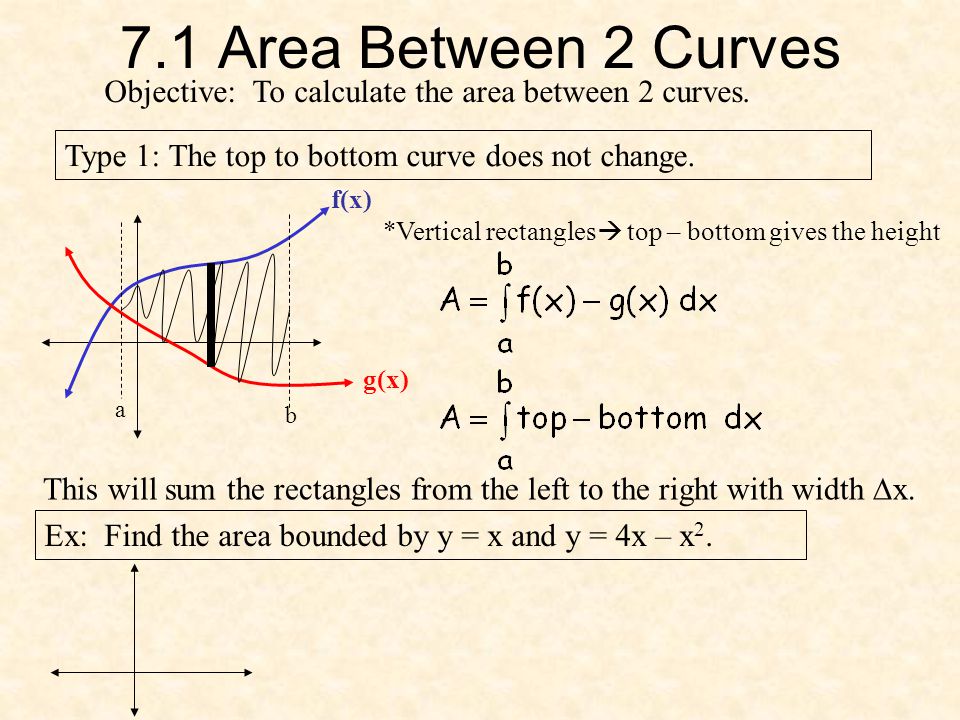
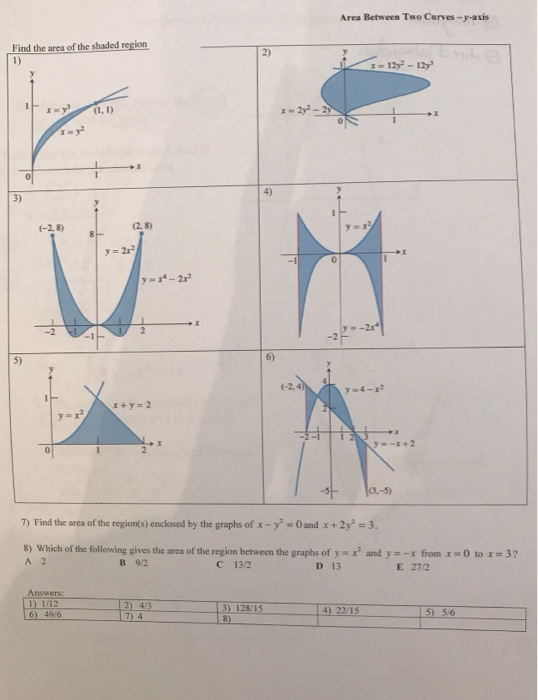
7.1 Area Between 2 Curves Objective: To calculate the area between 2 curves. Type 1: The top to bottom curve does not change. a b f(x) g(x) *Vertical.
Refer to the diagram to the right. The vertical difference between curve F and G measures
• Derivinggg g the general formula gives: • X = g 1 l/(g 1-g 2) = -g 1 /r where: X is the distance in stations from BVC to the high or low point. • Substitute in the tangent offset equation to get the elevation of that point. • El25Example 25-4 t th t ti d l ti f th4: compute the station and elevation of the highest point on the curve ...
Logistic functions are used in logistic regression to model how the probability of an event may be affected by one or more explanatory variables: an example would be to have the model = (+), where is the explanatory variable, and are model parameters to be fitted, and is the standard logistic function.. Logistic regression and other log-linear models are also commonly used in …
I've recently moved closer to the office, which allows me to be more focused in developing my career. I have more free time, feel healthier and fresher. This came at a great cost due to the increased rent. I believe in the long run, this maximizes my chances of FIREing, as sharp me is a better professional than tired me. Do you have a rule of thumb to measure the trade off between saving money and owning the possessions that money allows you to have?
In physics, spacetime is any mathematical model which fuses the three dimensions of space and the one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional manifold. Spacetime diagrams can be used to visualize relativistic effects, such as why different observers perceive differently where and when events occur.. Until the 20th century, it was assumed that the three-dimensional …
(1) y′(x) = f(y(x)). The right side of this equation is independent of x, hence there are no external control terms that depend on x. Due to the lack of external controls, the equation is said to be self-governing or autonomous. A phase line diagram for the autonomous equation y′ = f(y) is a line
Properties of a Vertical Curve 1. The difference in elevation between the BVC and a point on the g1 grade line at a distance X units (feet or meters) is g1X (g1 is expressed as a decimal). 2. The tangent offset between the grade line and the curve is given by ax2, where x is the horizontal distance from the BVC; (that is, tangent offsets
reverse curves. In the case of stream crossings or bluffs, it is a matter of not starting a curve until a certain point is reached. In the case of reverse curves, the total tangent distance between PI's must be shared by two curves and not overlap. Some road standards may call for a minimum tangent between curves. In any
I understand that 2 actin monomers put together make up the actin filament. So is it correct to say that the individual monomer is called G-actin and the 2 G-actins put together are called F-actin?
assumed vertical center of gravity, using the Cross Curves of Stability. 7. Correct a GZ curve for a shift of the ship's vertical center of gravity and interpret the curve. Draw the appropriate sectional vector diagram and use this diagram to show the derivation of the sine correction. 8.





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Guns-and-ButterCurve-f52db04559864b0ebce64aec2db5fe09.png)












0 Response to "39 refer to the diagram to the right. the vertical difference between curves f and g measures"
Post a Comment