41 mo diagram of h2
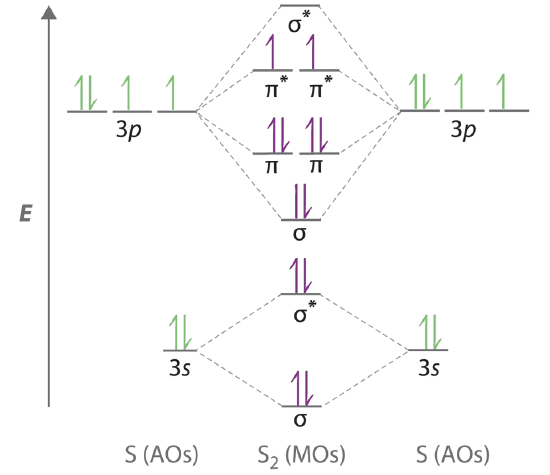
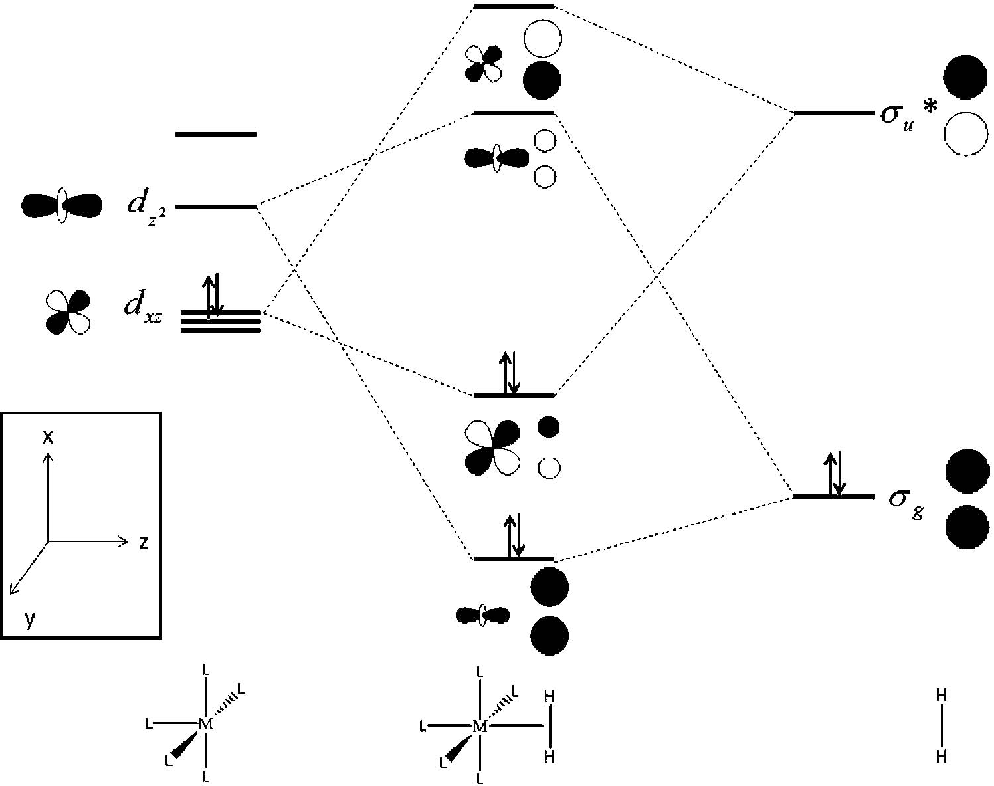
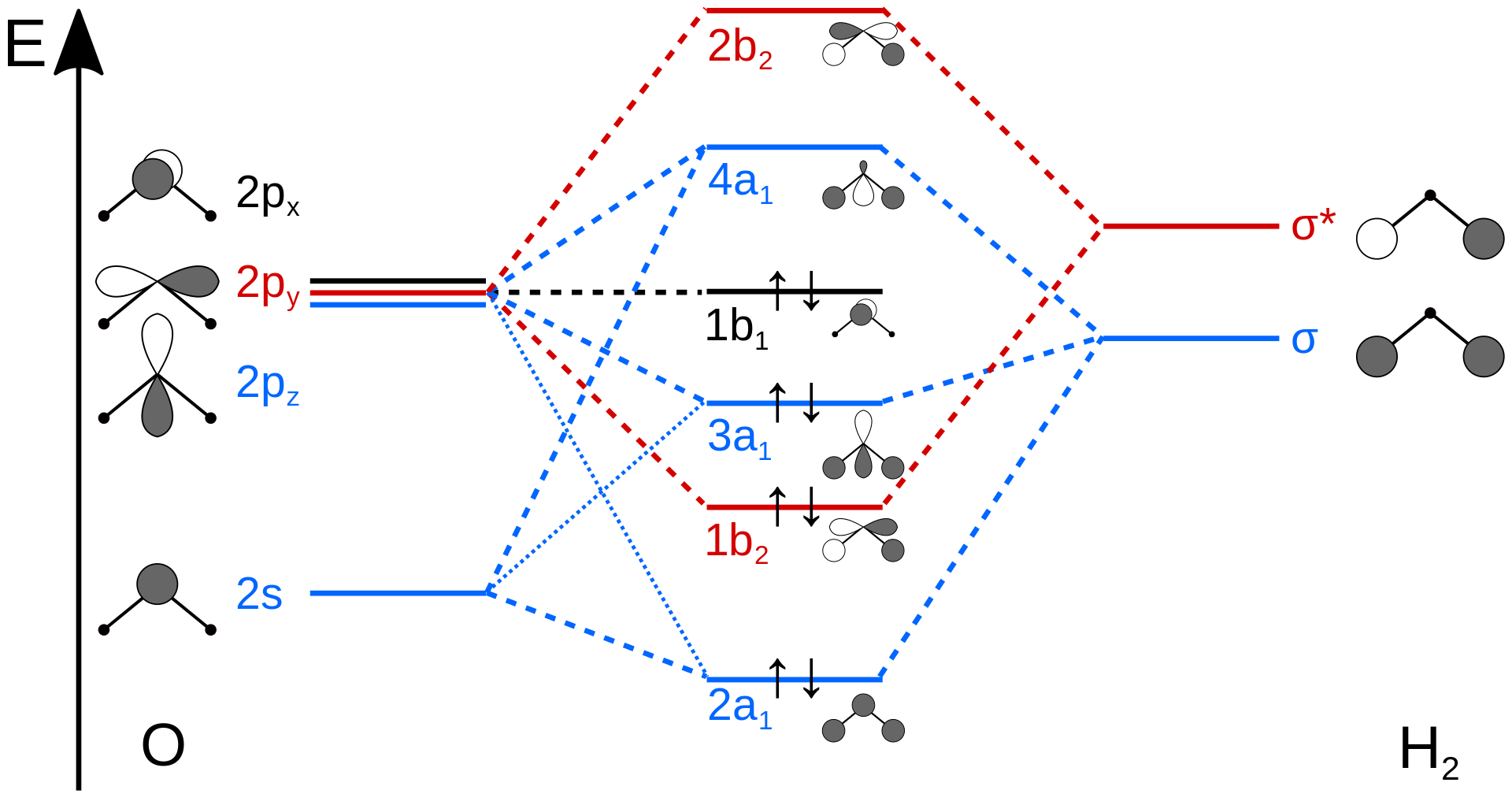
Molecular Orbital Theory - Walsh diagram The Walsh diagram shows what happens to the molecular orbitals for a set of molecules which are related in structure. In this case, the difference is the H-X-H bond angle which decreases from 180 o to 90 o Molecular Orbital Theory - Walsh diagram Water 104.5 ° X H H H O H Now, let us draw the molecular orbital diagram of ${N_2}$ . Now, first let us understand what magnetic behavior and bond order means. - Magnetic behavior: As we know the electron has an electron magnetic dipole moment, which is generally generated by the electron's spin property, which induces an electric charge into motion. As we can see the ...
Hydrogen Molecular Orbital Diagram Atomic hydrogen has 1 electron in a 1s orbital. Of course, there are 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, etc. empty orbitals at higher energy. Let's just consider the 1s orbitals. Remember that an orbital is a mathematical function that describes the probability of finding an electron in space.

Mo diagram of h2
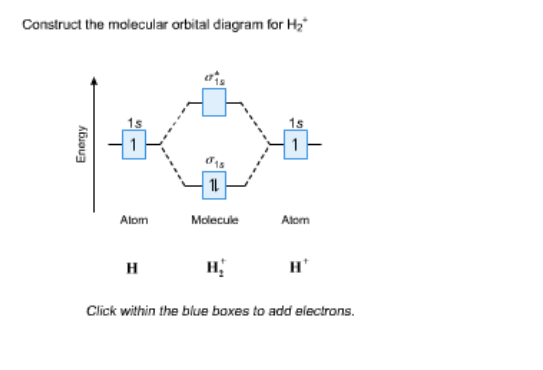
H2 Molecular Orbital Diagram MO diagram of dihydrogen Bond breaking in MO diagram The smallest molecule, hydrogen gas exists as dihydrogen (H-H) with a single covalent bond between two hydrogen atoms. As each hydrogen atom has a single 1s atomic orbital for its electron, the bond forms by overlap of these two atomic orbitals. Answer (1 of 2): According to the molecular orbital theory, a molecular is viable of its bond order is more than or equal to one. The bond order is defined as number of bond between to two atoms of that molecule. It is calculated as the difference of electrons in bonding molecules and anti-bondin... 1 Nov 2019 Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2 and then identify the bond order. Make sure you add electrons to the boxes corresponding to the MOs for the molecule and to the boxes corresponding to the AOs for the two atomic species. Bond order: 1s o 0.5 O 1.5 2 Atom Molecule Atom Click within the blue boxes to add electrons.
Mo diagram of h2. Molecular Orbital Diagrams, Bond Order, and Number of Unpaired Electrons Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O 2. From this diagram, calculate the bond order for O 2. How does this diagram account for the paramagnetism of O 2? Solution We draw a molecular orbital energy diagram similar to that shown in . MO Diagram of I 2 MO Diagram of I 2-Base Complex In this experiment we analyze the acid-base interaction by comparing the energies of the I2 transition to that of the donor-acceptor transition. The higher the energy the absorption, the stronger the acid-base interaction. Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory of the H2 molecule: ... Two electrons in Molecular Orbital ψ_+ 2) One electron in MO ψ_+ and one electron in MO ψ_‐ 3) Two electrons in MO ψ_‐. ... Qualitative MO theory orbital diagram for homonuclear diatomics composed of 1st or 2nd row elements: In this video, we take a detailed look at the molecular orbitals of the H2 molecule, with an introduction to molecular orbital diagrams. Discussed in this v...
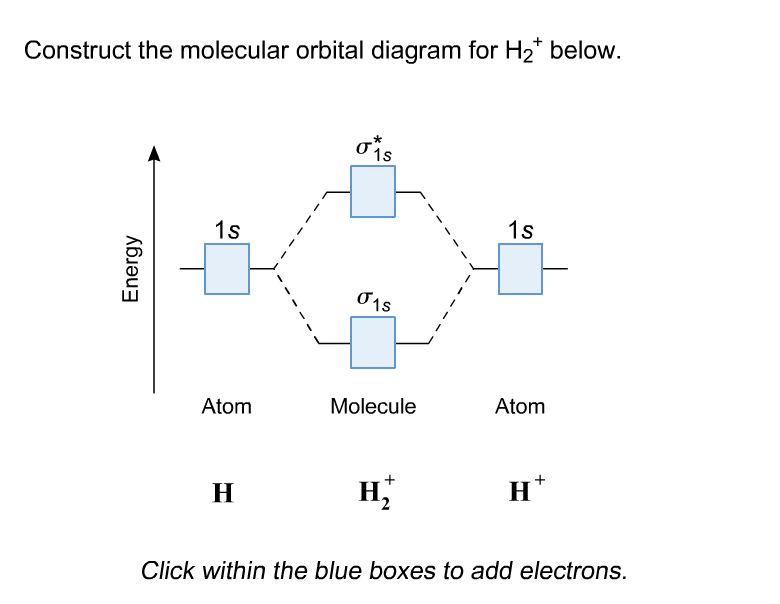
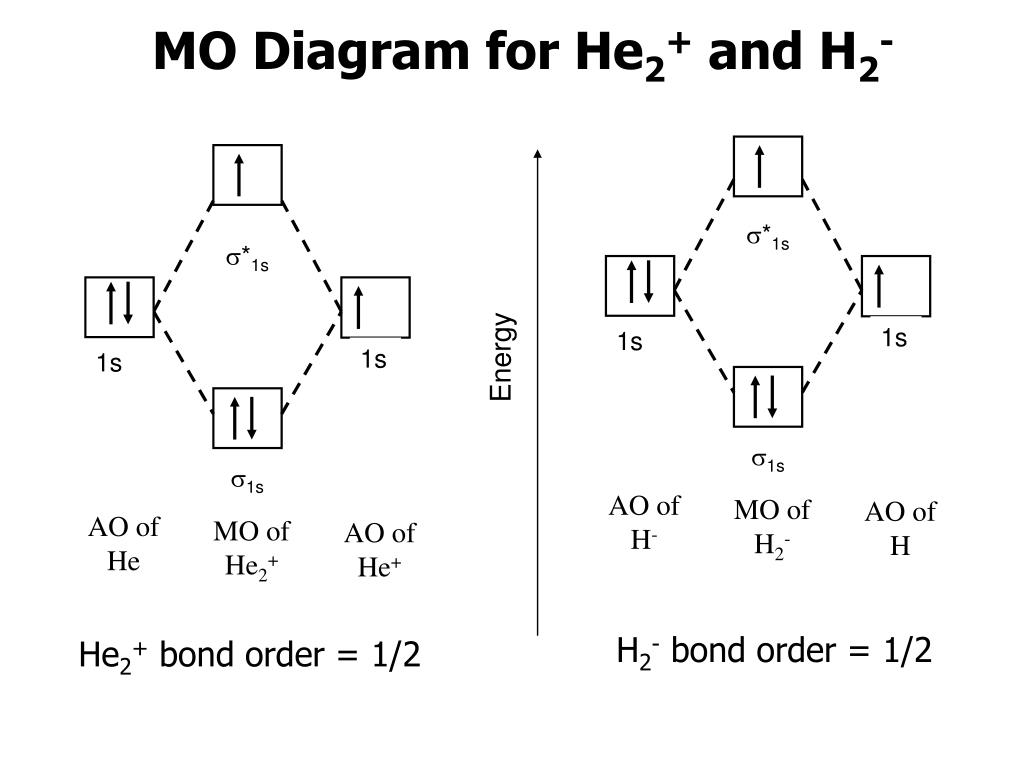
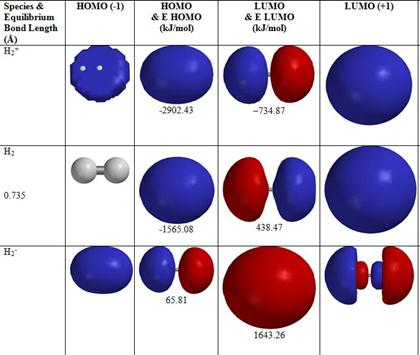
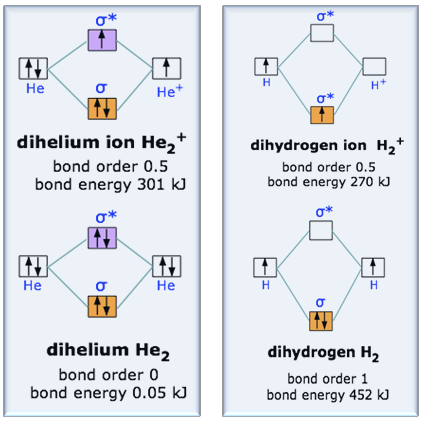
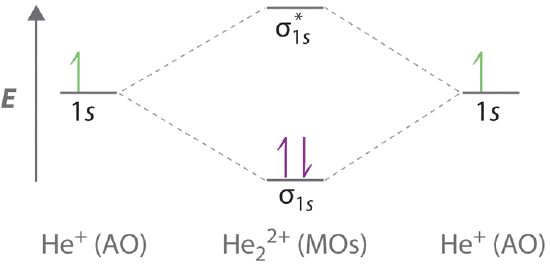
Introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory 1. Problem: Draw MO energy diagrams for the molecular ions H2+ and H Since both molecular ions have a bond order of 1/2, they are approximately equally.Solution: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 + and then identify the bond order. Problem Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He 2 + and then identify the bond order. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.The Hydrogen Molecule Ion H2+Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Diatomic Molecules - Chem To know the magnetic character of molecules we can use MO diagram. When we draw MO diagram for dihydrogen anion ( H2-) we find one unpaired electron in antibonding sigma orbital. For dihydrogen cation (H2+) there is one unpaired electron in bonding sigma orbital.
The head-to-head overlap giving σ molecular orbitals results in greater overlap, making its bonding molecular orbital the most stable and lowest energy, while the σ* antibonding is least stable and has the highest energy (Figure 9.24 "Molecular orbital energy diagram for homonuclear diatomic molecules made from atoms of atomic number 8-10"). N b = 2 , Na =0. Bond order = 1. Positive value of bond order indicates that H 2 molecule is stable.. Bond order value of 1 means that two hydrogen atoms are connected by a single bond.. Greater value of bond order for H 2 molecule than H 2 + ion shows that two H 2 molecule is more stable than H 2 +.. Bond length of H 2 is smaller than that of H 2 + ion.. As no unpaired electron is present ... Molecular Orbital Diagram for Hydrogen Gas (H2).Fill from the bottom up, with 2 electrons total.Bonding Order is 1, and it is Diamagnetic.sigma2s(2)Check me ... The bonding and anti-bonding orbitals are usually depicted by the molecular orbital diagram. Below mentioned is the molecular orbital diagram of the dihydrogen ion H2+. The atomic valence electrons (which are represented by the left and right boxes) at first fills the lower-energy molecular orbitals, and then it fills the higher ones.
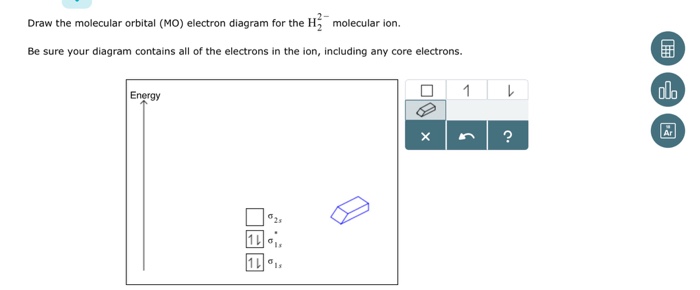
Problem: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Click thin the blue boxes to add electrons.Bond order: a) 0 b) 0.5c) 1 d) 1.5e) 2. FREE Expert Solution. Show answer. Answer: 80% (433 ratings) play-rounded-fill. play-rounded-outline.
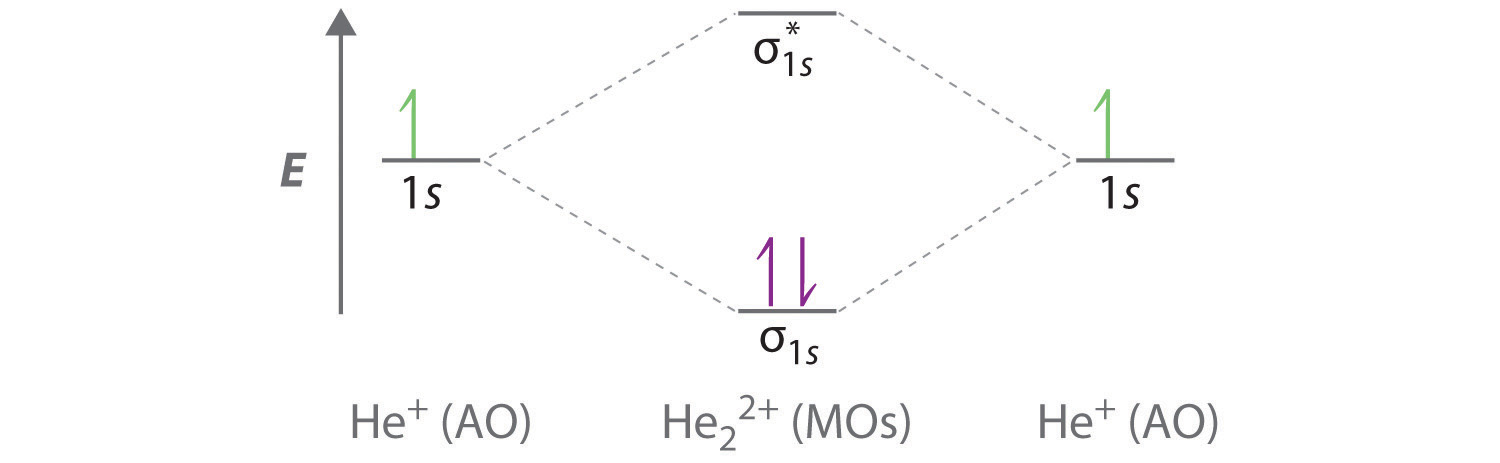
The molecular orbital energy-level diagram shown in Figure 13 also applies (with changes of detail in the energies of the molecular orbitals) to the hypothetical species He 2. However, this species has four valence electrons, and its configuration would be 1σ 2 2σ 2.
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
As a simple MO example, consider the electrons in a hydrogen molecule, H 2 (see molecular orbital diagram), with the two atoms labelled H' and H". The lowest-energy atomic orbitals, 1s' and 1s", do not transform according to the symmetries of the molecule.
Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click thin the blue boxes. The hydrogen atom is the simplest atom, and its molecule \ (\ce {H2}\) is get a sigma (s) bonding orbital, denoted as s1s in the diagram here.
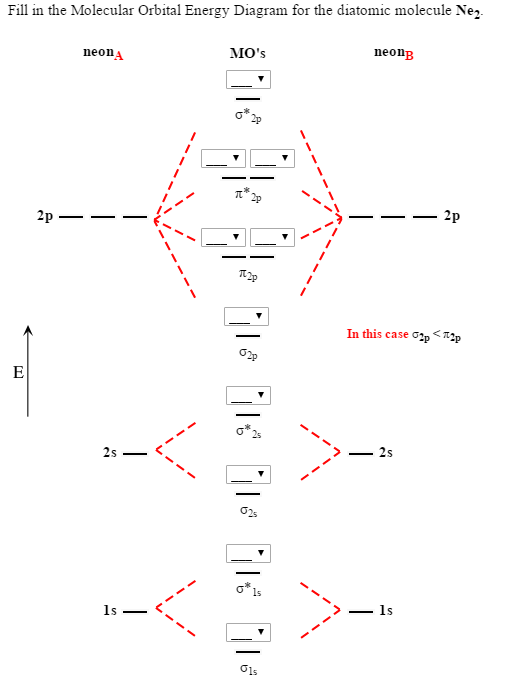
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
The MO for H X 2, which is shown in the figure below is taken from Wikipedia. The right side of the diagram you showed neither represents a hydrogen molecule, nor two independent (and hence equivalent) hydrogen atoms. Share Improve this answer answered Apr 17 '19 at 18:09 MaxW 21.3k 2 32 78 Add a comment Your Answer Post Your Answer
The electronic configuration of H2+. Answer to Create an MO diagram for H2+ H2 and H Post the Lumo, lumo -, homo, homo + near its energy level. σ bonding MO that is lower in energy than the constituent 1s AOs and an antibonding σ* MO that is at a higher energy than the 1s AOs.[1] Each. The molecular orbital energy level diagrams for H2, H2.
Relative AO Energies in MO Diagrams Use AO energies to draw MO diagram to scale (more or less). H He Li Be B C N O F Ne B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar Al Si P S Cl Ar 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p -19.4 eV -15.8 eV -32.4 eV -10.7 eV
The energy-level diagram for He2 is shown above, the two electrons in each of the 1s atomic orbital give total of 4 electrons in this molecule. Two are placed in the bonding orbital, the other two in antibonding orbital. The bond order = 1/2 x (Number of Bonding Electrons - Number of Antibonding Electrons) = .
Well, build the molecular orbital (MO) diagram. Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and thus, H− 2 has three electrons while H+ 2 has one. Each hydrogen atom contributes one 1s atomic orbital, and thus, the orbitals overlap according to MO theory to form one σ1s and one σ* 1s MO by conservation of orbitals.
1 Nov 2019 Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2 and then identify the bond order. Make sure you add electrons to the boxes corresponding to the MOs for the molecule and to the boxes corresponding to the AOs for the two atomic species. Bond order: 1s o 0.5 O 1.5 2 Atom Molecule Atom Click within the blue boxes to add electrons.
Answer (1 of 2): According to the molecular orbital theory, a molecular is viable of its bond order is more than or equal to one. The bond order is defined as number of bond between to two atoms of that molecule. It is calculated as the difference of electrons in bonding molecules and anti-bondin...
H2 Molecular Orbital Diagram MO diagram of dihydrogen Bond breaking in MO diagram The smallest molecule, hydrogen gas exists as dihydrogen (H-H) with a single covalent bond between two hydrogen atoms. As each hydrogen atom has a single 1s atomic orbital for its electron, the bond forms by overlap of these two atomic orbitals.




















0 Response to "41 mo diagram of h2"
Post a Comment