40 ray diagram for diverging lens
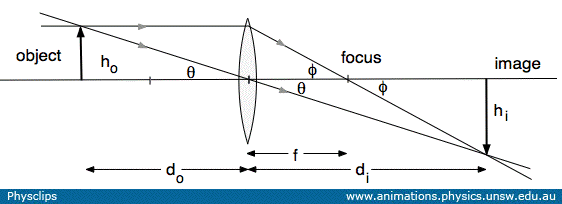
Ray Diagrams for Lenses - Georgia State University Ray Diagrams for Lenses The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image location and size are: PDF Converging and diverging lenses ray diagrams worksheet ... Converging and diverging lenses ray diagrams worksheet answers pdf The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length.
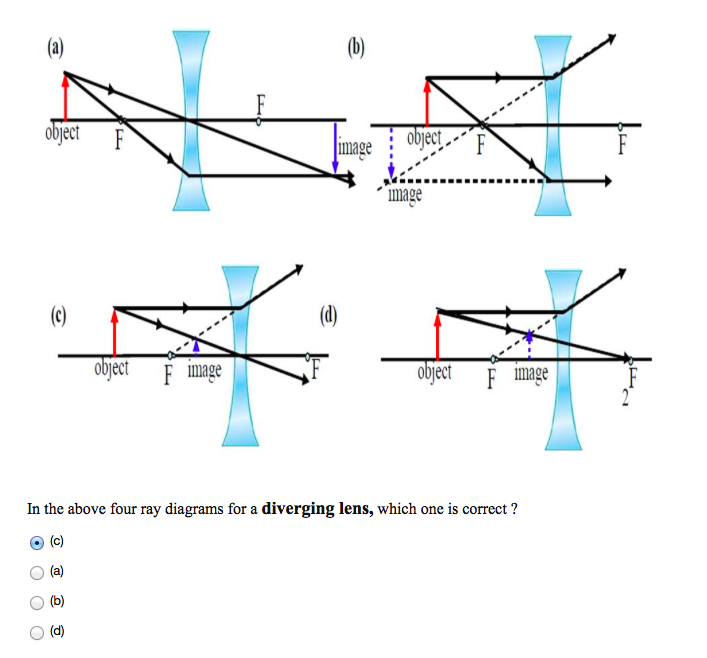
PDF Ray Diagrams Diverging Lenses - Verona Public Schools Diverging Lenses As such, the rules for how light behaves when going through a diverging lens is a little bit different. You will be expected to be able to draw a Ray Diagram of a converging and diverging lens on our upcoming test without the rules.
Ray diagram for diverging lens
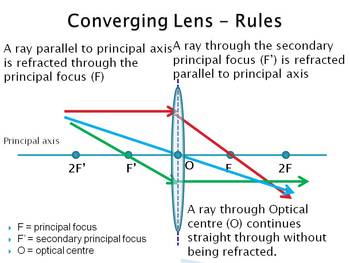
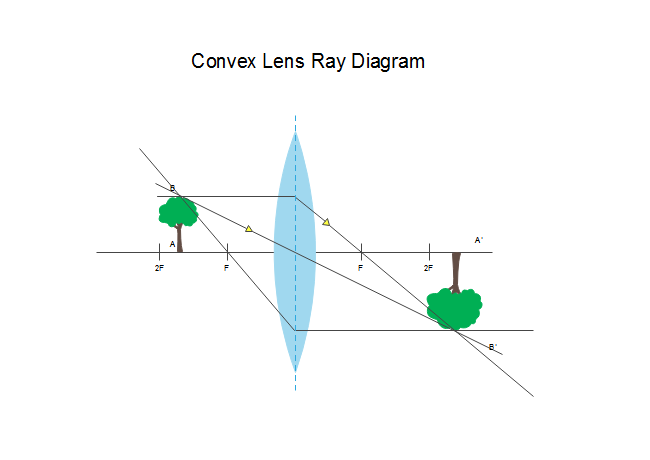
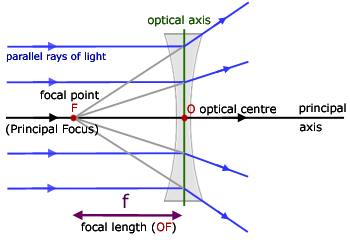
Converging Lenses - Ray Diagrams - Physics Classroom A virtual image is formed if the object is located less than one focal length from the converging lens. To see why this is so, a ray diagram can be used. A ray diagram for the case in which the object is located in front of the focal point is shown in the diagram at the right. Converging and diverging lenses - Lenses - Edexcel - GCSE ... A convex lens is thicker in the middle than it is at the edges. Parallel light rays that enter the lens converge. They come together at a point called the principal focus. In a ray diagram, a ... Lenses - Boston University Lenses 7-26-00 Sections 23.9 - 23.10 Ray diagram for a diverging lens. Consider now the ray diagram for a diverging lens. Diverging lenses come in a few different shapes, but all diverging lens are fatter on the edge than they are in the center. A good example of a diverging lens is a bi-concave lens, as shown in the diagram.
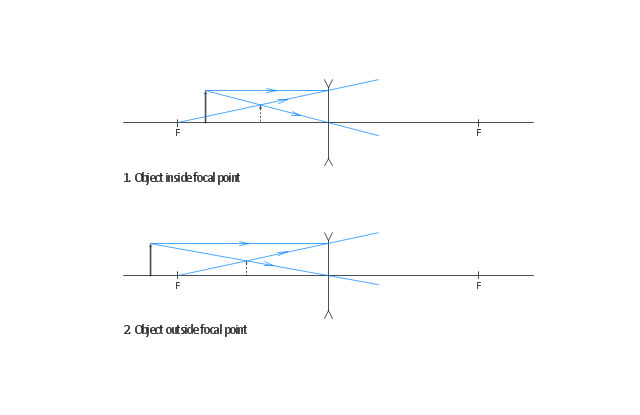
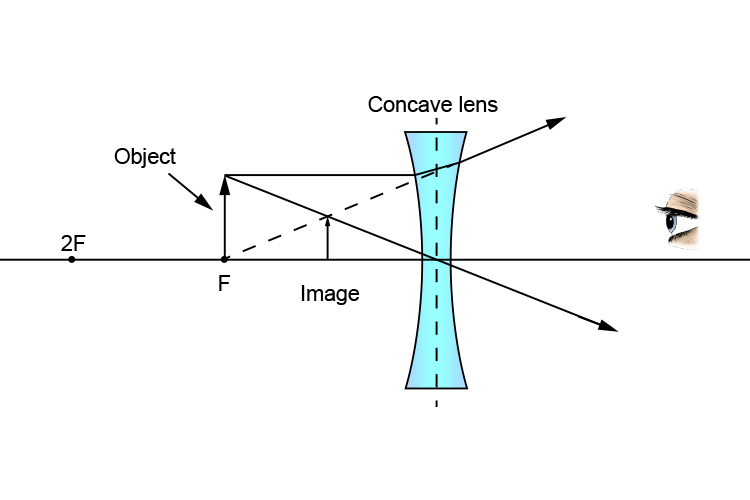
Ray diagram for diverging lens. Ray Diagrams for Lenses - Wolfram Demonstrations Project This Demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses. By manipulating the object and lens locations, you can create real or virtual images. The rays parallel to the principal axis and the ray through the center of the lens are drawn.Locators allow you to drag both the object and the lens. You can change the focal length using a slider. Ray Diagrams For Diverging Lenses - schematron.org The ray diagram constructed earlier for a diverging lens revealed that the image of the object was virtual, upright, reduced in size and located on the same side. Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of a diverging lens will refract through the lens and travel in line with the focal point (i.e., in a direction such. Convex Lens - Ray diagram, Image Formation, Table - Teachoo We draw another ray which passes through Optical Center So, the ray will go through without any deviation We observe that both refracted rays are diverging It means that they would have met at some point Hence, we extend both rays behind the lens We see that the rays form an image behind the lens (on the left side). So, the image is virtual Diverging Lenses - Ray Diagrams - 3/6/2011 Diverging ... Using a straight edge, extend each of the rays are diverging, they must be extended behind the lens in order to intersect. Using a straight edge, extend each of the rays using dashed lines. Draw the extensions until they intersect. All three extensions should intersect at the same location.
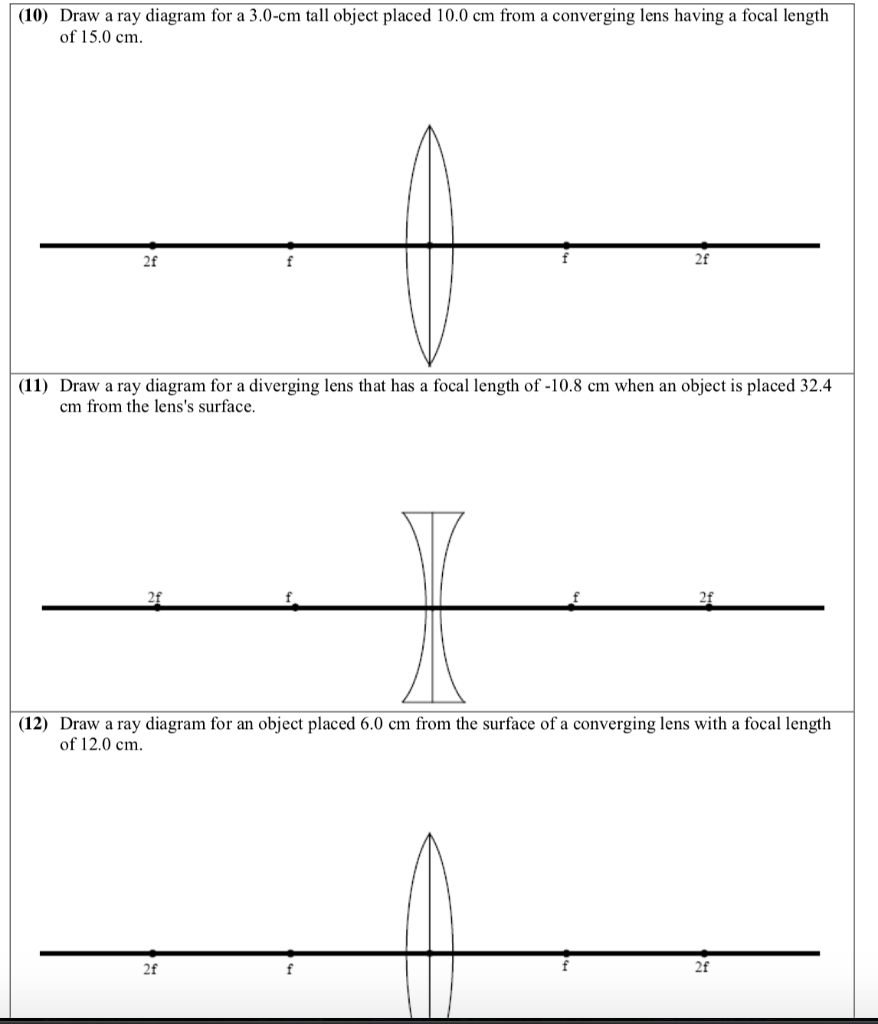
PDF Converging & Diverging Lenses Ray Diagrams (10) Draw a ray diagram for a 3.0-cm tall object placed 10.0 cm from a converging lens having a focal length of 15.0 cm. (11) Draw a ray diagram for a diverging lens that has a focal length of -10.8 cm when an object is placed 32.4 cm from the lens's surface. (12) Draw a ray diagram for an object placed 6.0 cm from the surface of a converging lens with a focal length Physics Tutorial: Refraction and the Ray Model of Light Since the three refracted rays are diverging, they must be extended behind the lens in order to intersect. Using a straight edge, extend each of the rays using dashed lines. Draw the extensions until they intersect. All three extensions should intersect at the same location. The point of intersection is the image point of the top of the object. Ray diagrams for diverging lenses - YouTube Description of how to draw ray diagrams for diverging lenses for grade 10 science. Of The Best Diverging Mirror Ray Diagram - Glaucoma Template Ray diagram for diverging lens Ray 1 is parallel to the axis and refracts as if from F. Mirror ray tracing is similar to lens ray tracingin that rays parallel to the optic axis and through the focal point are used. In each diagram use an arrow 10 cm tall pointing upwards as the object.
optics - Ray diagram for diverging lens with both object ... The top diagram shows the formation of the virtual object where converging rays are prevented from meeting by the diverging lens. Then those converging rays are made to diverge by the lens and so a virtual image is formed. Update as a result of a comment from @Floris. Ray Diagrams For Diverging Lenses - diagramweb.net The ray diagram constructed earlier for a diverging lens revealed that the image of the object was virtual, upright, reduced in size and located on the same side. Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of a diverging lens will refract through the lens and travel in line with the focal point (i.e., in a direction such. PDF Spherical lenses: converging, diverging Plane mirrors ... Ray 1 is parallel to the axis and refracts as if from F. Ray 2 heads towards F' before refracting parallel to the axis. Ray 3 passes straight through the center of the lens. image is always virtual, upright and reduced O F I F' Ray diagram for diverging lens Diverging lens - interactive simulations - eduMedia A diverging lens always form an upright virtual image. Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of two distinct rays from a single point on the object: A ray passing through the center of the lens will be undeflected. A ray proceeding parallel to the principal axis will diverge as if he came from the image focal point F'.
Two Converging Lens Ray Diagram - schematron.org Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length.
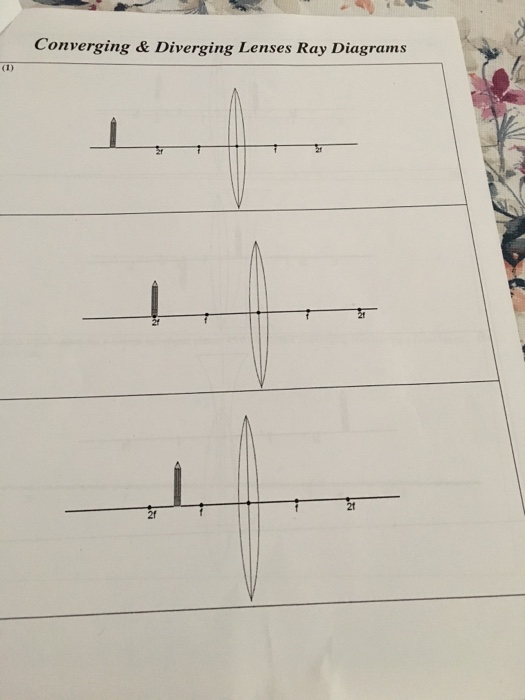
PhysicsLAB: Ray Diagrams for Diverging Lenses In this lab, you will construct the TWO ray diagrams for diverging lenses. In each diagram, use an arrow, 2.0 cm tall, pointing upwards as the object. Label it with an O. For your convenience, blank diagrams will objects already provided are located on this page -- in IE use landscape mode with margins of 0.5.
Ray diagrams for diverging (concave) lens - Basic Physics ... Ray diagrams for diverging (concave) lens. ... Ray 1 : Ray 1 that comes to the concave lens is drawn parallel to the principal axis and touches the top edge of the object, then refracted by the concave lens where the beam of light refracts as if coming from the focal point. The incoming rays and the refractive rays that are must meet the law of ...
Can ray diagrams be used with diverging lenses ... A light ray entering a concave lens diverges making the lens act like a diverging lens. What is a diverging lens ray diagram? A diverging lens ray diagram follows three basic rules: Any ray of light that is parallel to the principal axis of the lens will pass through its focal point after refraction.
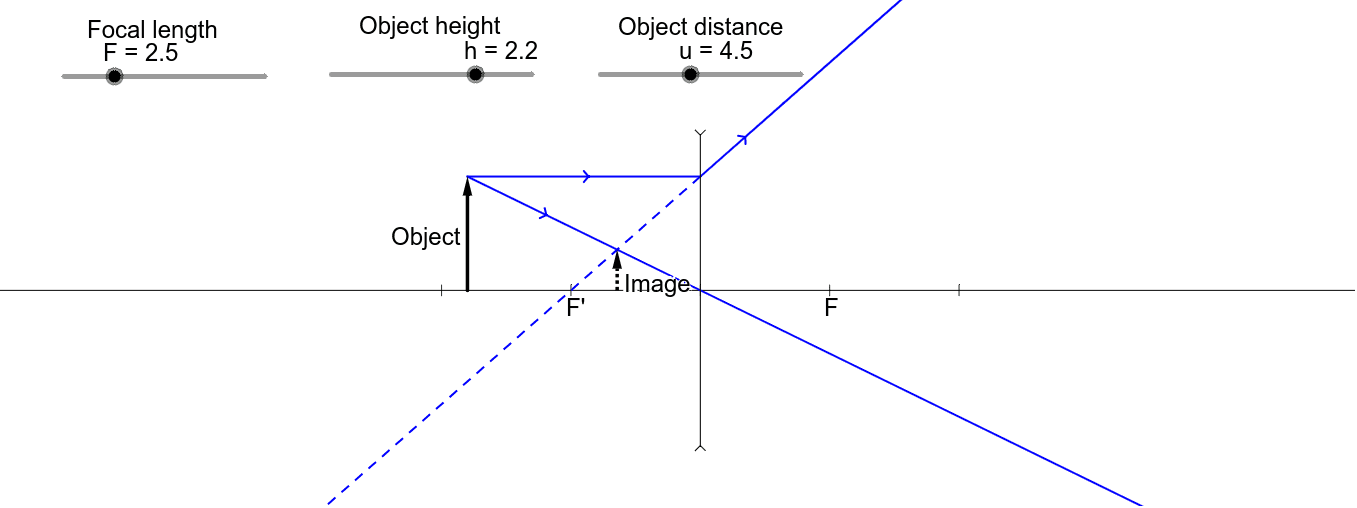
Diverging lens - GeoGebra Ray Tuck This simulation shows a ray diagram for a diverging lens. Use the slider to set the position of the object. The object is shown by a black arrow. Use the check boxes to choose which rays to show. You need any two to fix the position of the image. The image is shown by the red arrow. Extensions of rays are shown as dotted lines:
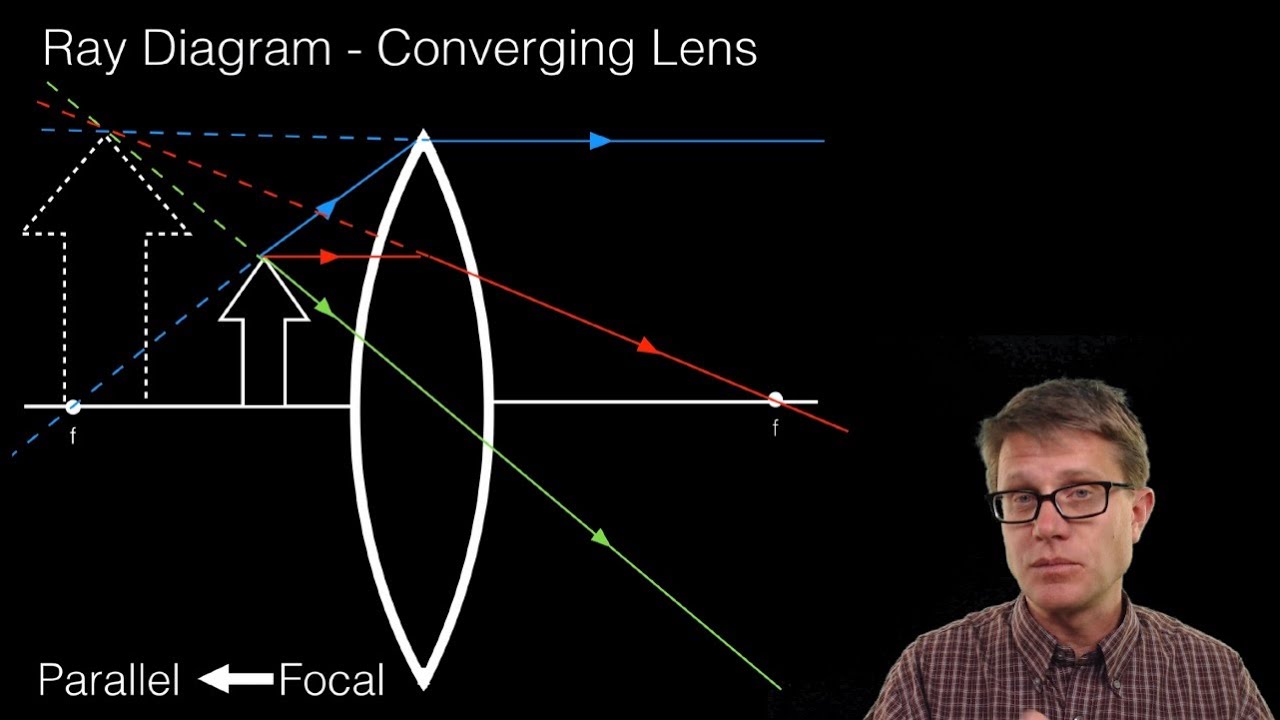
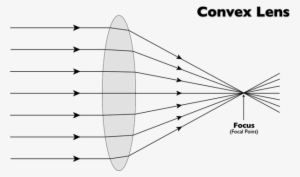
PDF Lecture 17: Lenses and ray tracing - Physics Ray tracing a convex lens: object inside focus The image appears larger (and farther away) than the object. This is a magnifying glass. (Remember: a magnifying glass is a convex lens.) Aside: near-sighted people need concave/diverging lenses; can a marooned myopic start a fire with his eye-glasses?
Thin Lenses Calculator - herramientasingenieria.com Diverging lenses always produce virtual images. This calculator shows a ray diagram when the image is real. Magnification The magnification m of an image is the ratio between the image and object height. It can be calculated by the formula: Magnification = -s' / s If the magnification sign is positive, then the image is upright.
Ray Diagrams - Lenses - YouTube 122 - Ray Diagrams - LensesIn this video Paul Andersen explains how ray diagrams for lenses can be used to determine the size and location of a refracted ima...
Solved An object is placed a distance of 36.0 cm from a ... An object is placed a distance of 36.0 cm from a diverging lens with a focal length of 20.0 cm. a. [5 pts] Draw the ray diagram using the 3 rays described in class. b. [5 pts] Calculate where the image is formed? c. [5 pts] Calculate what the magnification of the image is? d. [5 pts] Is the image real or virtual? Explain your reasoning!
PhysicsLAB: Diverging Lenses This position is usually labeled F in ray diagrams. A similar point the same distance behind the lens is called the lens' secondary focus , F'. When the actual rays of light diverge after passing through the lens, the image formed by the intersection of their "dotted back segments" is called a virtual image .
Lenses - Boston University Lenses 7-26-00 Sections 23.9 - 23.10 Ray diagram for a diverging lens. Consider now the ray diagram for a diverging lens. Diverging lenses come in a few different shapes, but all diverging lens are fatter on the edge than they are in the center. A good example of a diverging lens is a bi-concave lens, as shown in the diagram.
Converging and diverging lenses - Lenses - Edexcel - GCSE ... A convex lens is thicker in the middle than it is at the edges. Parallel light rays that enter the lens converge. They come together at a point called the principal focus. In a ray diagram, a ...
Converging Lenses - Ray Diagrams - Physics Classroom A virtual image is formed if the object is located less than one focal length from the converging lens. To see why this is so, a ray diagram can be used. A ray diagram for the case in which the object is located in front of the focal point is shown in the diagram at the right.






















0 Response to "40 ray diagram for diverging lens"
Post a Comment