38 reliability block diagram example
RBDs and Analytical System Reliability - ReliaWiki Example: Calculating the Reliability with Components in Parallel Consider a system consisting of three subsystems arranged reliability-wise in parallel. Subsystem 1 has a reliability of 99.5%, Subsystem 2 has a reliability of 98.7% and Subsystem 3 has a reliability of 97.3% for a mission of 100 hours. System Reliability & Availability Calculations - BMC ... A reliability block diagram (RBD) may be used to demonstrate the interconnection between individual components. Alternatively, analytical methods can also be used to perform these calculations for large scale and complex networks. ... For example, two components with 99% availability connect in series to yield 98.01% availability. The converse ...
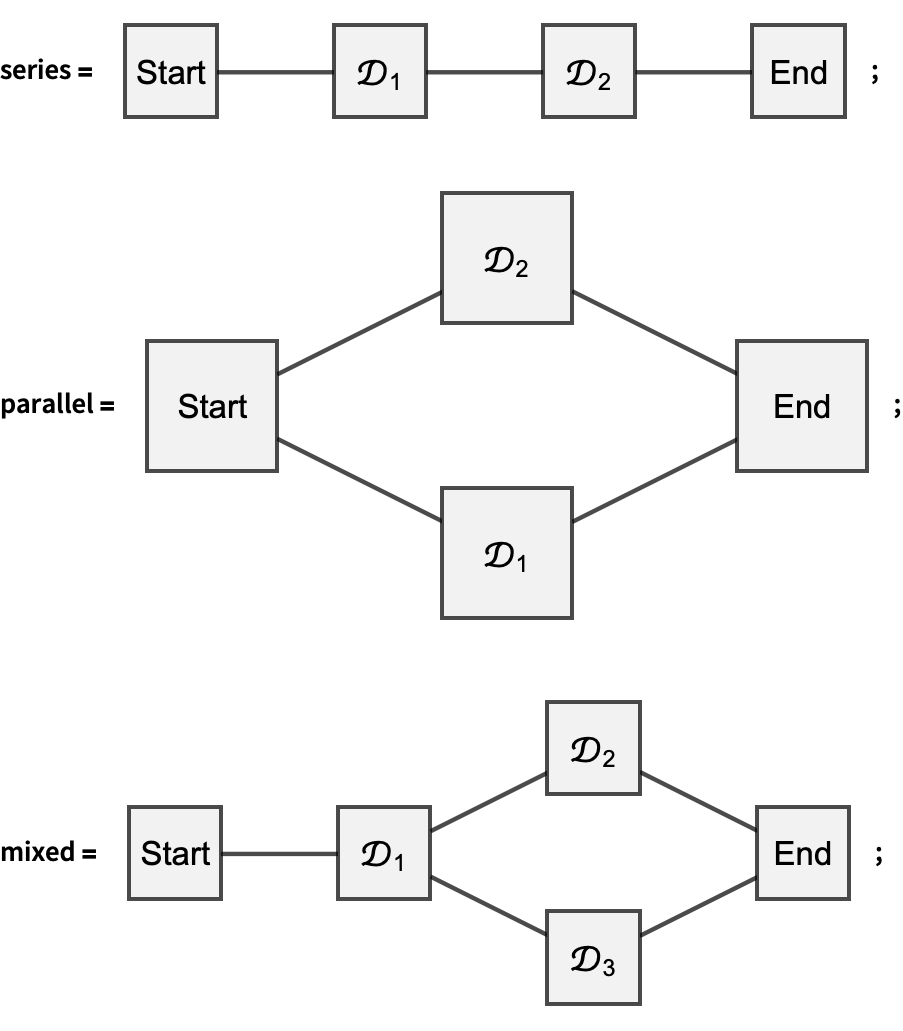
Reliability block diagram - Wikipedia Each block represents a component of the system with a failure rate. RBDs will indicate the type of redundancy in the parallel path. For example, a group of parallel blocks could require two out of three components to succeed for the system to succeed. By contrast, any failure along a series path causes the entire series path to fail.

Reliability block diagram example
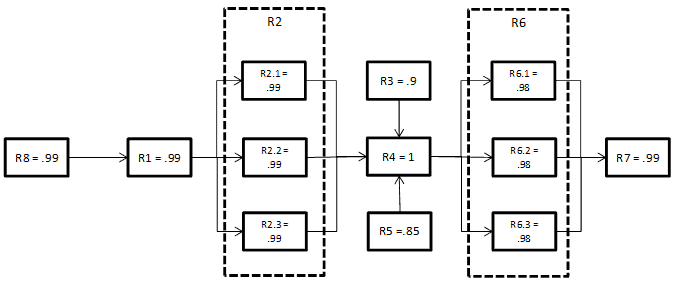
Understanding the Reliability Block Diagram Sample System RBD with Reliability Values Next, the reliability of R2 is calculated. Since it requires all three systems to operate a simple parallel formula would be used; R2 = R 3 R2 = (.99)3 R2 = .97 Next the same is done for R6 R6 = R3 R6 = (.98)3 R6 = .94 Lastly, since R4 is dependent on R3 & R5 it should treat it as a series system. Examples | SHARPE Portal Example 32: Reliability graph inside a reliability graph. Example 33: Reliability graph inside a block diagram. Example 34: Markov model (of a bridge system) inside a block diagram. Example 35: A non-series-parallel graph and an exact model decomposition. Example 36: A task graph with a cycle and its exact decomposition Reliability Block Diagram - sgs-tuev-saar.com For example, when examining a system in terms of achieving a safety objective, only the respective safety-relevant system components are investigated. The modelled blocks have the characteristic of being able to show an element only in two modes: functional or failure. The possible reasons for a failure are not graphically represented.
Reliability block diagram example. Understanding Reliability Block Diagrams Sample System RBD with Reliability Values Next, the reliability of R2 is calculated. Since it requires all three systems to operate a simple parallel formula would be used; R 2 = R 3 R 2 = (.99) 3 R 2 = .97 Next the same is done for R6 R 6 = R 3 R 6 = (.98) 3 R 6 = .94 Reliability Block Diagrams | Thomas Reiter In this example, each of the two paths consists of one engine. Depending on the capability of the Reliability Block Diagram software, many system parameters can be calculated, for example: Failure rate, MTBF Reliability R Availability A Repair cost, repair time Optimal maintenance interval (depending on criteria) A Guide to System Modeling Using Reliability Block Diagram ... Reliability Block Diagram (RBD) analysis is a methodology for assessing and calculating the reliability and availability metrics of complex systems using a graphical depiction of the system. RBDs are created in a visual format, using blocks to represent components or elements of the system and connections between the blocks to define their ... Reliability block diagrams examples (RBD): (a) series; (b ... Figure 3 depicts RBD examples, in which independent blocks are arranged through series ( Figure 3 a), parallel ( Figure 3 b) and k-out-of-n compositions ( Figure 3 c). In the series composition (...
PDF Chapter 30 Reliability Block Diagrams Contents An example of an RBD is shown in Figure 1. b c d a Figure 1: Example of Reliability Block Diagram 2.1.2 It is assumed here that both the system and its elements are in one of two states; either up or down. Hence, in an RBD, each element may be looked on as a switch that is closed when the element is up and open when the element is down. Reliability Block Diagram | ARMS Reliability Reliability Block Diagram Analyze the most complex systems with confidence A Reliability Block Diagram (RBD) is a method of modeling how components and sub-system failures combine to cause system failure. The diagram can be analyzed to predict the availability of a system and determine the critical components from a reliability viewpoint. BlockSim - Reliability block diagram (RBD) analysis ... A Reliability Block Diagram (RBD) is a graphical representation of the components of the system and how they are reliability-wise related. The diagram represents the functioning state (i.e., success or failure) of the system in terms of the functioning states of its components. Using Reliability Block Diagrams to Analyze Dependent and ... Figure 1: Reliability block diagram for mode A. The system reliability equation for this configuration is: R (t)=-2R T2 R S1 R S2 R T1 R Y +R T2 R S1 R S2 R T1 +R T2 R S1 R T1 R Y +R T2 R S2 R T1 R Y. Each mode is identified in the RBD. Furthermore, two additional items are included: a starting block ( NF) and an end node ( 2/2 ).
PDF Reliability Block Diagrams - aldsoftware.com Chapter 15Reliability Block Diagrams 377 To add an element to an RBD 1Activate the RBD viewer. 2Click on an insertion node. 3From the Itemmenu, create an RBD element or use the pop-up menu (see element descriptions on page 375). To create a SubRBD NoteSubRBDs are in rectangles with rounded corners. 1To insert a SubRBD, highlight an insertion node. Reliability Block Diagrams (RBDs) A reliability block diagram (RBD) is a graphical representation of how the components of a system are reliability-wise connected. Building RBDs in BlockSim involves adding blocks to a diagram and then arranging and connecting the blocks so that they represent the reliability-wise configuration of a system or process. Reliability Block Diagrams (RBDs) | SpringerLink The reliability block diagram (RBD) is perhaps the most popular and widely used approach to deal with safety and dependability modelling. This chapter describes its position within the probabilistic approaches in general and the Boolean family approaches in particular. This is a directed acyclic graph drafted by using specific symbols (blocks ... What is a Reliability Block Diagram (RBD)? - Leedeo These are the groups of elements in a system, for example: [equipment_1, equipment_3, equipment_4]; [equipment_1, equipment_5], that if each of them works (the equipment between [ ]), the system works correctly. Following the example, we would have two chains in parallel.
Reliability Block Diagrams Overview and Value Essentially the model represents the reliability structure of the system. If the system fails when any one element fails, then it's a series system. If there are redundant power supplies for example, then there is a parallel structure involved. Performance Criteria An RBD that is not used to make decisions is of little value.
A Reliability Block Diagram Highlights Where the Risks Are ... Example Reliability Block Diagram for an electric motor drive end bearing, illustrating how machines are made of parts in a series arrangement. This is a visual representation of the reliability and risk that exists in this machine sub-assembly. The reliability for each part is notated and used to calculate the reliability for the whole series.
Why do you need a Reliability Block Diagram? | ARMS ... Reliability Block Diagrams (RBDs) are a way of representing a system, including its subsystems and components, as a series of blocks in such a way that equipment failure rates, operating philosophies, and maintenance strategies can be quantitatively assessed in terms of the impact they are expected to have on system performance.
Fault Tree Analysis, Reliability Block Diagrams and ... First, Figure 2 presents a fault tree with a Voting OR gate along with the equivalent reliability block diagram. As you can see, a Voting OR gate in FTA is equivalent to a k-out-of- n parallel RBD configuration, in which some quantity (m) of all input events (qty = n) must occur for the output event to occur. Fault Tree RBD
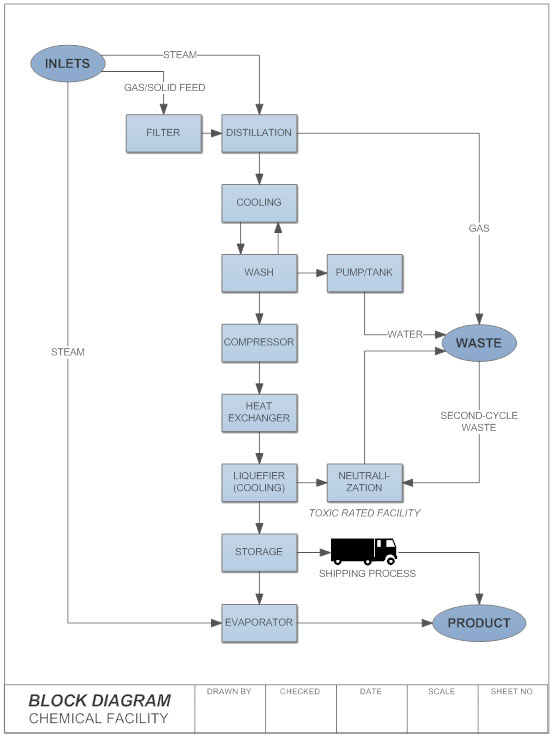
reliability block diagram software - hvacdist.com The reliability block diagram for such a system for the "fail short" mode of failure would be composed of two series blocks. The Reliability Block Diagram is a graphical methodology to describe a system in an intuitive way to represent the schematics of a system decomposing it into various sub-systems, components or functions.
Example reliability block diagram | Download Scientific ... Example reliability block diagram. Source publication +2. A conservative confidence bound for the probability of failure on demand of a software-based system based on failure-free tests of its ...
PDF L12 Relibility Block Diagram - University College Cork Reliability Block Diagram Model & Reliability Calculation RBD for Example Monitor Processor Keyboard Let 1 be the failure rate for Monitor Assume exponential distribution for the failures, then R monitor (t) = e - 1• t Similarly, R processor (t) =e - 2• t and R keyboardv (t) = e - 3• t R system (t) = R monitor (t) • R processor (t) • R
Reliability Block Diagram (RBD) - Reliability Block ... A Reliability Block Diagram is a method of modeling how components and sub-system failures combine to cause system failure . Reliability block diagrams may be analyzed to predict the availability of a system and determined the critical components from a reliability viewpoint .
How To Create Reliability Block Diagram - Edraw Simply click the Connection Point Tool under Home menu. Insert Text You can double click a shape to input text. Also, through the Text button under Home menu, you can insert text blocks anywhere you need. To insert a special symbol, you can go to the Insert menu, and click Font Symbol . An Reliability Block Diagram Example
PDF Reliability Block Diagram (RBD) A reliability block diagram (RBD) is a drawing and calculation tool used to model complex systems. An RBD is a series of images (blocks) representing portions of a system. Once the images (blocks) are configured properly and image data is provided, the failure rate, MTBF, reliability, and availability
Reliability Block Diagram - sgs-tuev-saar.com For example, when examining a system in terms of achieving a safety objective, only the respective safety-relevant system components are investigated. The modelled blocks have the characteristic of being able to show an element only in two modes: functional or failure. The possible reasons for a failure are not graphically represented.
Examples | SHARPE Portal Example 32: Reliability graph inside a reliability graph. Example 33: Reliability graph inside a block diagram. Example 34: Markov model (of a bridge system) inside a block diagram. Example 35: A non-series-parallel graph and an exact model decomposition. Example 36: A task graph with a cycle and its exact decomposition
Understanding the Reliability Block Diagram Sample System RBD with Reliability Values Next, the reliability of R2 is calculated. Since it requires all three systems to operate a simple parallel formula would be used; R2 = R 3 R2 = (.99)3 R2 = .97 Next the same is done for R6 R6 = R3 R6 = (.98)3 R6 = .94 Lastly, since R4 is dependent on R3 & R5 it should treat it as a series system.


![PDF] Reliability Block Diagram Method for RAM Study of ...](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/eeff51b9219cfc9a47ccb0c32155882be14e22f9/26-Figure3.1-1.png)





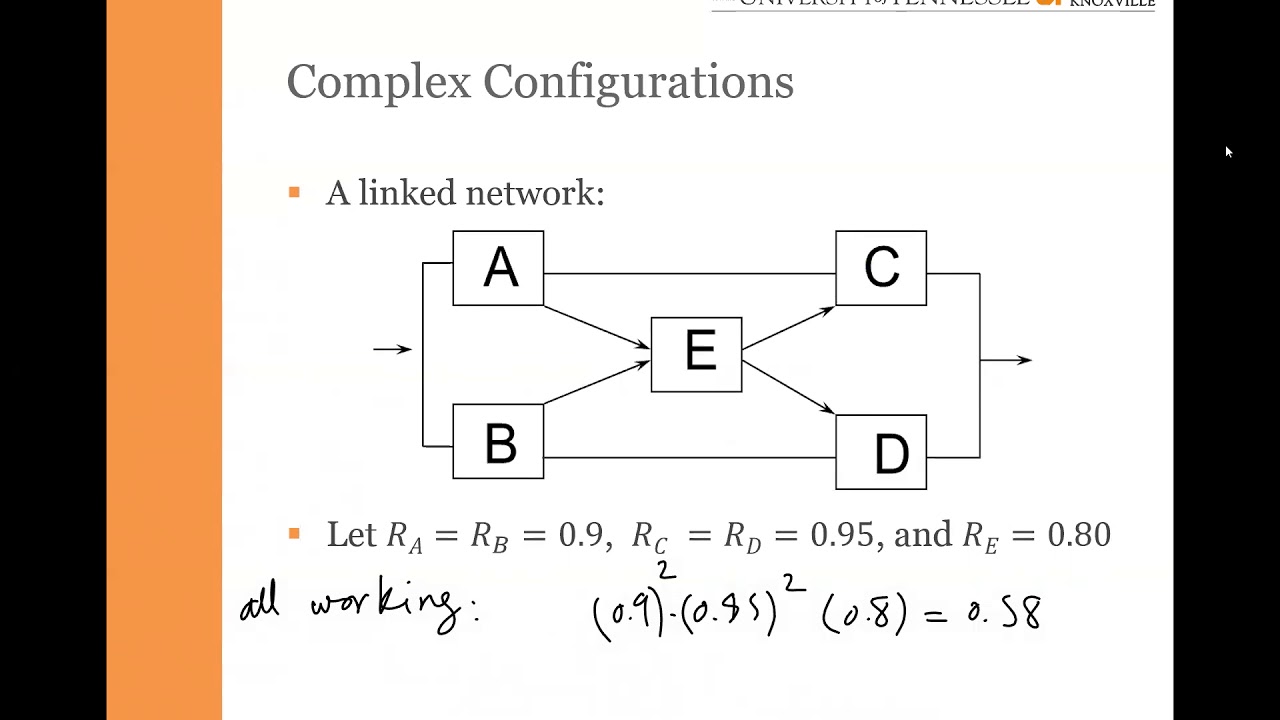
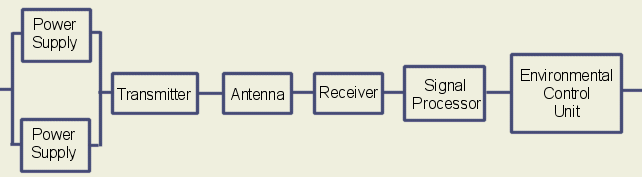


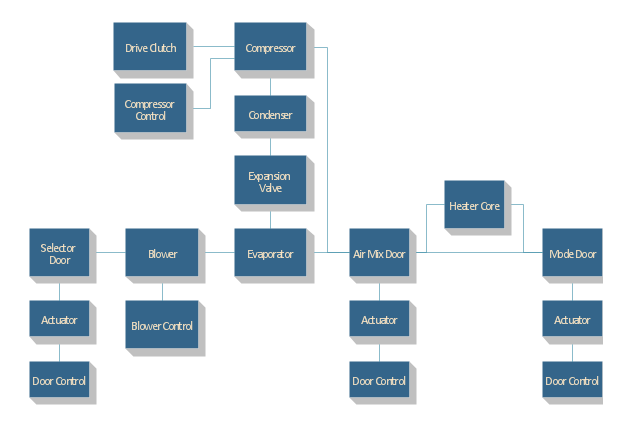
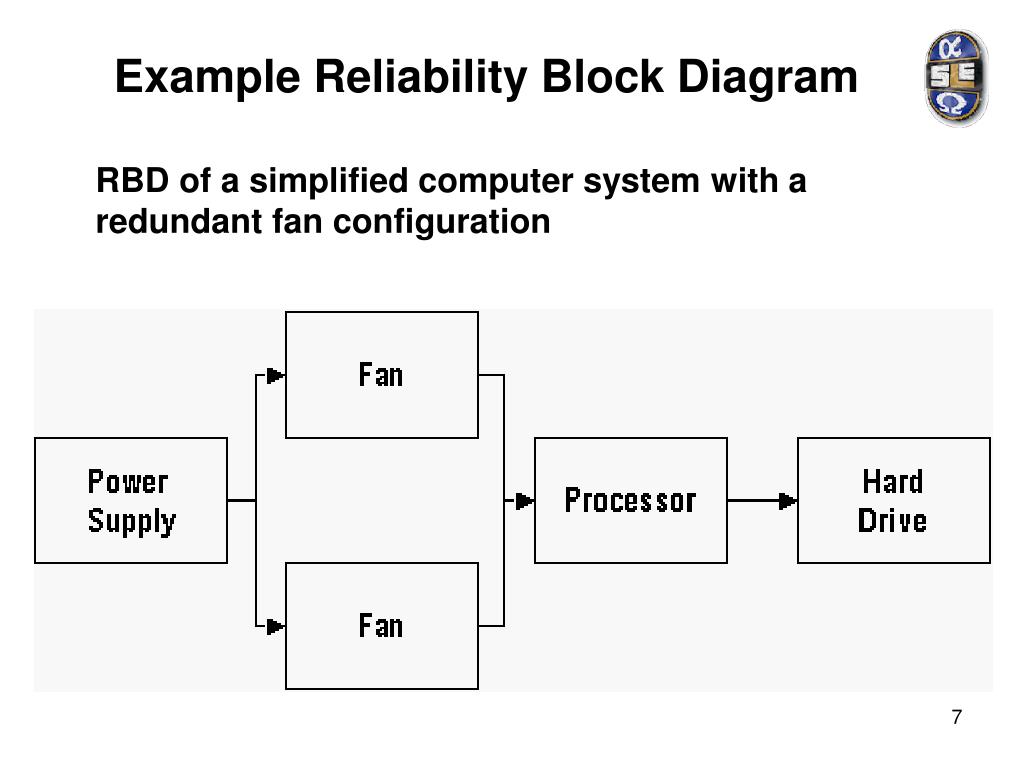







0 Response to "38 reliability block diagram example"
Post a Comment