39 enzyme reaction coordinate diagram
Reaction coordinate diagram for an enzyme-catalyzed ... Download scientific diagram | Reaction coordinate diagram for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. from publication: Design, synthesis and characterization of enzymeanalogue-built polymer catalysts as ... Enzymes - University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign Look at the oxidation state of sulfur in the reactants and product. Reaction Coordinate Diagram We've already seen that the rate of a chemical reaction depends on the height of the activation barrier in the reaction coordinate diagram. Consider the reaction below where reactants A and B combine to form the product C.
PDF Lehninger PPT ch06 - classes.biology.ucsd.edu Reaction Coordinate Diagram. ... transition state of the reaction - Enzymes bind transition states better than substrates - Stronger/additional interactions with the transition ...

Enzyme reaction coordinate diagram
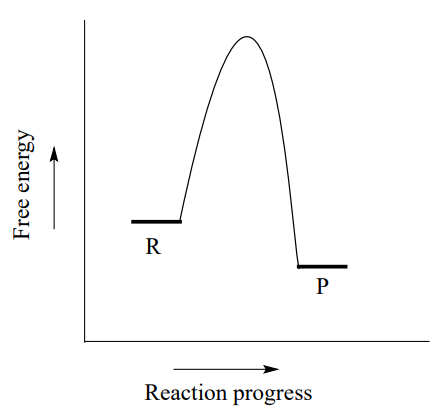
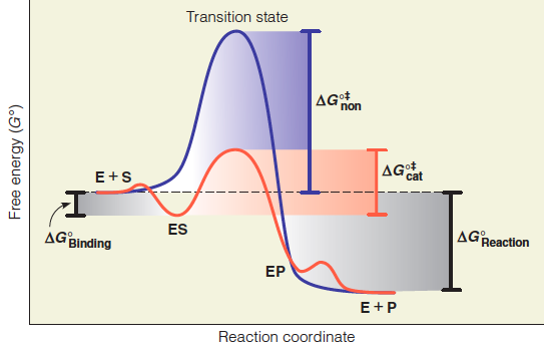
Compare and contrast the reaction coordinate diagrams for ... The reaction coordinate diagram for this reaction plots the changes in Gibbs free energy (ΔG) during the conversion of reac- tants (R) to TS to products (P; Figure 1B). It can be seen that P is of lower free energy than R, so this reaction is thermodynamically fa- vorable, that is, it proceeds in the direction of P with the release of PDF Enzyme An introduction to enzymes - University of Houston ... Fig. 1 Reaction coordinate diagram for a chemical reaction Fig. 2 Reaction coordinate diagram comparing enzyme-catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions. 3 of 16 As shown in Fig. 1, from starting material to product, the highest point in terms of energy is called transition Enzyme reaction coordinate diagrams (1) Quiz An unregistered player played the game 3 weeks ago About this Quiz This is an online quiz called Enzyme reaction coordinate diagrams (1) There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper.
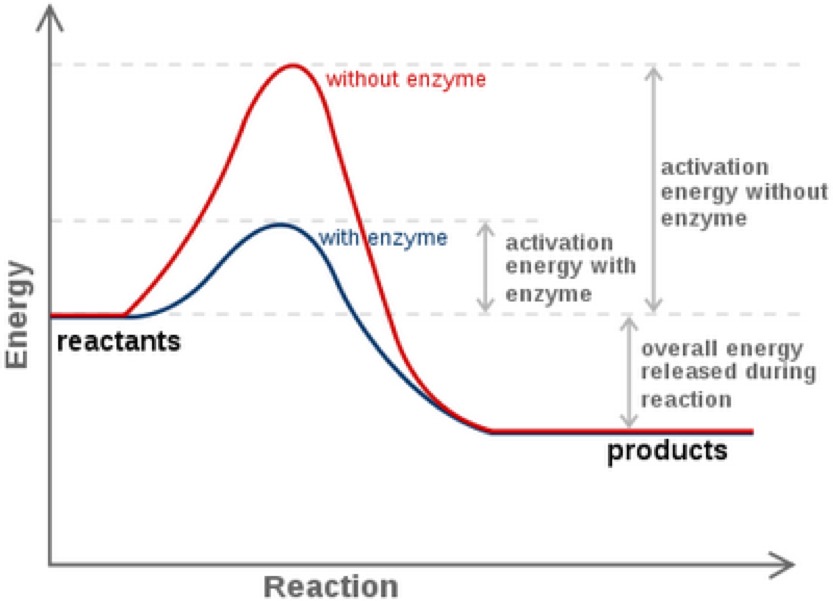
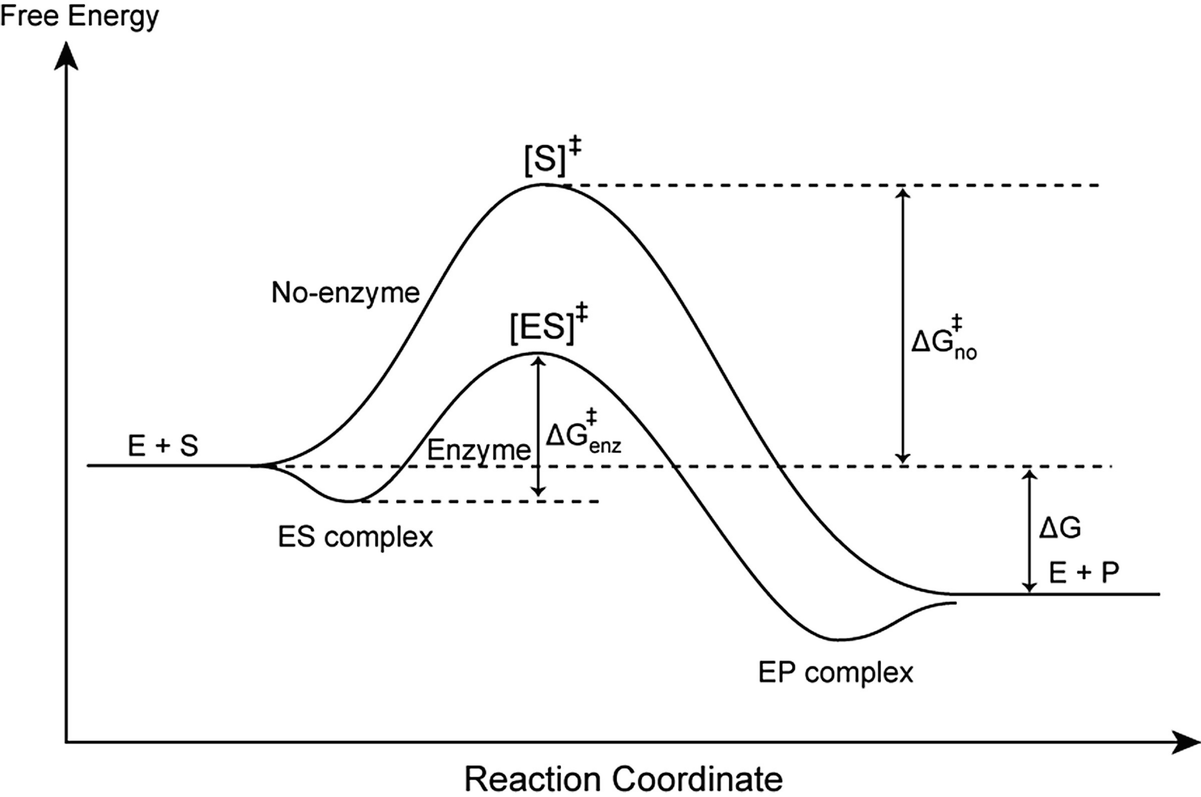
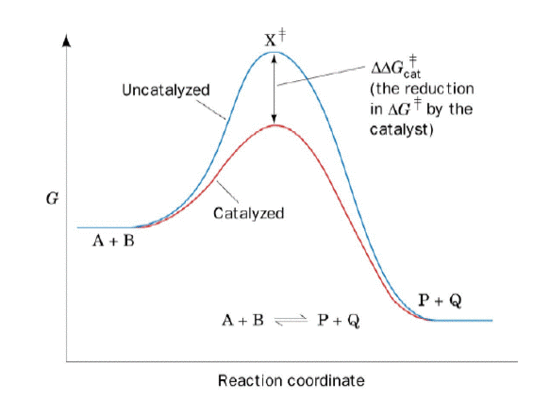
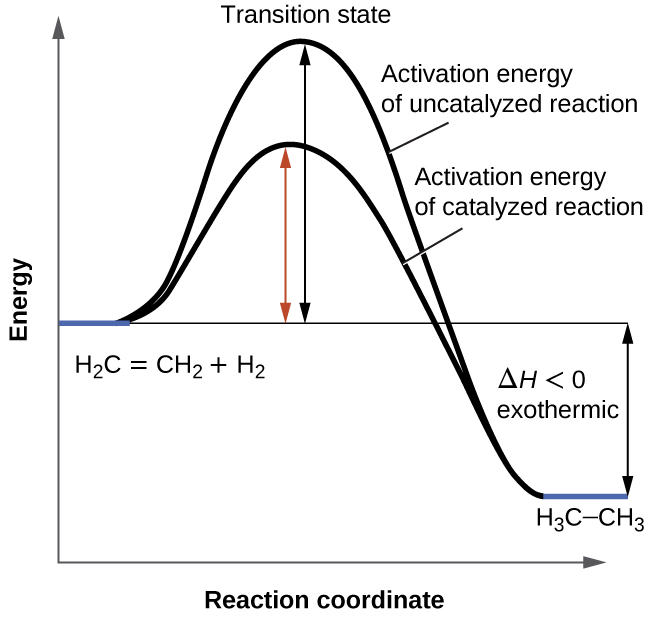
Enzyme reaction coordinate diagram. Energy Diagram Catalyzed Vs Uncatalyzed Reaction This effect can be illustrated with an energy profile diagram.Catalyzed reaction has a lower activation energy because there is an enzyme present in the reaction. Uncatalyzed reaction has a higher activation energy because there is no enzyme present in the reaction. Energy Diagrams for Catalyzed and Uncatalyzed Reactions. Enzyme reaction coordinate diagrams (1) Quiz This is an online quiz called Enzyme reaction coordinate diagrams (1) There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper. Reaction Coordinates in Potential Energy Diagrams ... Reaction potential energy diagrams are graphs that show the energy of a process as a function of the extent to which that process has occurred. As these are graphs showing mathematical functions, there must be a numerical coordinate axis that shows the independent variable. This coordinate is called the reaction coordinate, and it reflects the ... An energy profile diagram of an uncatalyzed reaction (grey ... An energy profile diagram of an uncatalyzed reaction (grey curve) and an enzymecatalyzed reaction (black curve) along a reaction coordinate. A reaction starts from free enzyme E and substrate S.
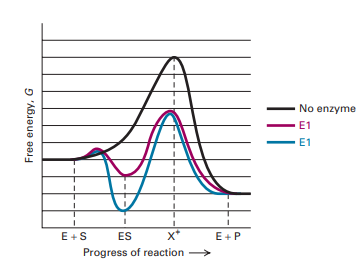
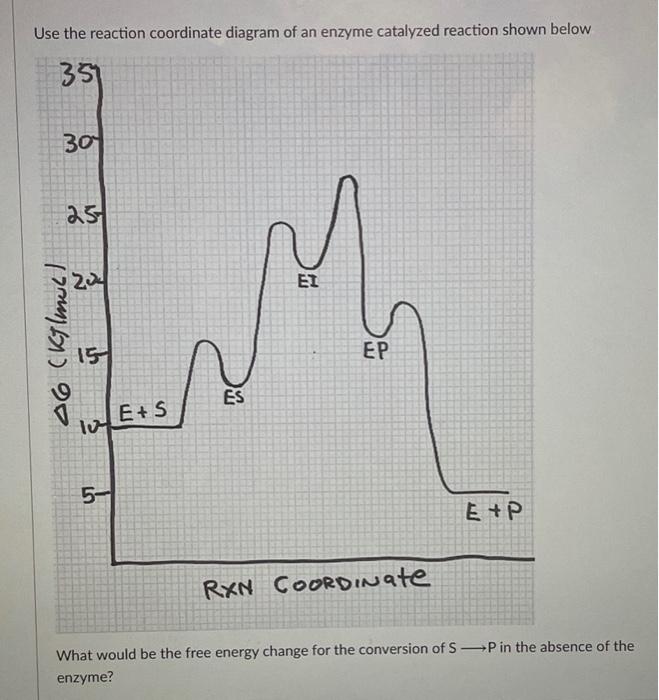
ENZYMES-PART I-2020.pdf - Enzymes • Enzyme structure ... View ENZYMES-PART I-2020.pdf from CHEM PHYSICAL C at Medical University of South Carolina. Enzymes • Enzyme structure • Reaction coordinate diagrams for catalyzed vs uncatalyzed reactions • Enzyme Energy diagrams for enzyme‐catalyzed reactions: Concepts ... The energy diagram for a reaction model consisting of one enzyme, one substrate, and one product is depicted in many books where it is compared with that for the uncatalyzed reaction. The survey of several Biochemistry textbooks reveals a high diversity of profiles for the same process. A, C, and D are adapted from Refs. 5, 3, and 2, respectively. Compare and contrast the reaction coordinate diagrams for ... FIGURE 2: Reaction coordinate diagram of an idealized enzyme-catalyzed reaction. The reaction coordinate diagram shows that, to enhance the rate constants for crossing the activation energy barrier, S or P must obtain an amount of energy equal to that by which the activation energy is lowered. Solved Use the reaction coordinate diagram of an enzyme ... Transcribed image text: Use the reaction coordinate diagram of an enzyme catalyzed reaction shown below to answer Questions 5 through 10 From this diagram you can conclude: (A) The forward reaction is endergonic. (B) The forward reaction is exothermic. (C) The forward reaction is endothermic. (D) The forward reaction is at equilibrium.
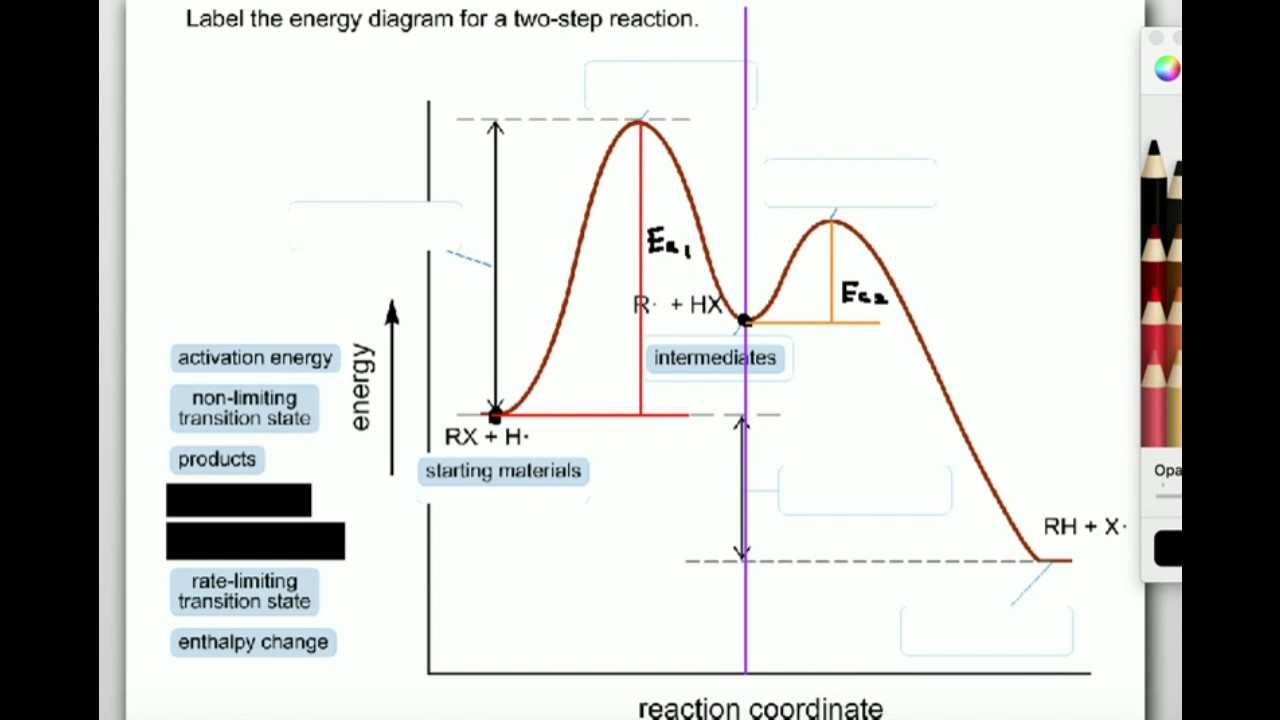
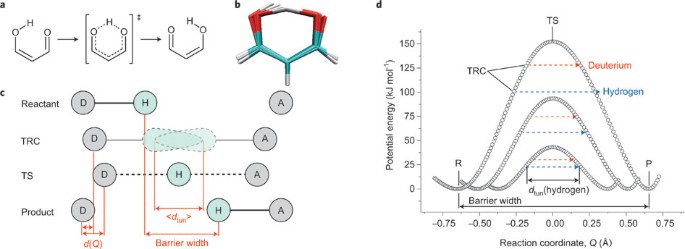
Answered: a) Draw the reaction coordinate diagram… | bartleby a) Draw the reaction coordinate diagram (reaction progress vs. energy) that is consistent with this mechanism. Assume the reaction is exothermic. Label where is ES appears in the diagram. The Michaelis-Menten equation gives the rate law for this mechanism: Rate = k2 [E]o [S]/ (Ka + [S]) b) With an understanding of this rate law, identify which ... Answered: Which of the following diagrams best… | bartleby Transcribed Image Text: Question 6 Which of the following diagrams best represents the potential-energy diagram for the enzyme-catalyzed hydrolysis of salicin? a) Reaction Coordinate b) Reaction Coordinate Reaction Coordnate d) Reaction Coordinate e) Reaction Coordinate f) Reaction Coordinate Expert Solution Want to see the full answer? Reaction coordinate - Wikipedia In chemistry, a reaction coordinate is an abstract one-dimensional coordinate which represents progress along a reaction pathway. It is usually a geometric parameter that changes during the conversion of one or more molecular entities. In molecular dynamics simulations, a reaction coordinate is called collective variable. PDF CHAPTER 11 Mechanism of Enzyme Action Transition state diagram/reaction coordinate diagram: Plot of free energy versus the reaction coordinate. Transition State Diagram (Symetrical)! Substrate! Product! Transition ... Enzymes catalyze reactions by preferentially binding the transition state An enzyme may binds the transition state of the
Covalent modifications to enzymes (video) | Khan Academy And looking at a reaction coordinate diagram you notice that enzymes do this by lowering the reaction's activation energy. Also, before we talk about covalently modified enzymes, I want to remind you that not all enzymes are proteins. And often, when we think of enzymes we think of proteins, which are amino acid polymers with primary, secondary ...
CHEM 440 - Enzyme kinetics - Gonzaga University The reaction coordinate diagram shows that the energy of activation for the reverse reaction is lowered by the catalyst as well. Enzymatic catalysis The ability of enzymes to catalyze reactions depends on their ability to interact directly and specifically with reactants The reactant of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is termed the substrate.
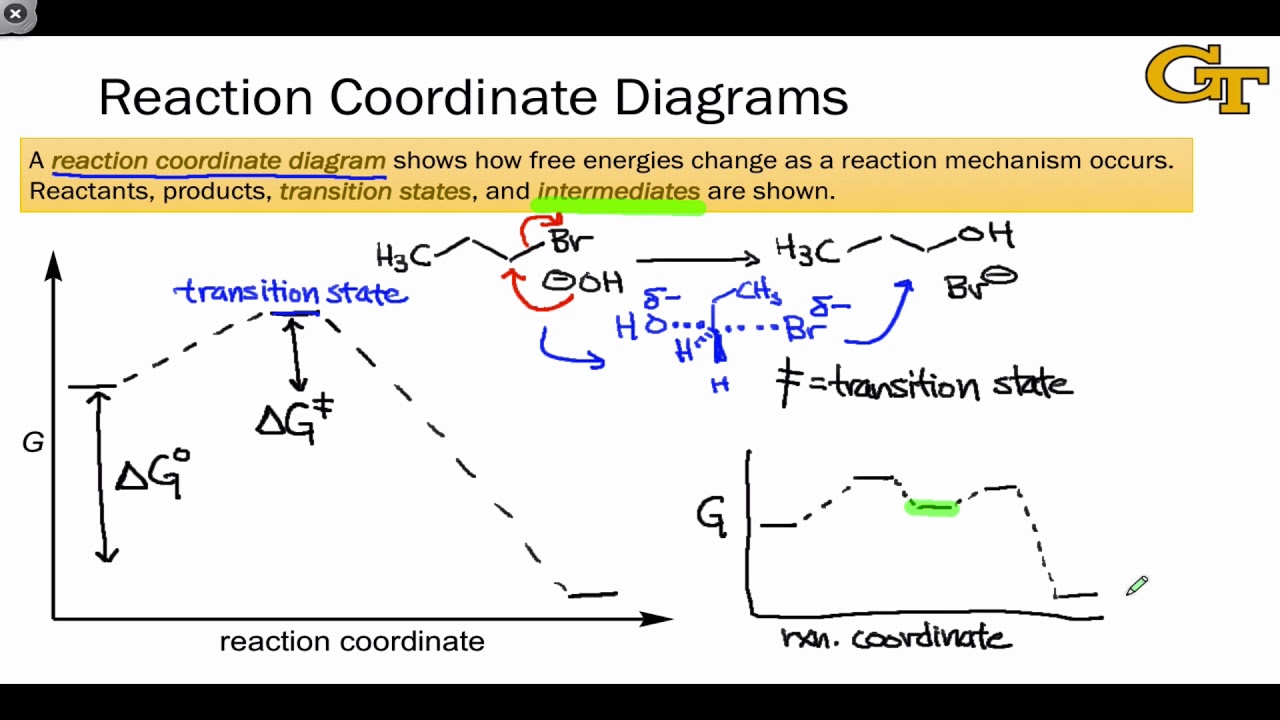
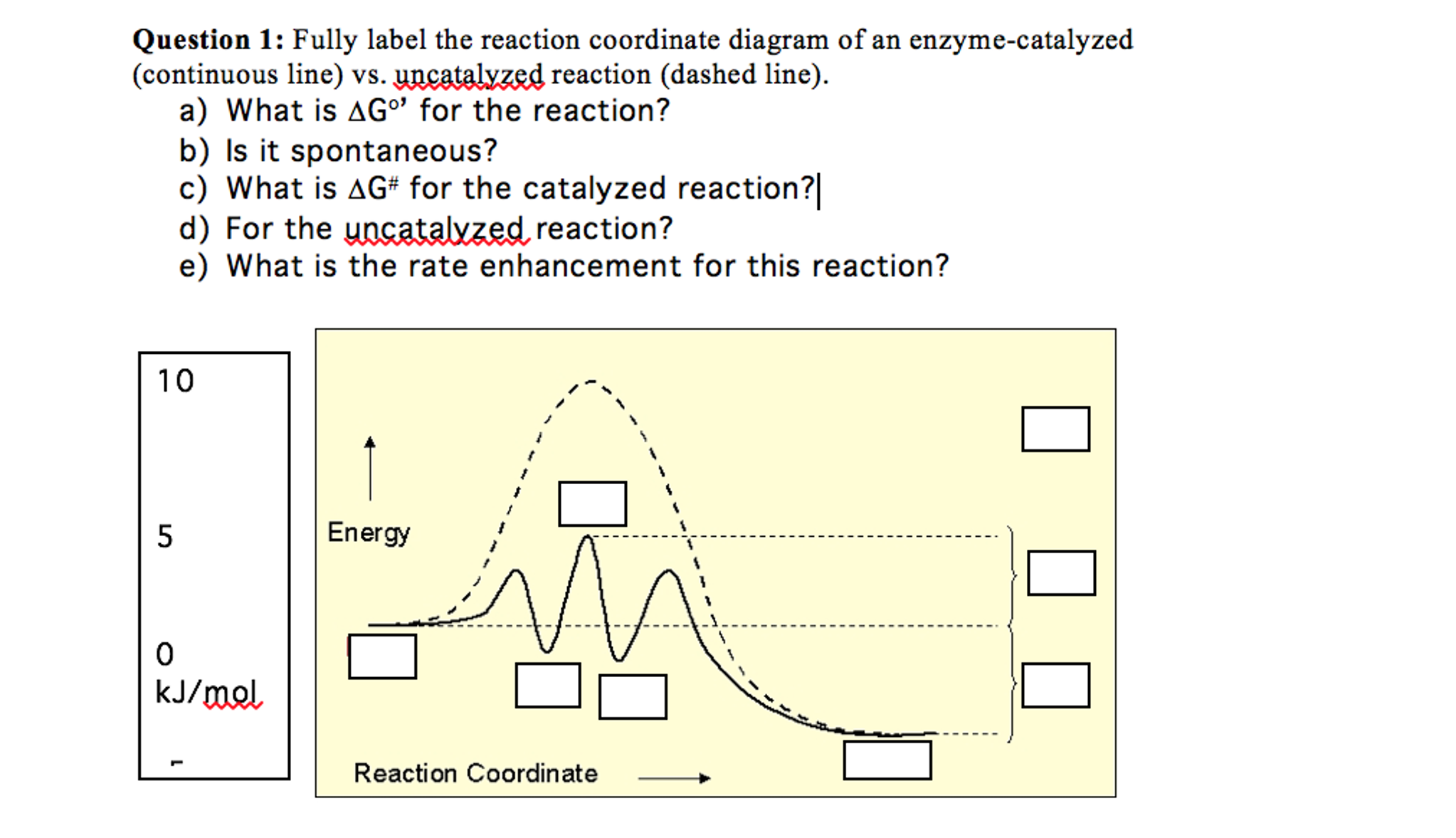
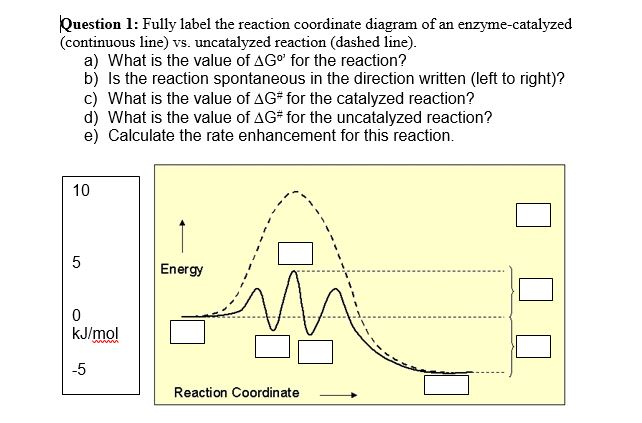
Enzymes.docx - BCHM 3114 Learning Goals: ENZYMES 1 ... Draw a reaction coordinate diagram of a simple reaction (i.e., with reactant(s) and product(s) but no intermediates). Label G, G ‡, and the position of the transition state. Indicate whether the reaction is spontaneous, nonspontaneous or at equilibrium. 7.
PDF Energy/Reaction Coordinate Diagrams Energy/Reaction Coordinate! Diagrams! Thermodynamics, Kinetics ! Dr. Ron Rusay" A Reaction Coordinate (Energy) Diagram Thermodynamic Quantities Gibbs standard free energy change (ΔGo) Enthalphy (ΔHo): the heat given off or absorbed during a reaction Entropy (ΔSo): a measure of freedom of motion ΔGo = ΔHo - TΔSo ΔG,ΔH,ΔS, ΔE are state ...
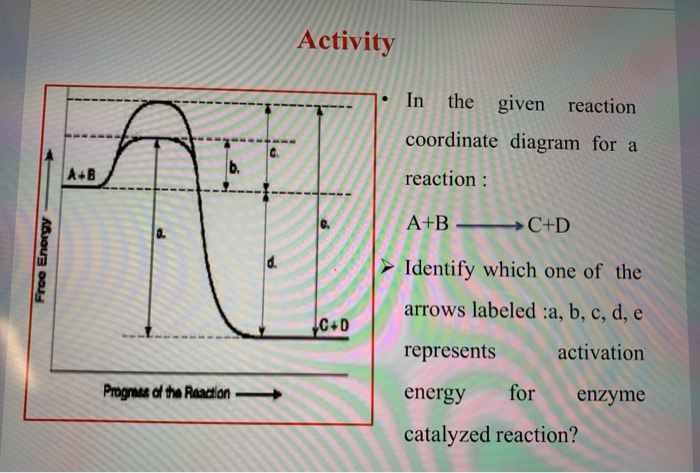
Solved Questiul 17 1 pts A reaction coordinate diagram ... transcribed image text: questiul 17 1 pts a reaction coordinate diagram comparing an uncatalyzed reaction with an enzyme- catalyzed reaction can directly illustrate that the enzyme -, but will not directly illustrite that the enzyme provides an alternative path for product formation; stabilizes the transition state stabilizes the transition …
PDF The Molecular Basis of Enzymatic Catalysis Shown are two reaction coordinate diagrams for a catalyzed reaction (blue line) and its corresponding uncatalyzed reaction (red line). The Gibbs free energy difference of the products and reactants is the same regardless of whether or not the reaction is catalyzed; consequently, ΔG° rxn is the same for both the catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions.
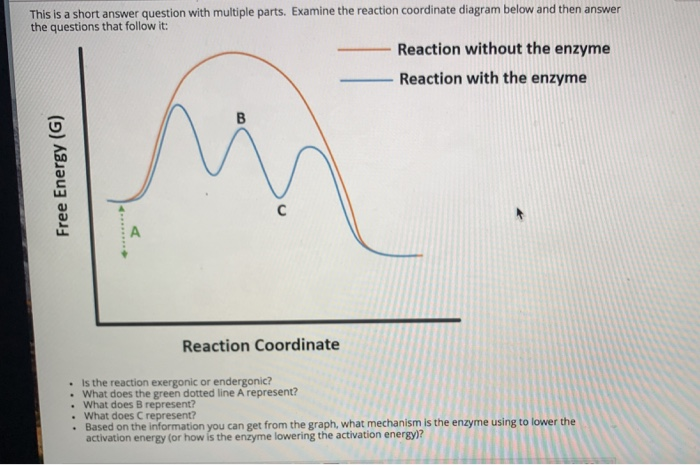
Exam 2 HW 6 Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the reaction coordinate diagram below. At what point is there a maximum number of interactions between the enzyme and the compound that it is binding? D A B A and D are the same C C An enzyme has a single active site at which it can bind and hydrolyze either X or Y; however, the enzyme cannot bind X and Y at the same time.
Enzymes and activation energy (video) - Khan Academy Now, we can look at the process of this reaction using something called a reaction coordinate diagram. And here, we'll plot the energy state of our molecules against the progress of the reaction.
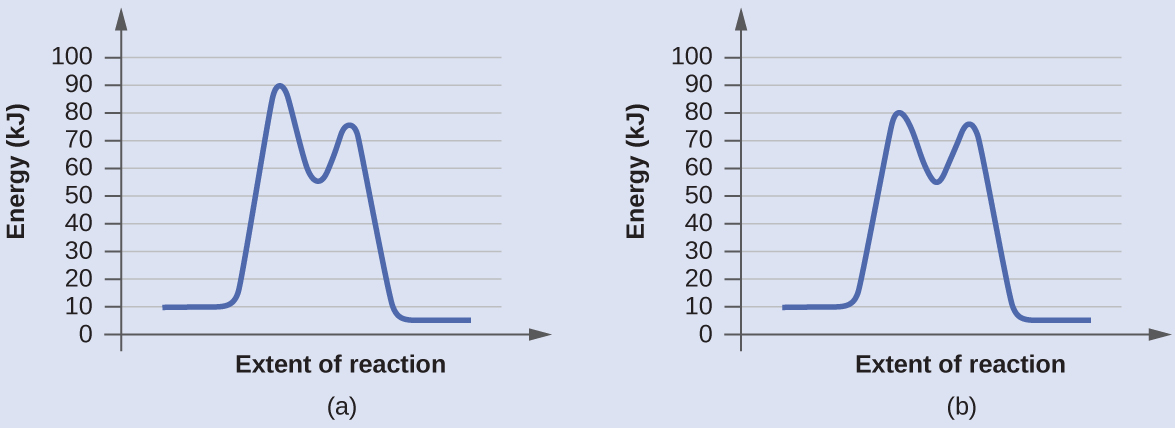
Biochem Chapter 6 question flashcards Flashcards - Quizlet 12) Which of the following is seen in a reaction coordinate diagram for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction that uses covalent catalysis? A) an intermediate B) two distinct transition states C) reactants that are lower in energy than an intermediate D) products that are lower in energy than an intermediate E) all of the above E
04.02 Reaction Coordinate Diagrams and Stability Trends ... General structure of a reaction coordinate diagram, including transition states and intermediates. Overall free energy change and activation energy. Definiti...
Enzyme reaction coordinate diagrams (1) Quiz An unregistered player played the game 3 weeks ago About this Quiz This is an online quiz called Enzyme reaction coordinate diagrams (1) There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper.
PDF Enzyme An introduction to enzymes - University of Houston ... Fig. 1 Reaction coordinate diagram for a chemical reaction Fig. 2 Reaction coordinate diagram comparing enzyme-catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions. 3 of 16 As shown in Fig. 1, from starting material to product, the highest point in terms of energy is called transition
Compare and contrast the reaction coordinate diagrams for ... The reaction coordinate diagram for this reaction plots the changes in Gibbs free energy (ΔG) during the conversion of reac- tants (R) to TS to products (P; Figure 1B). It can be seen that P is of lower free energy than R, so this reaction is thermodynamically fa- vorable, that is, it proceeds in the direction of P with the release of






.png)










0 Response to "39 enzyme reaction coordinate diagram"
Post a Comment