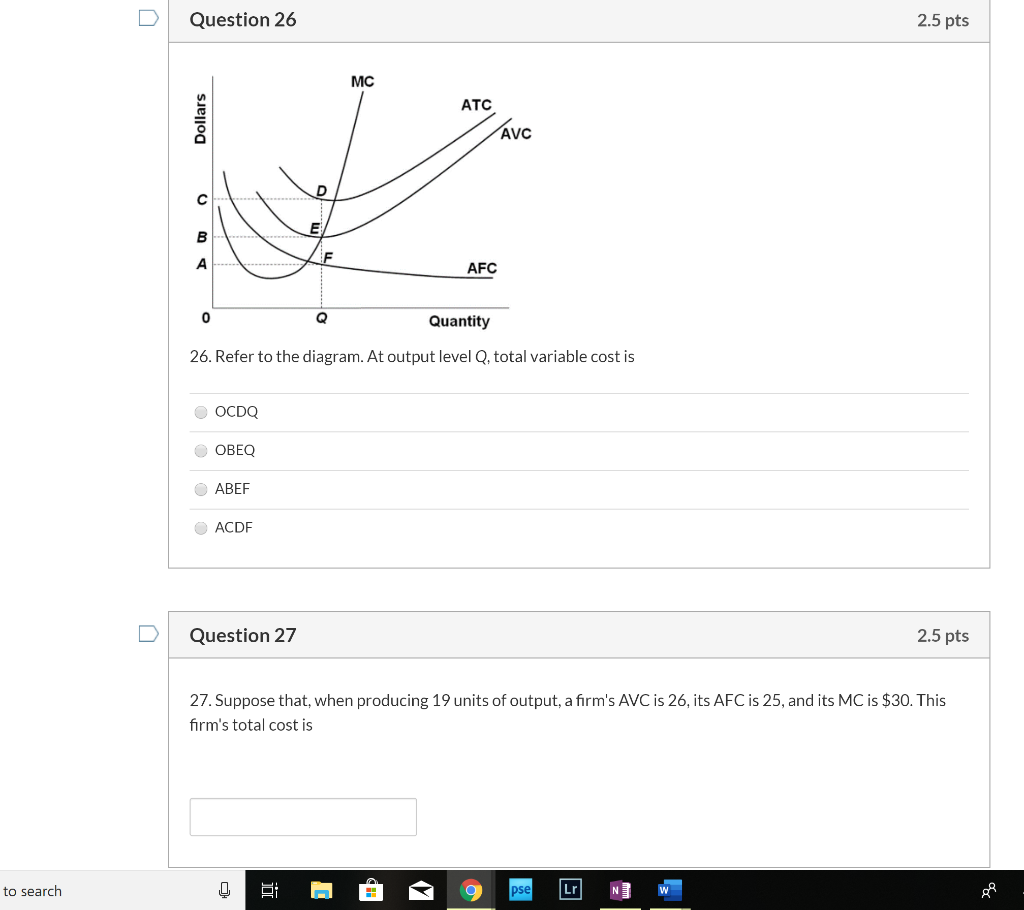
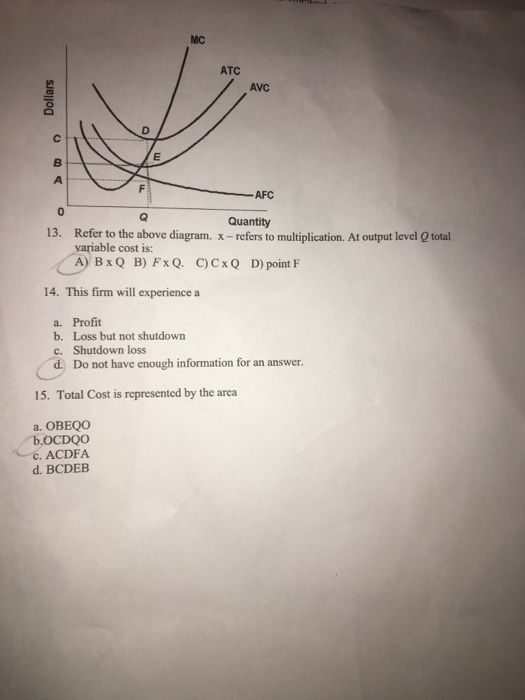
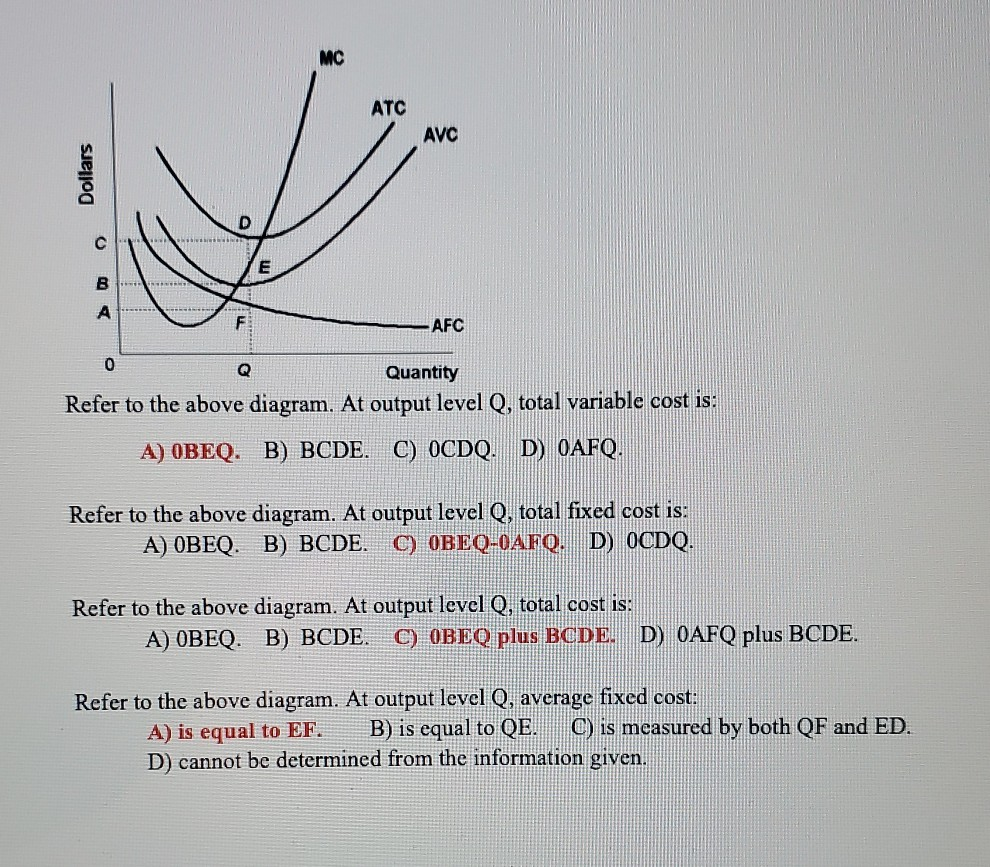
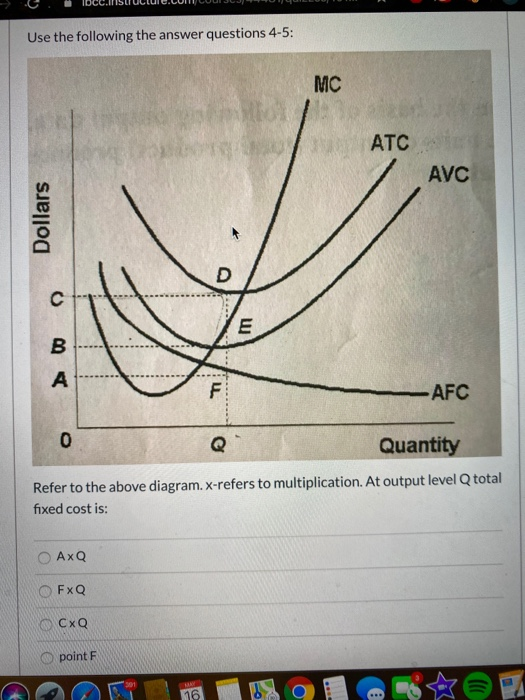
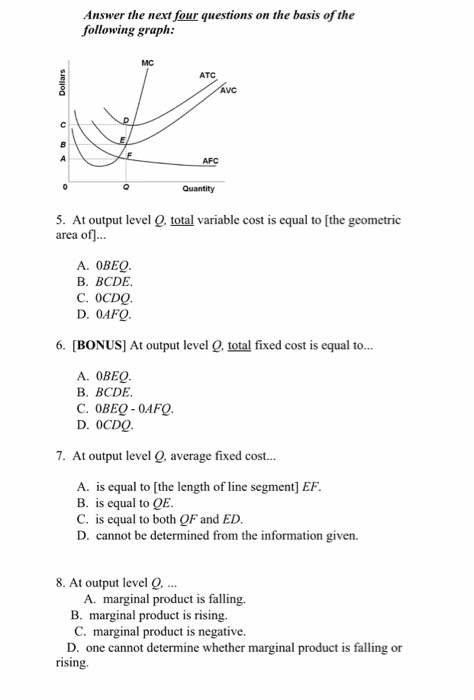
39 refer to the diagram. at output level q, total variable cost is
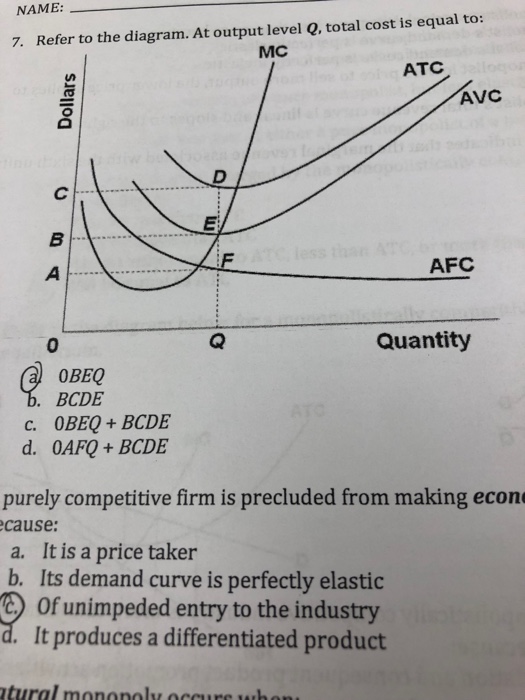
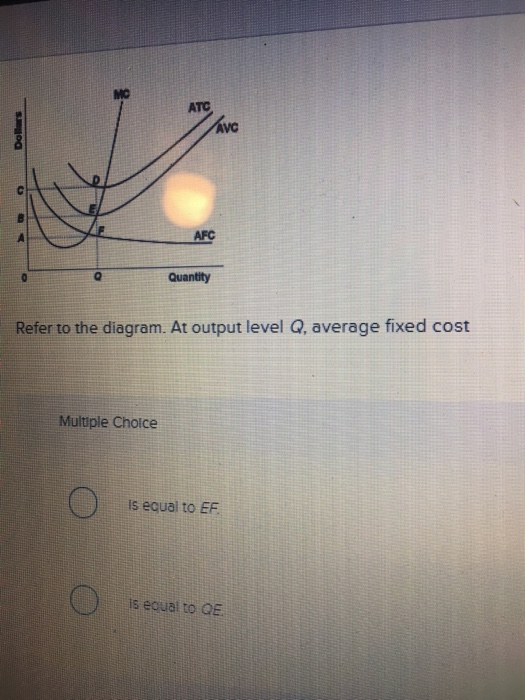
15) If a perfectly competitive firm's price is less than its average total cost but greater than its average variable cost, the firm 15) A) is incurring a loss. B) should shut down. C) is earning a profit. D) is breaking even. Figure 12 -4 Figure 12 - 4 shows the cost and demand curves for a profit - maximizing firm in a perfectly competitive ... Jan 24, 2021 — ATC Dollars Avc AFC lo Quantity 1. Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q total variable cost is: A. OBEQ. B. BCDE. C. OCDQ. D.OAFQ.
Answer-1 The correct option is A.) 0BEQ Total Variable Cost= (Average Variable Cost)* Output =0BEQ Answer-2 The correct option …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: ATC AVC Dollars D AFC o Quantity Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q, total variable cost is: A) OBEQ.
Refer to the diagram. at output level q, total variable cost is
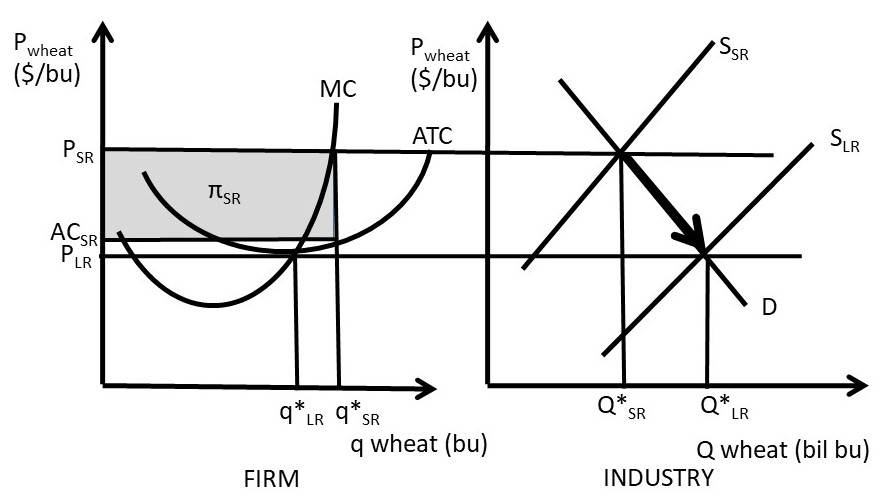
Refer to the above diagram showing the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's total revenue: 400 Marginal cost intersects average fixed cost at the latter's minimum point. Page 31. 4. Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q total variable cost is:.35 pages change in average total cost which results from producing one more unit of output. 10. Assume that in the short run a firm is producing 100 units of output, has average total costs of $200, and average variable costs of $150.
Refer to the diagram. at output level q, total variable cost is. C) marginal cost at each level of output. B) the average fixed cost at each level of output. D) the presence of economies of scale. 21. Marginal cost: A) equals both average variable cost and average total cost at their respective minimums. B) is the difference between total cost and total variable cost. 41. Refer to the above diagram. At output C total variable cost is FGKJ. True False 42. Refer to the above diagram. At output C average fixed cost is GF. True False 43. Refer to the above diagram. At any price below R the firm will shut down in the short run. True False 44. Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q, the total variable cost is OBEQ. It is because OQ is the quantity that the firm is producing at... See full answer below.1 answer · Top answer: The correct answer is A) OBEQ At output level Q, the total variable cost is OBEQ. It is because OQ is the quantity that the firm is producing at...Missing: diagram. | Must include: diagram. Get the detailed answer: Refer to the above diagram, at the output level Q, the total variable cost is: a. 0BEQ b. BCDE c. 0CDQ d. 0AFQ
Scenario 2: The production function for earthquake detectors (Q) is given as follows:Q = 4K 1/2 L 1/2 , where K is the amount of capital employed and L is the amount of labor employed.The price of capital, P K, is $18 and the price of labor, P L, is $2Refer to Scenario 2.Suppose that in order to produce Q=48 detectors 16 units of labor and 9 units of capital were being used. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's total cost. answer choices . is $10. is $40. is $400. ... marginal cost equals average variable cost. price is equal to average revenue. ... Refer to the diagram. At output level Q2, Refer to the diagram At output level Q total variable cost is A 0BEQ B BCDE C from ECONOMICS 111 at Middle East Technical University At output level Q average fixed cost: is measured by both QF and ED. Assume that in the short run a firm is producing 100 units of output, has average total costs of $200, and has average variable costs of $150.
A) Average total cost is the difference between average variable cost and average fixed cost. B) Marginal cost measures the cost per unit of output associated with any level of production. C) When marginal product rises, marginal cost must also rise. 1. the level of output that coincides with the intersection of the MC and AVC curves. 2. minimization of the AFC in the production of any good. 3. the production of the product-mix most desired by consumers. 4. the production of a good at the lowest average total cost. 5. If the price of product Y is $25 and its marginal cost is $18: 1. At output level Q total fixed cost is: A. 0BEQ. B. BCDE. C. 0BEQ, -0AFQ. D. 0CDQ. Explain your answer: This problem has been ... The fixed cost of the firm is $500. The firm's total variable cost is indicated in the table. output Total Variable Cost 1 $400 2 $720 3 $1,000 4 $1,400 5 $2,000 6 $3,600 The average total cost of the firm when 3 units of output are being produced is Multiple Choice A) $500. B) $350. C) $700. D) $400.
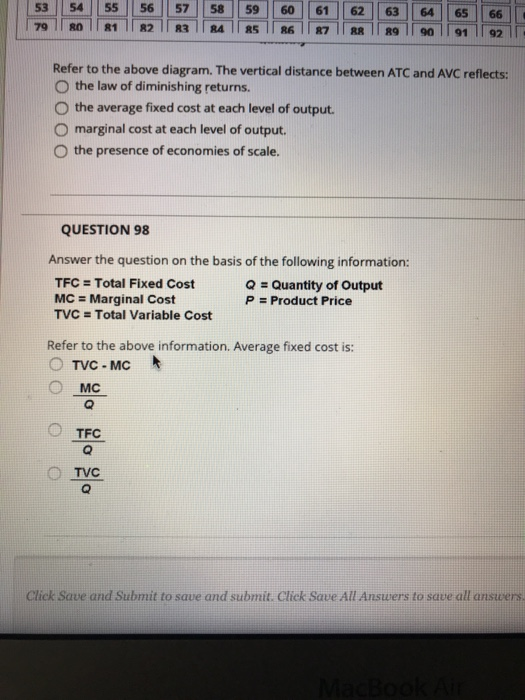
At output level Q : 61. Refer to the above diagram. The vertical distance between ATC and AVC reflects: 62. Marginal cost: A. equals both average variable cost and average total cost at their respective minimums. B. is the difference between total cost and total variable cost. C. rises for a time, but then begins to decline when diminishing ...
Refer to the diagram. At output level Q: Multiple Choice marginal product is falling. ... is the difference between total cost and total variable cost. rises for a time, but then begins to decline when diminishing returns set in. declines continuously as output increases. A.
marginal cost intersects average total cost at the latter's minimum point. refer to the above diagram. at output level q total variable cost is: 0beq. marginal cost: marginal cost, average variable cost, and average total cost would all fall: if a firm decides to produce no output in the short run, its costs will be: its fixed costs.
177. Refer to the above diagram. For output level Q, per unit costs of B are: A) unobtainable and imply the inefficient use of resources. B) unobtainable, given resource prices and the current state of technology. C) obtainable, but imply the inefficient use of resources. D) obtainable and imply least-cost production of this output. Answer: D
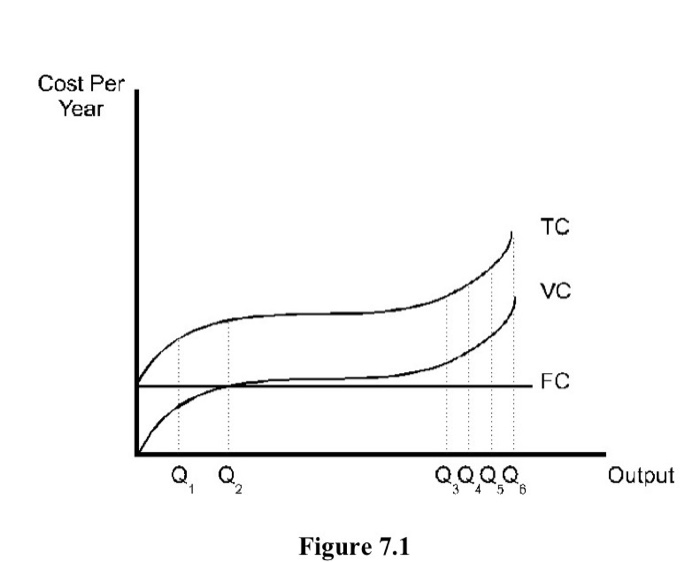
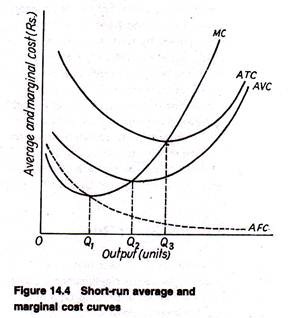
The average total cost of a given level of output is the slope of the line from the origin to the total cost curve at that level of output. II. The marginal cost of a given level of output is the slope of the line that is tangent to the variable cost curve at that level of output. A) Both I and II are true. ... Refer to Figure 7.1. The diagram ...
Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q average fixed cost: A. is equal to EF. B. is equal to QE. C. is measured by both QF and ED. D. cannot be determined from the information given. AACSB: Reflective Thinking Skills Bloom's: Application Learning Objective: 8-3 Topic: Short-run costs 73. Refer to the above diagram.

Microeconomics Quiz 24 Pdf 70 Award 1 00 Point Refer To The Diagram At Output Level Q Total Variable Cost Is 0beq Bcde 0cdq 0afq References Multiple Course Hero
Ans: B Q39.Marginal cost: A) equals both average variable cost and average total cost at their respective minimums. B) is the difference between total cost and total variable cost. C) rises for a time, but then begins to decline when diminishing returns set in. D) declines continuously as output increases.

Microeconomics Quiz 24 Pdf 70 Award 1 00 Point Refer To The Diagram At Output Level Q Total Variable Cost Is 0beq Bcde 0cdq 0afq References Multiple Course Hero
The Sunshine Corporation finds that its costs are $40 when it produces no output. Its total variable costs (TVC) change with output as shown in the accompanying table. Use this information to answer the following question(s). Refer to the above information. The total cost of producing 3 units of output is:
2) Refer to Figure 9-1. The diagram shows cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. If the market price is P3, the profit-maximizing firm in the short run should A) produce output A. B) produce output F or shut down, as it doesnʹt matter which. C) produce output D.
Solution for MC ATC AVC F AFC A Quantity Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q total variable cost is: Dollars.
Scenario 2: The production function for earthquake detectors (Q) is given as follows: Q = 4K 1/2 L 1/2, where K is the amount of capital employed and L is the amount of labor employed.The price of capital, P K, is $18 and the price of labor, P L, is $2 Refer to Scenario 2.Suppose that in order to produce Q=48 detectors 16 units of labor and 9 units of capital were being used.
change in average total cost which results from producing one more unit of output. 10. Assume that in the short run a firm is producing 100 units of output, has average total costs of $200, and average variable costs of $150.
Marginal cost intersects average fixed cost at the latter's minimum point. Page 31. 4. Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q total variable cost is:.35 pages
Refer to the above diagram showing the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's total revenue: 400

At Output Level Q Total Variable Cost Is Equal To The Generic Area Of A 0beq B Bcde C 0cdq D 0afq Study Com
















0 Response to "39 refer to the diagram. at output level q, total variable cost is"
Post a Comment