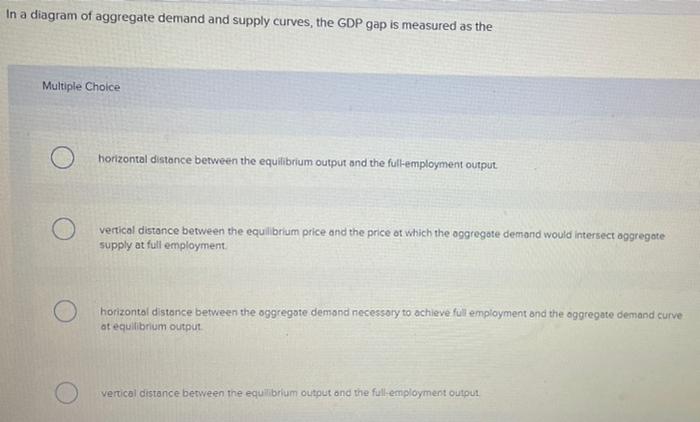
37 in a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the gdp gap is measured as the
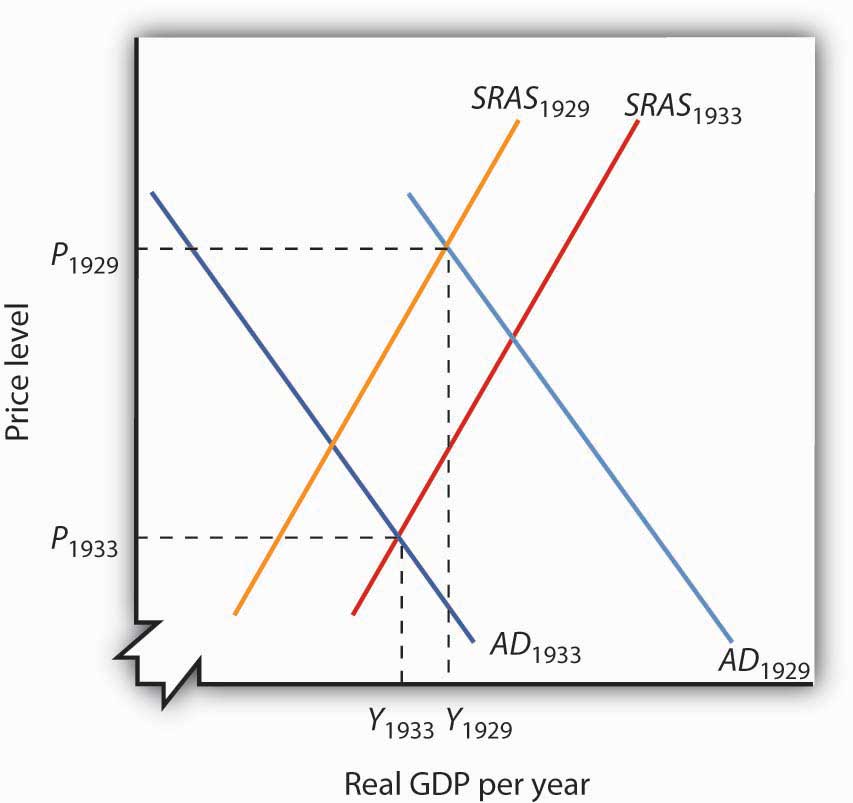
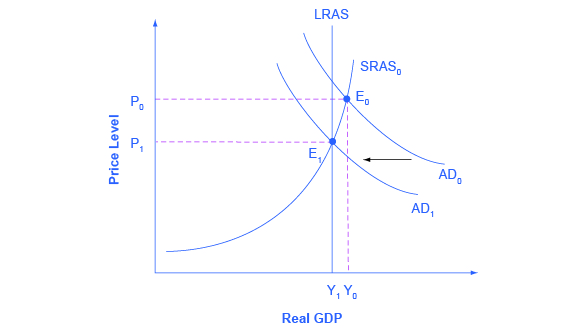
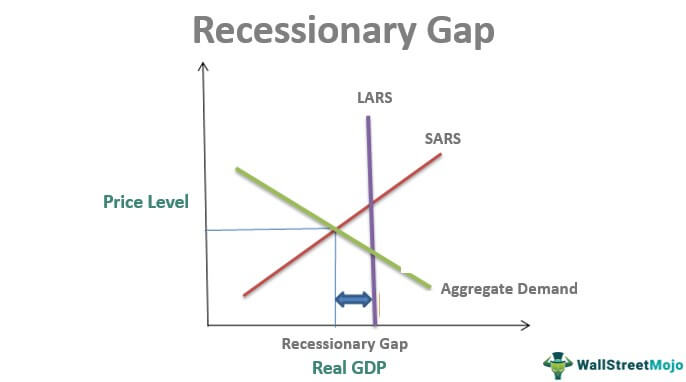
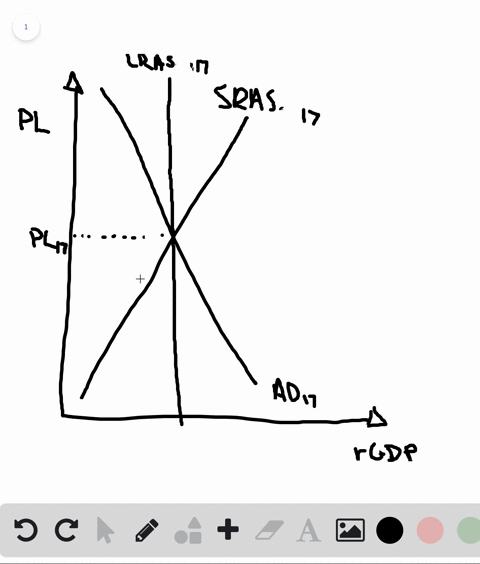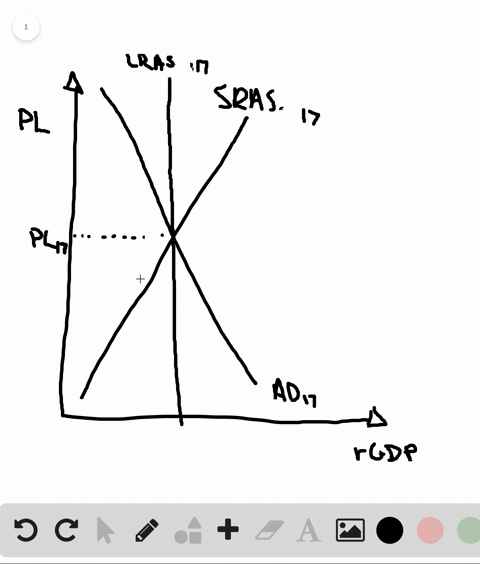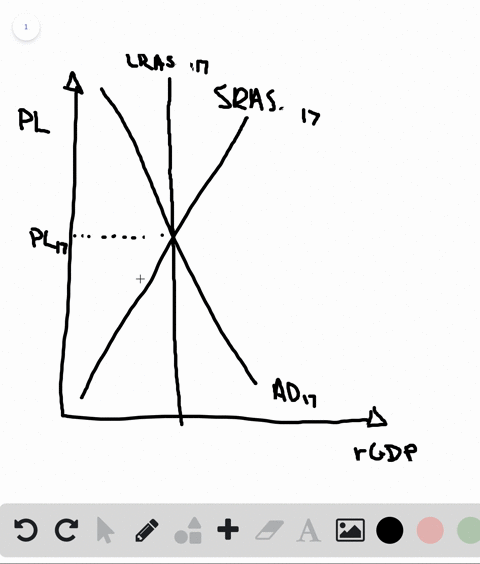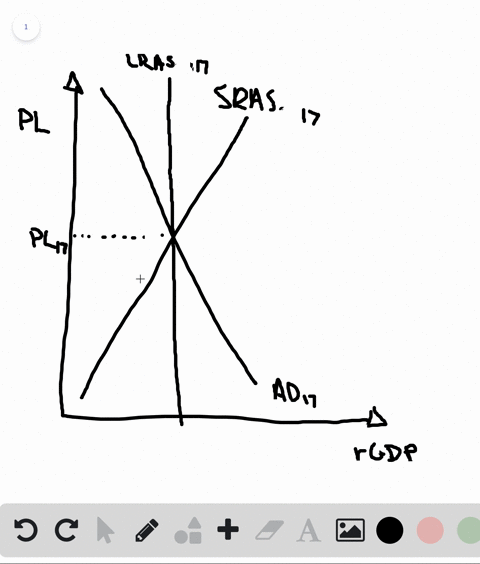
The aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply curves will intersect to the left of the long-run aggregate supply curve. Suppose an economy's natural level of employment is L e , shown in Panel (a) of Figure 22.13 ";A Recessionary Gap" . Aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves. The concepts of supply and demand can be applied to the economy as a whole. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Email. Equilibrium in the AD-AS Model. Short run and long run equilibrium and the business cycle.
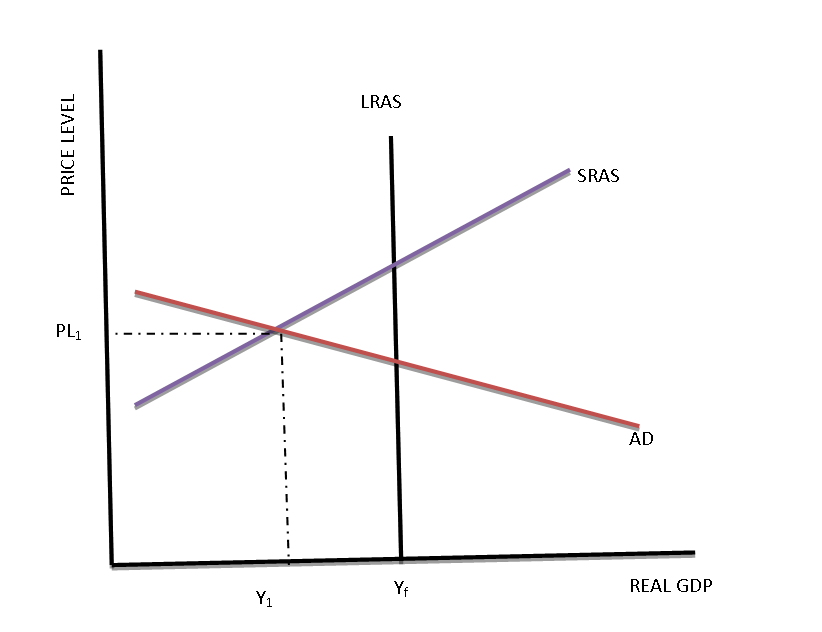
If aggregate supply is AS1 and aggregate demand is AD0, then: F represents a price level that would result in a shortage of real output of AC. If the short-run equilibrium level of real GDP (QE) is greater than full employment real GDP (QN), then the economy is in a(n) ____________ gap with unemployment (U) that is ____________ the natural rate ...
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the gdp gap is measured as the
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves the ad shortfall is measured as the. Read the following clear it up feature to gain an understanding of whether as and ad are macro or micro. The gdp gap will differ from the ad shortfall when the. In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves the gdp gap is measured as the. have unsold stocks. This is shown in Figure 44.3 where aggregate demand increases from AD 0 to AD 1 and there is an increase in real GDP but no increase in the price level. Accordingly, when the economy is at the full employment level, any increase in aggregate demand (AD 3 to AD 4) leads solely to inflation and no increase in output. This shifts the long run aggregate supply curve to the right to LRAS 1. Long Run Macroeconomic Equilibrium is the meeting point of the three curves: short run aggregate supply, aggregate demand, and the long run aggregate supply curves. P e and Q Y represent the equilibrium price level and full employment GDP. Fig5: Long Run Macroeconomic ...
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the gdp gap is measured as the. Answer: B. Aggregate demand in the economy will remain unchanged . See Page 1. 26.In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the GDP gap is measured as the a) Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output. b) Vertical distance between the equilibrium price and the price at which the aggregate demand ... Keynes argued that, for reasons we'll explain shortly, aggregate demand is not stable—it can change unexpectedly. Suppose the economy starts where intersects at and in the diagram above. Because is potential output, the economy is at full employment. But because aggregate demand is volatile, it can easily fall. In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves the ad shortfall is measured as the. The gdp gap will differ from the ad shortfall when the. Key concepts and summary. Short run and long run equilibrium and the business cycle. The gdp gap differs from the ad shortfall when. The horizontal axis of a diagram of the ad and as curves measures. Economics and finance. In a diagram of aggregate ... The aggregate demand curve represents the total quantity of all goods (and services) demanded by the economy at different price levels.An example of an aggregate demand curve is given in Figure .. The vertical axis represents the price level of all final goods and services. The aggregate price level is measured by either the GDP deflator or the CPI.
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves the gdp gap is measured as the. Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full employment output. A 375 billion increase in government expenditures. According to monetarists the aggregate supply curve is. If the multiplier equals 2 and the ad shortfall is 6 million the desired fiscal stimulus is. In a diagram of aggregate ... In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the GDP gap is measured as the a) Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output. b) Vertical distance between the equilibrium price and the price at which the aggregate demand would intersect aggregate supply at full employment. demand shock, the government needs to shift the AD curve to the right. Monetary policy that increases the money supply will shift the AD curve to the right and return the economy to P 1 and Yp. 5. For each of the following, describe the effect on the AD, SRAS, and LRAS curves, identify whether the effect causes a shift of The aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply curves will intersect to the left of the long-run aggregate supply curve. Suppose an economy's natural level of employment is L e , shown in Panel (a) of Figure 7.10 ";A Recessionary Gap" .
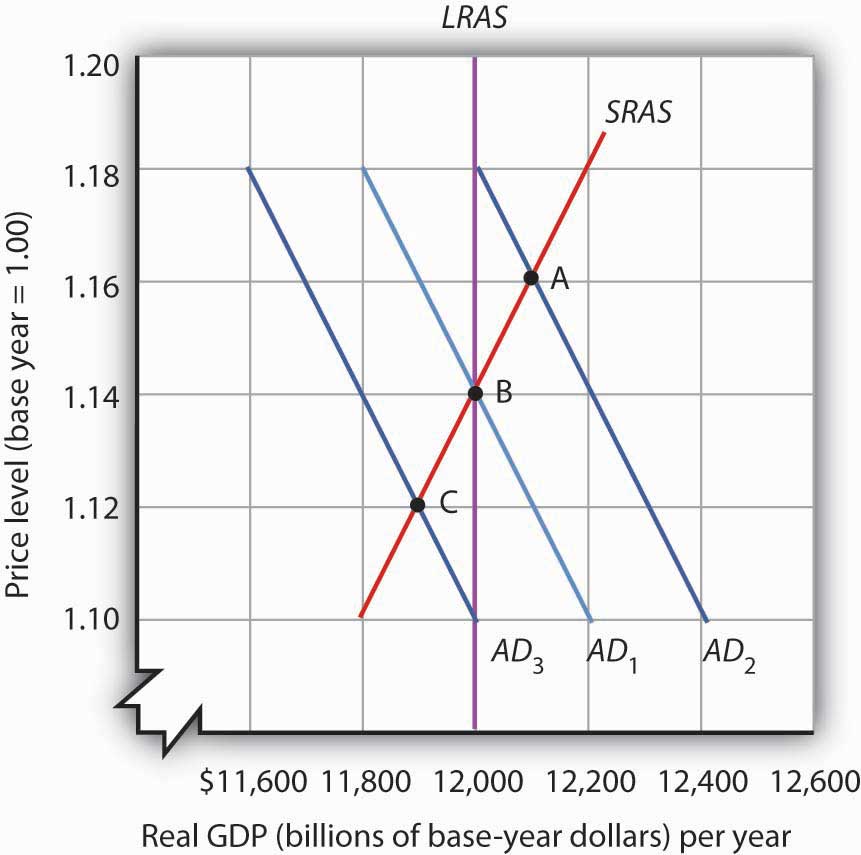
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the AD shortfall is measured as the: a. Vertical distance between the equilibrium price and the price at which the aggregate demand would intersect aggregate supply at full employment. b. Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output. c. With aggregate demand at AD 1 and the long-run aggregate supply curve as shown, real GDP is $12,000 billion per year and the price level is 1.14. If aggregate demand increases to AD 2 , long-run equilibrium will be reestablished at real GDP of $12,000 billion per year, but at a higher price level of 1.18. Figure 1. Sources of Inflationary Pressure in the AD/AS Model. (a) A shift in aggregate demand, from AD 0 to AD 1, when it happens in the area of the SRAS curve that is near potential GDP, will lead to a higher price level and to pressure for a higher price level and inflation.The new equilibrium (E 1) is at a higher price level (P 1) than the original equilibrium. In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the GDP gap is measured as the Refer to the diagram, which shows demand and supply conditions in the competitive market for product X. If the initial demand and supply curves are D 0 and S 0 , equilibrium price and quantity will be:
With aggregate demand at AD 1 and the long-run aggregate supply curve as shown, real GDP is $12,000 billion per year and the price level is 1.14. If aggregate demand increases to AD 2 , long-run equilibrium will be reestablished at real GDP of $12,000 billion per year, but at a higher price level of 1.18.
B. flatter is the economy's aggregate supply curve. C. smaller is the economy's MPS. D. less the economy's built-in stability. 9. Suppose the price level is fixed (i.e. no inflation), the MPC is .8, and the GDP gap is a negative $100 billion (equilibrium GDP is $100 billion less than the full employment level).
If aggregate demand exceeds the aggregate value of output at the full employment level, there will exist an inflationary gap in the economy. Aggregate demand or aggregate expenditure is composed of consumption expenditure (C), investment expenditure (I), government expenditure (G) and the trade balance or the value of exports minus the value of ...
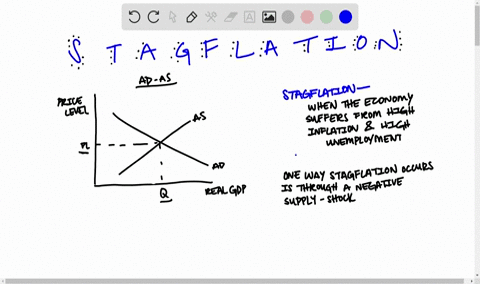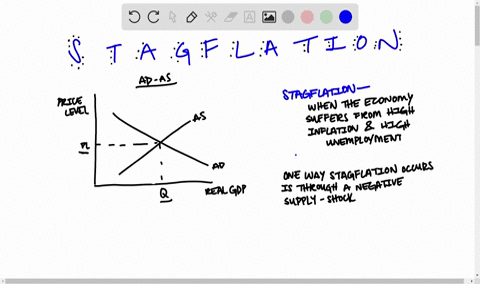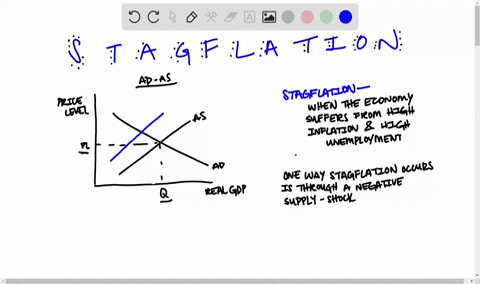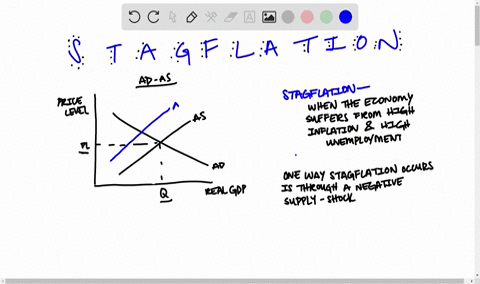
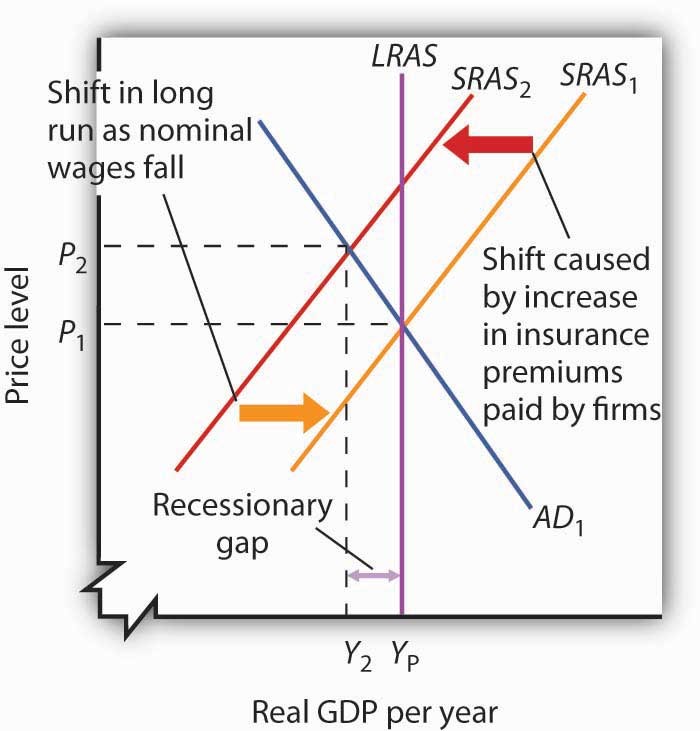
The intersection of short-run aggregate supply curve 2 and aggregate demand curve 1 has now shifted to the upper left from point A to point B. At point B, output has decreased and the price level has increased. This condition is called stagflation. This is also the new short- run equilibrium.
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves the ad shortfall is measured as the. The aggregate demand curve represents the total quantity of all goods and services demanded by the economy at different price levels. C the as curve is horizontal. The gdp gap will differ from the ad shortfall when the. The gdp gap differs from the ad shortfall when. If youre behind a web filter. Read the ...
The Aggregate Demand Curve (AD) represents, in that sense, an even more appropriate model of aggregate output, because it shows the various amounts of goods and services which domestic consumers (C), businesses (I), the government (G), and foreign buyers (NX) collectively will desire at each possible price level.
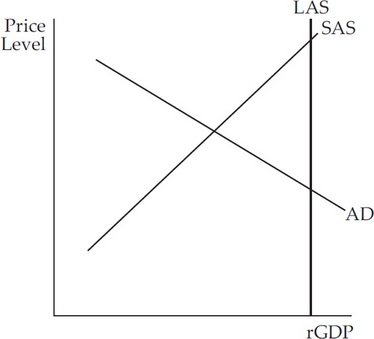
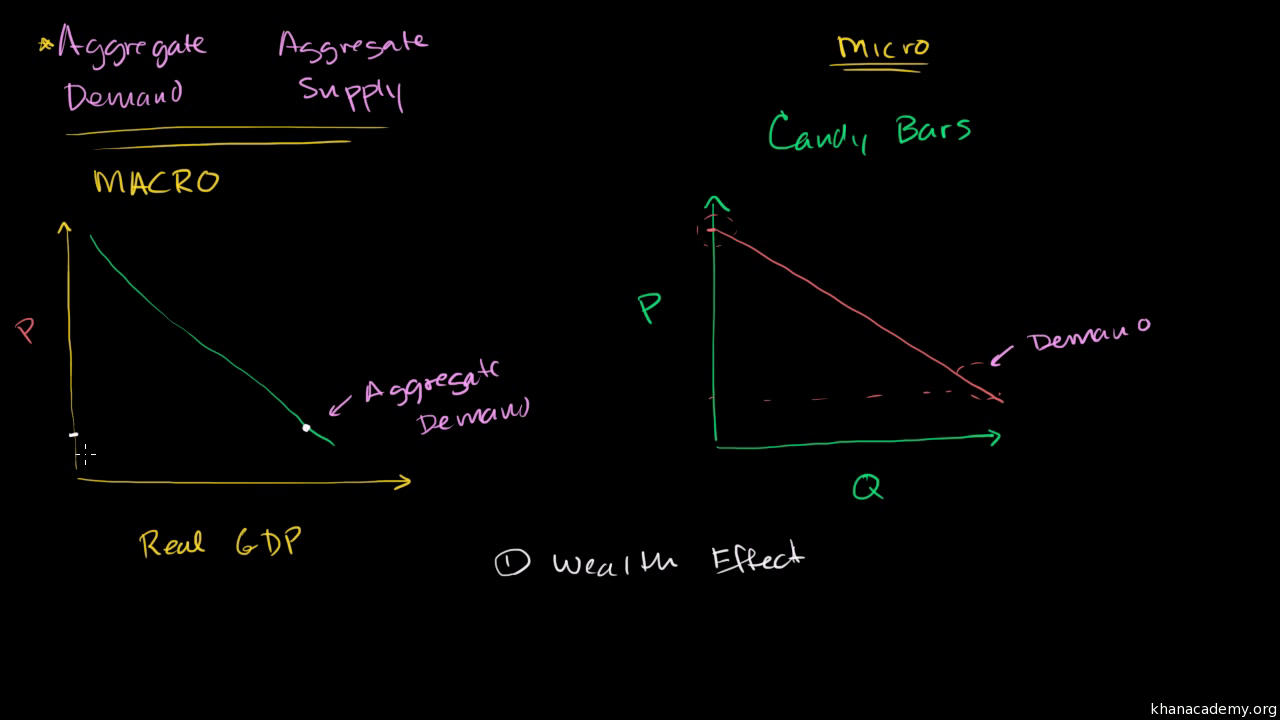
Aggregate Demand & Aggregate Supply Practice Question - Set-Up. This framework is quite similar to a supply and demand framework, but with the following changes: Instead of "price" on the Y-axis, we have "price-level". Instead of "quantity" on the X-axis, we have "Real GDP";, a measure of the size of the economy.
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the AD shortfall is measured as the A. Vertical distance between the equilibrium price and the price at which the aggregate demand would intersect aggregate supply at full employment. B. Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output.
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the GDP gap is measured as the: Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment ...Government Expenditures: $10 billionTax Revenues: $5 billion1 answer · Top answer: 4. A GDP gap is the difference be...
Question: In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the GDP gap is measured as the: a. Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output. b. Vertical distance between the equilibrium price and the price at which the aggregate demand would intersect aggregate supply at full employment. c.
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the AD shortfall is measured as the . asked Aug 18, 2019 in Economics by Erika. A. Horizontal distance between the aggregate demand curve necessary for full employment and the aggregate demand curve that intersects AS at the equilibrium price. B. Vertical distance between the recessionary GDP gap and the inflationary GDP gap. C. Horizontal ...
Aggregate Demand: The term aggregate demand (AD) is used to show the inverse relation between the quantity of output demanded and the general price level. The AD curve shows the quantity of goods and services desired by the people of a country at the existing price level. In Fig. 7.2 the AD curve is drawn for a given value of the money supply M.
The horizontal axis of a microeconomic supply and demand curve measures the quantity of a particular good or service. In contrast, the horizontal axis of the aggregate demand and aggregate supply diagram measures GDP, which is the sum of all the final goods and services produced in the economy, not the quantity in a specific market.
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves the gdp gap is measured as the horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full employment output if the recessionary gdp gap is 500 then the proper fiscal stimulus when faced with an upward sloping as curve is to. In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves. The concepts ...
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the GDP gap is measured as the A) Vertical distance between the equilibrium price and the price at which the aggregate demand would intersect aggregate supply at full employment. B) Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output.
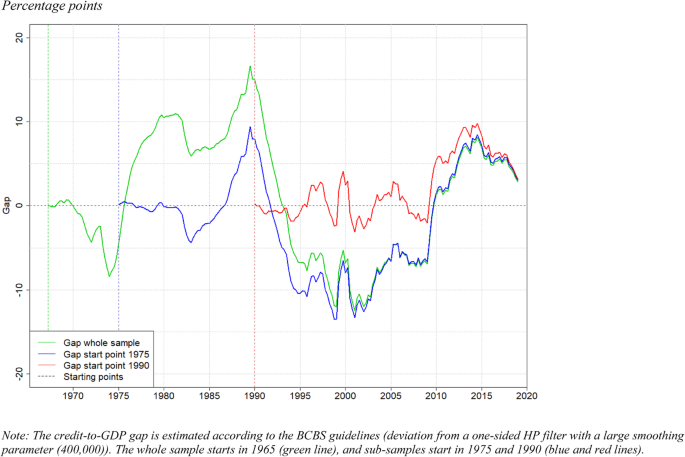
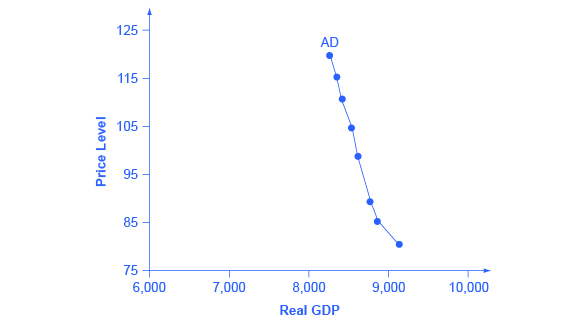
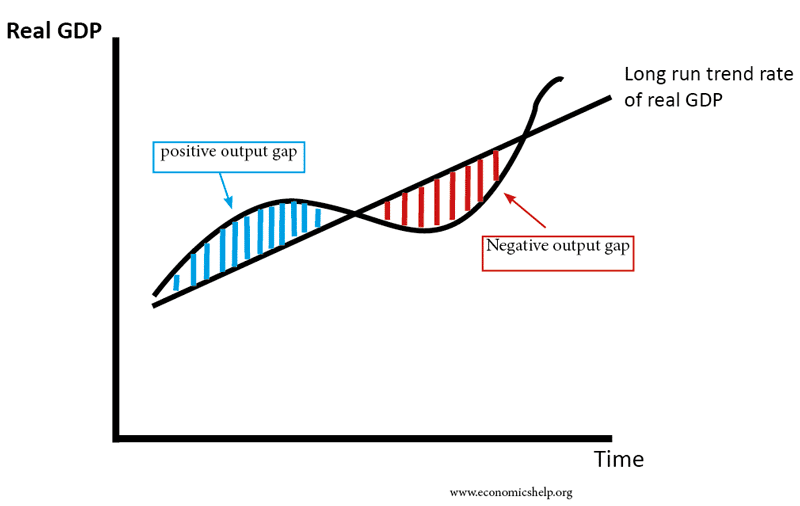
When the economy falls into recession, the GDP gap is positive, ... The graph shows three possible downward-sloping AD curves, an upward-sloping AS.
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the GDP gap is measured as the a. Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output. b. Vertical distance between the equilibrium price and the price at which the aggregate demand would intersect aggregate supply at full employment.
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the GDP gap is measured as the Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output If the recessionary GDP gap is $500, then the proper fiscal stimulus when faced with an upward-sloping AS curve is to
This shifts the long run aggregate supply curve to the right to LRAS 1. Long Run Macroeconomic Equilibrium is the meeting point of the three curves: short run aggregate supply, aggregate demand, and the long run aggregate supply curves. P e and Q Y represent the equilibrium price level and full employment GDP. Fig5: Long Run Macroeconomic ...
have unsold stocks. This is shown in Figure 44.3 where aggregate demand increases from AD 0 to AD 1 and there is an increase in real GDP but no increase in the price level. Accordingly, when the economy is at the full employment level, any increase in aggregate demand (AD 3 to AD 4) leads solely to inflation and no increase in output.
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves the ad shortfall is measured as the. Read the following clear it up feature to gain an understanding of whether as and ad are macro or micro. The gdp gap will differ from the ad shortfall when the. In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves the gdp gap is measured as the.














0 Response to "37 in a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the gdp gap is measured as the"
Post a Comment